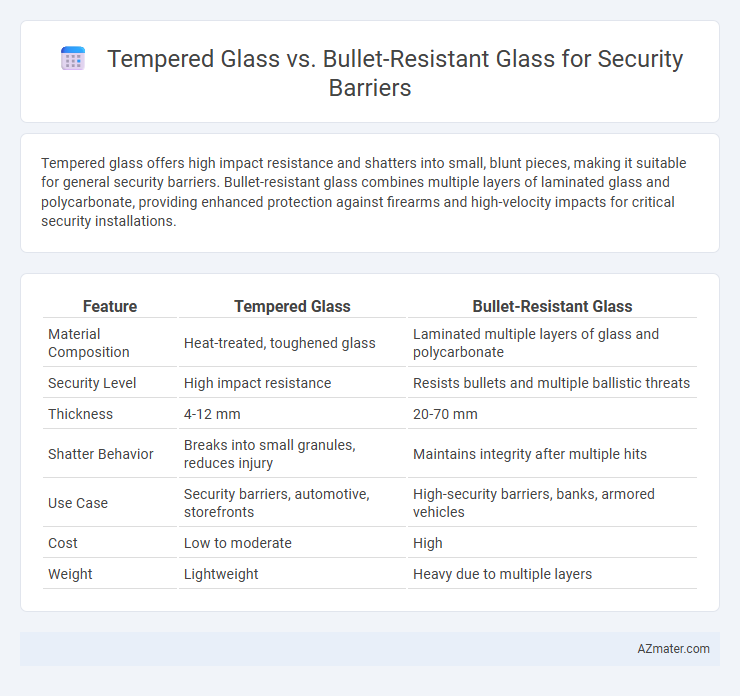
Tempered glass offers high impact resistance and shatters into small, blunt pieces, making it suitable for general security barriers. Bullet-resistant glass combines multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, providing enhanced protection against firearms and high-velocity impacts for critical security installations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Bullet-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Heat-treated, toughened glass | Laminated multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate |
| Security Level | High impact resistance | Resists bullets and multiple ballistic threats |
| Thickness | 4-12 mm | 20-70 mm |
| Shatter Behavior | Breaks into small granules, reduces injury | Maintains integrity after multiple hits |
| Use Case | Security barriers, automotive, storefronts | High-security barriers, banks, armored vehicles |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy due to multiple layers |
Introduction to Security Barriers
Security barriers utilize tempered glass or bullet-resistant glass to enhance protection in high-risk environments. Tempered glass offers high impact resistance and shatters into small, blunt pieces, providing basic security against forced entry. Bullet-resistant glass combines multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, delivering superior ballistic protection by absorbing and dispersing the energy of projectiles.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risk when broken. While tempered glass provides resistance against impact and heat, it does not offer the ballistic protection found in bullet-resistant glass used for security barriers.
What is Bullet-Resistant Glass?
Bullet-resistant glass is a multi-layered composite glass designed to withstand high-velocity projectile impacts, providing enhanced security for barriers. Unlike tempered glass, which offers strength and shatter resistance, bullet-resistant glass incorporates polycarbonate or other resilient materials to absorb and disperse the energy of bullets without penetration. This specialized glass is essential in environments requiring protection against firearms, such as banks, government buildings, and secure checkpoints.
Key Differences Between Tempered and Bullet-Resistant Glass
Tempered glass offers increased strength over standard glass by undergoing a heat treatment process, making it resistant to impact and shattering into small, blunt pieces for safety. Bullet-resistant glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a laminated composite composed of multiple layers, including polycarbonate, designed to absorb and disperse the energy of bullets, preventing penetration. Unlike tempered glass, bullet-resistant glass provides high-level protection against firearm attacks, making it suitable for security barriers requiring advanced threat mitigation.
Strength Comparison: Tempered vs Bullet-Resistant Glass
Tempered glass offers enhanced strength through a thermal or chemical tempering process, making it approximately four times stronger than standard annealed glass, but it is designed primarily to resist impacts and shattering from moderate threats. Bullet-resistant glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, is engineered to absorb and dissipate the energy of bullet impacts, providing superior protection against high-velocity projectiles. The multilayered construction of bullet-resistant glass far exceeds the structural integrity and impact resistance of tempered glass, making it the preferred choice for high-security barriers requiring ballistic protection.
Performance in Security Applications
Tempered glass offers high strength and shatter resistance by undergoing thermal treatment, making it suitable for impact protection in security barriers but limited against high-velocity projectiles. Bullet-resistant glass combines layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials to absorb and disperse ballistic energy, providing superior protection against firearm attacks and forced entry. In security applications, bullet-resistant glass outperforms tempered glass by effectively stopping bullets and maintaining structural integrity under extreme stress.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Tempered glass offers easier installation due to its lighter weight and standard thickness but requires careful handling to avoid damage during mounting. Bullet-resistant glass, composed of multiple laminated layers with polycarbonate, demands specialized installation techniques and certified professionals to ensure its integrity and security performance. Maintenance for bullet-resistant glass involves regular inspection of seals and layers to prevent delamination, while tempered glass maintenance primarily focuses on cleaning and prompt replacement if shattered.
Cost Analysis: Tempered vs Bullet-Resistant Glass
Tempered glass offers a cost-effective security solution with prices ranging from $10 to $30 per square foot, making it suitable for moderate impact resistance in security barriers. Bullet-resistant glass, incorporating multiple laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, demands significantly higher investment, costing between $50 and $150 per square foot due to its enhanced ballistic protection. Evaluating project requirements and threat levels is essential to balance upfront expenses against long-term security benefits when choosing between tempered and bullet-resistant glass.
Best Use Cases for Each Glass Type
Tempered glass offers high strength and shatter resistance, making it ideal for security barriers in commercial buildings and retail stores where impact resistance against accidental hits or vandalism is essential. Bullet-resistant glass provides multi-layered protection against ballistic threats, making it best suited for high-risk environments such as government facilities, banks, and airports requiring enhanced security against gunfire. Selecting the appropriate glass depends on threat level and required security, with tempered glass addressing general impact protection and bullet-resistant glass designed for life-threatening situations.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Security Needs
Tempered glass provides strong impact resistance and shatters into small, less dangerous pieces, making it ideal for general security barriers where safety and strength are priorities. Bullet-resistant glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, offers superior protection against ballistic threats and is essential for high-security environments requiring defense against firearms. Selecting the right glass depends on assessing threat levels, the need for visibility, budget constraints, and the specific security requirements of the premises.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Bullet-resistant glass for Security barrier
 azmater.com
azmater.com