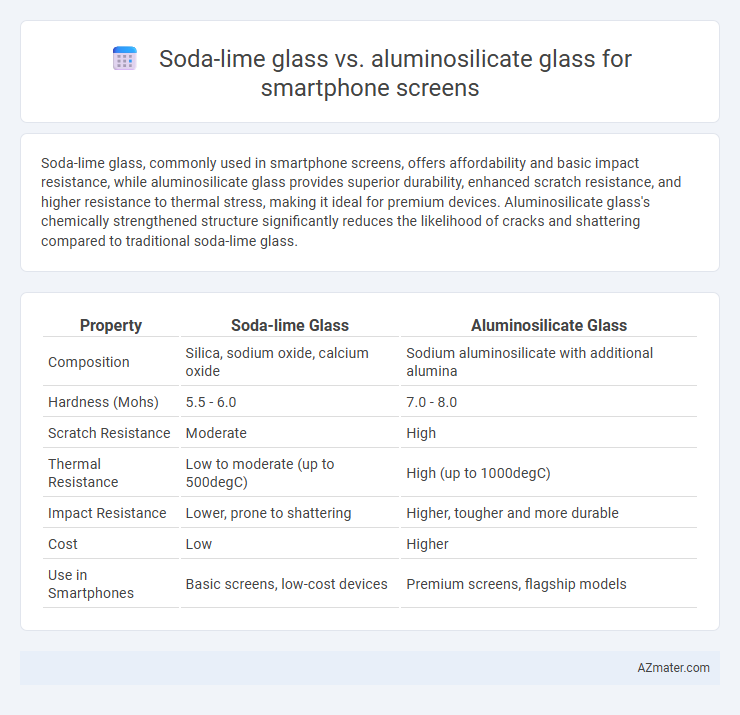
Soda-lime glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers affordability and basic impact resistance, while aluminosilicate glass provides superior durability, enhanced scratch resistance, and higher resistance to thermal stress, making it ideal for premium devices. Aluminosilicate glass's chemically strengthened structure significantly reduces the likelihood of cracks and shattering compared to traditional soda-lime glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Soda-lime Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, sodium oxide, calcium oxide | Sodium aluminosilicate with additional alumina |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 5.5 - 6.0 | 7.0 - 8.0 |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Resistance | Low to moderate (up to 500degC) | High (up to 1000degC) |
| Impact Resistance | Lower, prone to shattering | Higher, tougher and more durable |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
| Use in Smartphones | Basic screens, low-cost devices | Premium screens, flagship models |
Overview of Soda-Lime Glass and Aluminosilicate Glass
Soda-lime glass, composed primarily of silica, soda, and lime, is the most common and cost-effective material used in traditional smartphone screens, offering decent clarity and moderate scratch resistance. Aluminosilicate glass incorporates aluminum oxide into its silica base, significantly enhancing strength, toughness, and resistance to scratches and impacts, making it the preferred choice for high-end smartphones. The increased durability and thermal stability of aluminosilicate glass optimize device longevity compared to the more brittle soda-lime variant.
Composition and Material Differences
Soda-lime glass primarily consists of silica (SiO2), sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), providing basic durability and cost-effectiveness but lower resistance to scratches and impacts. Aluminosilicate glass incorporates aluminum oxide (Al2O3) alongside silica, enhancing hardness, strength, and thermal stability, making it significantly more resistant to mechanical stress and chemical corrosion. The superior composition of aluminosilicate glass results in improved performance for smartphone screens, offering enhanced protection against drops and daily wear compared to soda-lime glass.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Soda-lime glass manufacturing involves melting a mixture of silica, soda ash, and lime at high temperatures, followed by annealing and tempering to enhance strength, which is cost-effective but offers moderate durability for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass requires a more complex process with additional alumina oxide incorporation, molten at higher temperatures, and often undergoes an ion-exchange strengthening treatment that significantly improves scratch resistance and impact durability. The increased manufacturing complexity and energy consumption for aluminosilicate glass results in higher production costs offset by enhanced performance and longevity in smartphone screen applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced impact resistance compared to soda-lime glass, making it the preferred choice for smartphone screens. Its chemically strengthened properties provide higher scratch resistance and better durability under daily wear and tear. Soda-lime glass, while cost-effective, lacks the toughness and prolonged lifespan required for premium smartphone displays.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to soda-lime glass due to its enhanced chemical composition and harder surface structure. Impact resistance in aluminosilicate glass is significantly higher, making it more effective at preventing screen cracks and shattering during drops. Soda-lime glass, commonly used in everyday applications, lacks the durability required for high-stress environments like smartphone screens, resulting in easier damage under impact and abrasion.
Clarity and Optical Properties
Soda-lime glass offers excellent clarity with high light transmittance and low haze, making it suitable for vibrant smartphone displays. Aluminosilicate glass provides superior optical properties, including enhanced scratch resistance and durability while maintaining high transparency and minimal color distortion. The aluminosilicate composition ensures better resistance to impact and reduces the likelihood of micro-cracks, preserving screen clarity over extended use.
Cost and Economic Factors
Soda-lime glass is significantly cheaper than aluminosilicate glass, making it a cost-effective option for budget smartphone screens but with lower durability and scratch resistance. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in premium smartphones like Gorilla Glass, offers superior strength and impact resistance at a higher production cost, justifying its price in higher-end markets. The economic trade-off hinges on performance longevity and consumer willingness to pay for enhanced screen protection versus initial material expenses.
Use in Modern Smartphone Screens
Soda-lime glass, commonly used in traditional smartphone screens, offers affordability and ease of mass production but lacks the durability and scratch resistance essential for modern devices. Aluminosilicate glass, such as Corning Gorilla Glass, is engineered with enhanced chemical strength and impact resistance, making it the preferred choice for premium smartphones. Its superior hardness and ability to withstand drops and scratches significantly improve screen longevity and user experience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Soda-lime glass, widely used in smartphone screens, has a higher environmental impact due to its energy-intensive production and lower durability, leading to more frequent replacements and increased waste. In contrast, aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and scratch resistance, extending device lifespan and reducing electronic waste. Sustainability improves with aluminosilicate glass by lowering resource consumption and enhancing recyclability compared to traditional soda-lime glass.
Which Glass is Best for Smartphone Screens?
Aluminosilicate glass is generally the best choice for smartphone screens due to its superior strength, scratch resistance, and impact durability compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass, commonly used in windows and bottles, lacks the hardness and chemical stability required for high-performance mobile devices. Smartphone manufacturers prefer aluminosilicate glass like Corning Gorilla Glass for enhanced protective features that improve device longevity and user experience.
Infographic: Soda-lime glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com