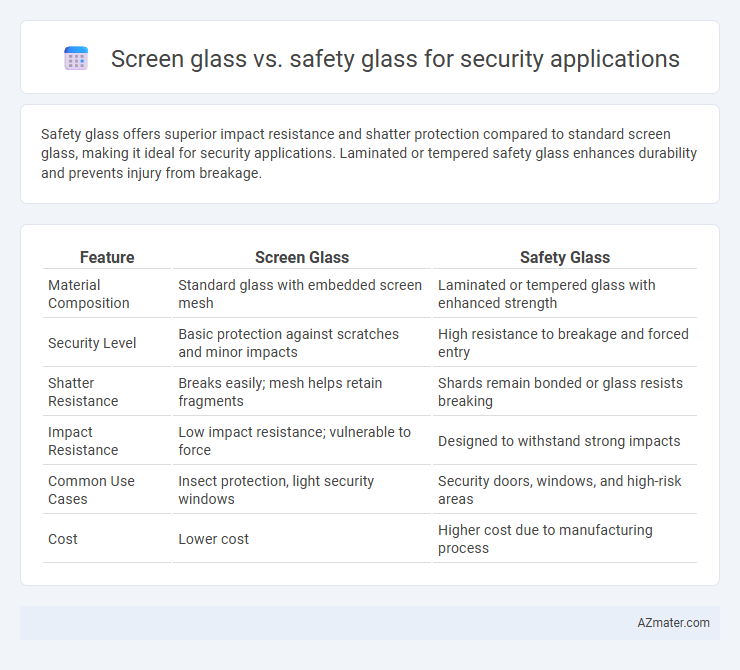
Safety glass offers superior impact resistance and shatter protection compared to standard screen glass, making it ideal for security applications. Laminated or tempered safety glass enhances durability and prevents injury from breakage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screen Glass | Safety Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Standard glass with embedded screen mesh | Laminated or tempered glass with enhanced strength |
| Security Level | Basic protection against scratches and minor impacts | High resistance to breakage and forced entry |
| Shatter Resistance | Breaks easily; mesh helps retain fragments | Shards remain bonded or glass resists breaking |
| Impact Resistance | Low impact resistance; vulnerable to force | Designed to withstand strong impacts |
| Common Use Cases | Insect protection, light security windows | Security doors, windows, and high-risk areas |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing process |
Understanding Screen Glass and Safety Glass
Screen glass, commonly a tempered or laminated product, enhances security applications by combining clarity with impact resistance, effectively preventing easy breakage and intrusion. Safety glass, such as laminated glass with an interlayer or toughened tempered glass, is designed to resist shattering into sharp pieces, ensuring occupant safety during forced entry or accidents. Understanding the material composition and purpose of each glass type is crucial in selecting the right option for security solutions, balancing visibility, strength, and protection.
Key Differences Between Screen Glass and Safety Glass
Screen glass primarily functions as a protective barrier designed to prevent damage to LCD or OLED panels in electronic devices, offering minimal impact resistance and no shatter protection. Safety glass, such as tempered or laminated glass, enhances security by providing high impact resistance and minimizing injury risks through controlled breakage patterns or layered construction. In security applications, safety glass is preferred for its durability and ability to maintain barrier integrity under force, whereas screen glass serves mainly to protect delicate display surfaces.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Screen glass typically consists of chemically strengthened soda-lime silica glass, enhancing scratch resistance but maintaining standard breakage patterns. Safety glass, such as laminated or tempered varieties, incorporates materials like polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers or undergoes heat treatment to increase impact resistance and hold fragments together upon breakage. Manufacturing processes for safety glass involve precise thermal tempering or lamination under high pressure and temperature, ensuring superior durability and safety performance compared to standard screen glass.
Impact Resistance: Which Glass Offers Better Protection?
Safety glass, including tempered and laminated varieties, offers superior impact resistance compared to standard screen glass, making it the preferred choice for security applications. Tempered safety glass is designed to withstand higher impact forces, shattering into small, less harmful pieces, while laminated glass contains an interlayer that holds shards together, preventing penetration and enhancing protection. Screen glass lacks these reinforcement features, making it more vulnerable to breakage and less effective in preventing forced entry or impact-related damage.
Breakage Patterns and Security Implications
Screen glass typically shatters into large, sharp shards upon impact, posing significant risks of injury and easier breach points in security applications. Safety glass, such as laminated or tempered glass, breaks into small, blunt fragments or remains adhered to an interlayer, enhancing resistance to forced entry and reducing injury hazards. The inherent breakage patterns of safety glass contribute to stronger physical barriers, making it the preferred choice for secure environments requiring enhanced protection against vandalism and intrusion.
Cost Considerations for Security Applications
Screen glass offers a cost-effective solution for security applications, providing basic protection at a lower price point compared to safety glass. Safety glass, including tempered and laminated types, demands higher initial investment but delivers superior impact resistance, enhanced durability, and compliance with safety standards crucial for high-risk environments. When evaluating cost considerations, the long-term benefits of reduced replacement frequency and increased protection often justify the premium for safety glass in security-sensitive settings.
Installation Requirements and Compatibility
Screen glass requires precise framing and sealing during installation to ensure optimal clarity and secure fit, often compatible with standard window frames but less effective under high-impact conditions. Safety glass, such as laminated or tempered variants, demands specialized handling and mounting techniques to maintain its structural integrity and shock resistance, compatible with reinforced frames designed for security applications. Proper installation of safety glass mitigates risks of breakage and enhances overall security, making it more suitable for environments requiring stringent protective measures.
Maintenance and Longevity in Security Settings
Safety glass, such as laminated or tempered variants, offers superior durability and resistance to impact, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing maintenance costs in security applications. Screen glass, often thinner and less robust, tends to scratch and break more easily under high-stress conditions, leading to increased upkeep and shorter lifespan in secure environments. Choosing safety glass enhances long-term performance by maintaining structural integrity and clarity, crucial for effective security monitoring and protection.
Industry Standards and Compliance Regulations
Safety glass, including tempered and laminated variants, is preferred over standard screen glass in security applications due to its compliance with stringent industry standards such as ANSI Z97.1 and EN 12600, which certify impact resistance and shatterproof properties. Screen glass lacks these certifications and is more prone to breakage, posing a risk in high-security environments requiring adherence to building codes and safety regulations like OSHA and IBC. Selecting safety glass ensures both regulatory compliance and enhanced protection against forced entry and accidental impact.
Choosing the Right Glass for Maximum Security
Safety glass, such as tempered or laminated glass, offers enhanced impact resistance and shatterproof properties crucial for security applications. Screen glass, typically thinner and less durable, lacks the ability to withstand forced entry or high-impact scenarios effectively. Choosing laminated safety glass with interlayer films maximizes security by preventing glass penetration and reducing the risk of injury during breakage.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Safety glass for Security application
 azmater.com
azmater.com