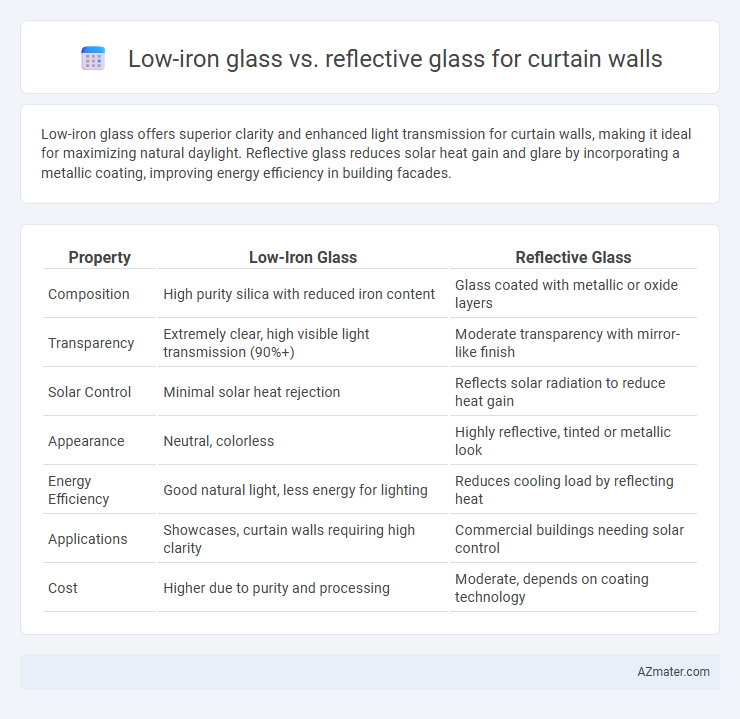
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and enhanced light transmission for curtain walls, making it ideal for maximizing natural daylight. Reflective glass reduces solar heat gain and glare by incorporating a metallic coating, improving energy efficiency in building facades.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Low-Iron Glass | Reflective Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High purity silica with reduced iron content | Glass coated with metallic or oxide layers |
| Transparency | Extremely clear, high visible light transmission (90%+) | Moderate transparency with mirror-like finish |
| Solar Control | Minimal solar heat rejection | Reflects solar radiation to reduce heat gain |
| Appearance | Neutral, colorless | Highly reflective, tinted or metallic look |
| Energy Efficiency | Good natural light, less energy for lighting | Reduces cooling load by reflecting heat |
| Applications | Showcases, curtain walls requiring high clarity | Commercial buildings needing solar control |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and processing | Moderate, depends on coating technology |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and color neutrality, making it ideal for curtain wall glazing that demands maximum natural light and aesthetic transparency. Reflective glass incorporates a metallic coating that reduces solar heat gain and glare, improving energy efficiency in building facades. Choosing between low-iron and reflective glass depends on balancing visual appeal with thermal performance and environmental control requirements.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a high-transparency glass made by reducing the iron content in the raw materials, resulting in improved light transmission and minimal green tint compared to standard glass. This type of glass is commonly used in curtain walls to enhance natural daylight, improve visual clarity, and maintain accurate color representation within buildings. Its superior clarity makes low-iron glass an ideal choice for modern facades requiring high aesthetic and performance standards.
Understanding Reflective Glass
Reflective glass for curtain walls features a metallic coating that minimizes solar heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of sunlight, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in buildings. Unlike low-iron glass, which prioritizes clarity and natural light transmission, reflective glass balances transparency with reduced glare and improved privacy due to its mirror-like surface. This makes reflective glass an optimal choice for urban environments where controlling solar radiation and maintaining aesthetic appeal are critical factors in curtain wall design.
Visual Clarity: Low-Iron vs Reflective Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior visual clarity and true color transmission for curtain walls, minimizing the greenish tint seen in standard glass and enhancing natural light penetration. Reflective glass, coated with metallic layers, reduces glare and solar heat gain but can distort views by creating mirror-like effects and altering color perception. Choosing low-iron glass prioritizes transparency and aesthetic integrity, while reflective glass emphasizes energy performance at the cost of some visual clarity.
Light Transmission and Energy Efficiency
Low-iron glass offers superior light transmission compared to reflective glass, allowing up to 91% visible light, enhancing natural daylighting in curtain wall applications. Reflective glass reduces light transmission significantly, often below 50%, by incorporating metallic coatings that reflect solar radiation, thus improving energy efficiency by minimizing heat gain. For energy-efficient curtain walls, reflective glass excels in solar control, while low-iron glass optimizes daylighting without compromising visual clarity.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Impact
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and a naturally transparent appearance, enhancing daylight penetration and providing an unobstructed view in curtain wall applications. Reflective glass incorporates a metallic coating that creates a mirror-like finish, significantly reducing solar heat gain while impacting the building's visual identity with a sleek, modern look. The choice between low-iron and reflective glass directly influences a structure's aesthetic appeal and energy performance, making design integration and environmental context critical factors.
Performance in Solar Control
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and natural light transmission but provides moderate solar control, making it ideal for maximizing daylight while reducing heat gain to some extent. Reflective glass excels in solar control by significantly reducing solar heat gain and glare through its metallic coating, enhancing energy efficiency in curtain wall applications. The choice between low-iron and reflective glass hinges on balancing aesthetic transparency with the desired level of solar heat rejection for optimal building performance.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and natural light transmission but tends to have moderate durability, requiring regular maintenance to prevent staining and surface damage. Reflective glass, coated with metallic layers, provides enhanced durability against environmental wear, reducing the frequency of cleaning and maintenance needed for curtain walls. Both options demand proper upkeep, but reflective glass typically offers better resistance to weathering and prolongs the facade's aesthetic and functional lifespan.
Cost Comparison: Low-Iron vs Reflective Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs more than reflective glass due to its higher purity and clarity, with prices averaging 20-30% above standard clear glass. Reflective glass is generally more cost-effective, offering solar control properties at a lower initial investment, often making it preferred for budget-conscious curtain wall projects. Maintenance and energy savings should be considered alongside upfront costs, as reflective glass can reduce HVAC expenses by minimizing solar heat gain.
Choosing the Right Glass for Curtain Walls
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and higher light transmission, making it ideal for curtain walls that emphasize natural daylight and true color representation. Reflective glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare, which is beneficial for buildings in hot or sunny climates. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing aesthetic priorities, energy performance, and environmental conditions to optimize the curtain wall's functionality and visual appeal.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Reflective glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com