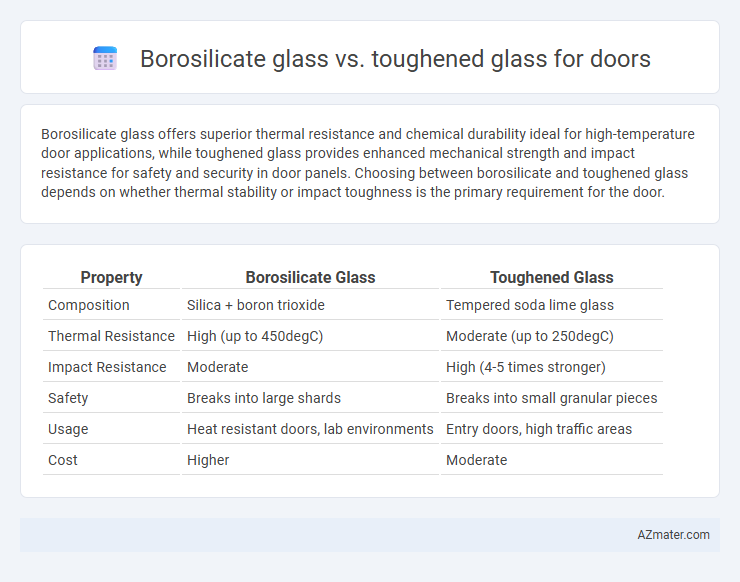
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability ideal for high-temperature door applications, while toughened glass provides enhanced mechanical strength and impact resistance for safety and security in door panels. Choosing between borosilicate and toughened glass depends on whether thermal stability or impact toughness is the primary requirement for the door.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Toughened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica + boron trioxide | Tempered soda lime glass |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Moderate (up to 250degC) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High (4-5 times stronger) |
| Safety | Breaks into large shards | Breaks into small granular pieces |
| Usage | Heat resistant doors, lab environments | Entry doors, high traffic areas |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Borosilicate and Toughened Glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its low thermal expansion and high resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under temperature fluctuations. Toughened glass, also called tempered glass, undergoes a specialized heat treatment process to enhance its strength and ensure it breaks into small, less harmful pieces, improving safety in architectural uses. Both glass types are commonly used in doors for their strength and safety features, with borosilicate glass favored for thermal resistance and toughened glass preferred for impact resistance.
Key Differences Between Borosilicate and Toughened Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for environments with high temperature variations, while toughened glass is engineered for enhanced mechanical strength and impact resistance, suitable for safety-critical door applications. Borosilicate glass features low thermal expansion, reducing the risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes, whereas toughened glass undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment process that increases its surface compressive stress for improved fracture resistance. Toughened glass tends to shatter into small granular chunks upon breakage, enhancing safety, while borosilicate glass breaks into larger, sharp shards, making it less safe for door usage in high-impact areas.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal shock resistance and chemical durability, offers excellent strength under high temperature fluctuations but has moderate impact resistance compared to toughened glass. Toughened glass undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatments, increasing its mechanical strength up to four to five times that of standard glass, making it highly resistant to impact and bending stresses encountered in door applications. For door installations requiring maximum impact resistance and safety, toughened glass is typically preferred, whereas borosilicate glass suits environments with significant temperature variations and chemical exposure.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal resistance and can withstand temperature changes up to approximately 450degC without cracking, making it ideal for environments with extreme heat fluctuations. Toughened glass, while stronger against impact due to its tempering process, typically tolerates temperatures only up to around 250degC before risking structural damage. For door applications where high thermal resistance and temperature tolerance are critical, borosilicate glass offers a more durable solution compared to toughened glass.
Safety Features in Door Applications
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and shatterproof properties due to its chemical composition, making it highly safe for door applications exposed to temperature fluctuations. Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, undergoes a heat-treatment process that increases its strength and, upon breakage, shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk. Both types enhance door safety, but toughened glass is preferred for impact resistance while borosilicate glass excels in thermal durability.
Appearance and Design Flexibility
Borosilicate glass offers a sleek, clear appearance with high transparency and excellent resistance to thermal stress, making it ideal for modern door designs requiring minimal distortion and maximum clarity. Toughened glass provides enhanced strength and safety with a slightly textured surface that can incorporate various patterns, offering greater design flexibility for decorative or privacy door applications. Both materials cater to different aesthetic preferences, with borosilicate emphasizing refined elegance and toughened glass supporting versatile stylistic options.
Cost Analysis: Borosilicate vs Toughened Glass
Borosilicate glass typically costs 20-40% more than toughened glass due to its superior thermal and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance door applications. Toughened glass, favored for its impact strength and safety features, is more cost-effective for standard door installations, with prices generally 30-50% lower than borosilicate. The choice hinges on balancing budget constraints against the need for durability and specialized properties in door design.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Borosilicate glass requires minimal maintenance due to its chemical resistance and ability to withstand thermal shock, making it easy to clean with standard glass cleaners without risk of damage. Toughened glass, while highly durable and resistant to impact, needs careful cleaning with non-abrasive materials to avoid surface scratches that could weaken its structural integrity. Both materials benefit from regular wiping with soft cloths, but borosilicate glass offers superior longevity with less frequent maintenance interventions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Borosilicate glass offers superior environmental benefits due to its high thermal resistance, reducing energy consumption during manufacturing and extending product lifespan. Toughened glass, while stronger and safer under impact, requires more energy-intensive processes and has a shorter lifecycle, leading to higher carbon emissions. Choosing borosilicate glass for doors supports sustainability through durability and lower environmental footprint in production and disposal phases.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Doors
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for doors in environments exposed to rapid temperature changes or corrosive elements. Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, provides superior strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces on impact, which is essential for high-traffic areas or doors subject to heavy use. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing the need for thermal stability with impact resistance and safety requirements specific to your door's location and purpose.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Toughened glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com