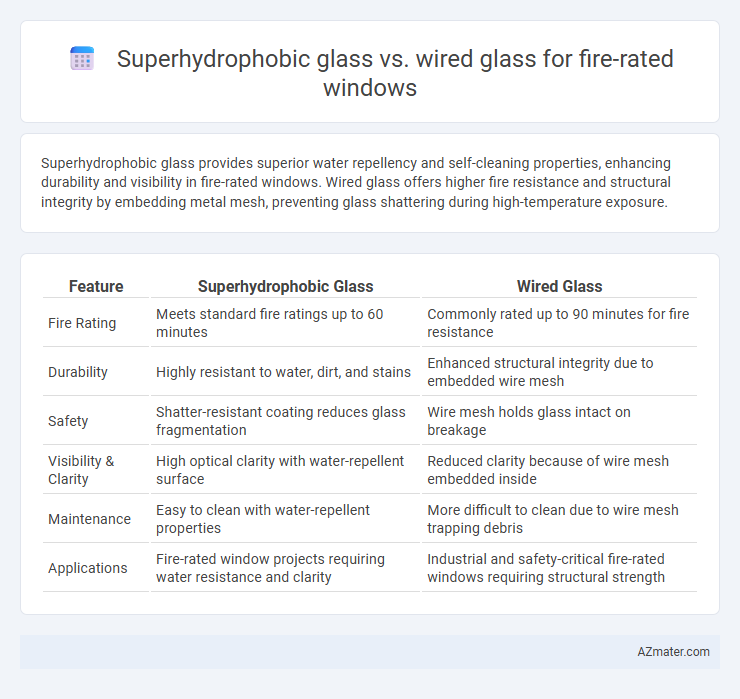
Superhydrophobic glass provides superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, enhancing durability and visibility in fire-rated windows. Wired glass offers higher fire resistance and structural integrity by embedding metal mesh, preventing glass shattering during high-temperature exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Rating | Meets standard fire ratings up to 60 minutes | Commonly rated up to 90 minutes for fire resistance |
| Durability | Highly resistant to water, dirt, and stains | Enhanced structural integrity due to embedded wire mesh |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant coating reduces glass fragmentation | Wire mesh holds glass intact on breakage |
| Visibility & Clarity | High optical clarity with water-repellent surface | Reduced clarity because of wire mesh embedded inside |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean with water-repellent properties | More difficult to clean due to wire mesh trapping debris |
| Applications | Fire-rated window projects requiring water resistance and clarity | Industrial and safety-critical fire-rated windows requiring structural strength |
Introduction to Fire-Rated Window Technologies
Fire-rated windows are engineered to prevent the spread of fire and smoke while maintaining visibility and light transmission. Superhydrophobic glass enhances fire-rated windows by repelling water and contaminants, reducing the risk of damage from moisture and maintaining optical clarity during fire events. Wired glass features embedded wire mesh that provides structural integrity under heat, but its visual distortion and lower water resistance limit its applications compared to advanced superhydrophobic coatings in fire safety technology.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features a nanoscale coating that repels water, creating an ultra-water-resistant surface ideal for maintaining clear visibility in fire-rated windows by preventing condensation and water damage. This innovative material enhances durability and safety by minimizing thermal stress and corrosion during fire exposure. Wired glass, embedded with metal mesh, primarily provides fire resistance and structural integrity but lacks the water-repelling benefits critical for preventing fogging in high-moisture environments.
Understanding Wired Glass in Fire-Rated Applications
Wired glass consists of a glass pane embedded with a wire mesh designed to maintain integrity during fire exposure by holding glass fragments in place, enhancing safety and fire resistance. It is commonly used in fire-rated windows and doors to meet building codes requiring fire containment while allowing visibility. Despite its fire-retardant benefits, wired glass is less impact-resistant compared to laminated or tempered glasses, limiting its use in high-impact scenarios.
Key Performance Differences: Superhydrophobic vs Wired Glass
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, which enhance visibility and reduce maintenance compared to wired glass. Wired glass provides embedded steel mesh reinforcement for fire resistance and structural integrity, but it often compromises optical clarity due to its wired pattern. In fire-rated window applications, wired glass excels in preventing fire spread, while superhydrophobic glass primarily improves durability against environmental factors without significant fire protection.
Fire Resistance Capabilities of Both Glass Types
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced fire resistance due to its ability to repel water and prevent heat transfer, maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that holds the glass together during fire exposure, reducing breakage and providing a barrier to flames and smoke. While wired glass is traditionally recognized for fire-rated applications, superhydrophobic glass combines water repellency with fire resistance, potentially improving safety performance in fire-rated windows.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass demonstrates superior durability due to its water-repellent coating that minimizes corrosion and surface degradation, extending the lifespan of fire-rated windows compared to conventional wired glass. Wired glass, while providing effective fire resistance, is prone to rust and weakening over time as the embedded wire mesh corrodes, increasing maintenance requirements. Maintenance for superhydrophobic fire-rated glass involves minimal cleaning to preserve its hydrophobic properties, whereas wired glass demands regular inspections and potential wire replacement to maintain structural integrity and fire performance.
Safety Features: Impact Resistance and Breakage
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced safety features with superior impact resistance due to its hydrophobic coating that repels water and reduces surface damage, maintaining integrity under stress. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, provides robust structural reinforcement, preventing shattering and containing glass fragments during breakage, which is crucial for fire-rated windows. The wire mesh in wired glass also aids in heat resistance, whereas superhydrophobic glass excels in durability against moisture-related wear while maintaining clarity and strength.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass offers a sleek, clear appearance with minimal maintenance, enhancing modern fire-rated windows through its water-repellent surface that resists stains and smudges, preserving visual clarity. Wired glass, characterized by embedded metal mesh, compromises aesthetic appeal with visible grid patterns and a more industrial look, limiting design flexibility. Choosing superhydrophobic glass enhances the architectural elegance of fire-rated windows while maintaining safety standards, making it ideal for contemporary design-focused applications.
Cost Analysis: Superhydrophobic vs Wired Glass
Superhydrophobic glass for fire-rated windows generally incurs higher initial costs compared to wired glass due to advanced nanocoating technologies and specialized manufacturing processes. Wired glass offers a more cost-effective solution with established production and installation methods, reducing upfront investment for fire safety compliance. However, superhydrophobic glass may provide long-term value through enhanced durability, easier maintenance, and superior resistance to water and contaminants, potentially offsetting initial expenses over the window's lifespan.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire-Rated Windows
Superhydrophobic glass offers water-repellent properties enhancing durability, while wired glass provides critical fire resistance by holding shattered glass fragments together under heat exposure. For fire-rated windows, wired glass is often preferred due to its proven ability to maintain integrity and prevent fire and smoke spread during emergencies. Selecting the right glass hinges on balancing fire safety requirements with maintenance and environmental conditions of the installation site.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Wired glass for Fire-rated window
 azmater.com
azmater.com