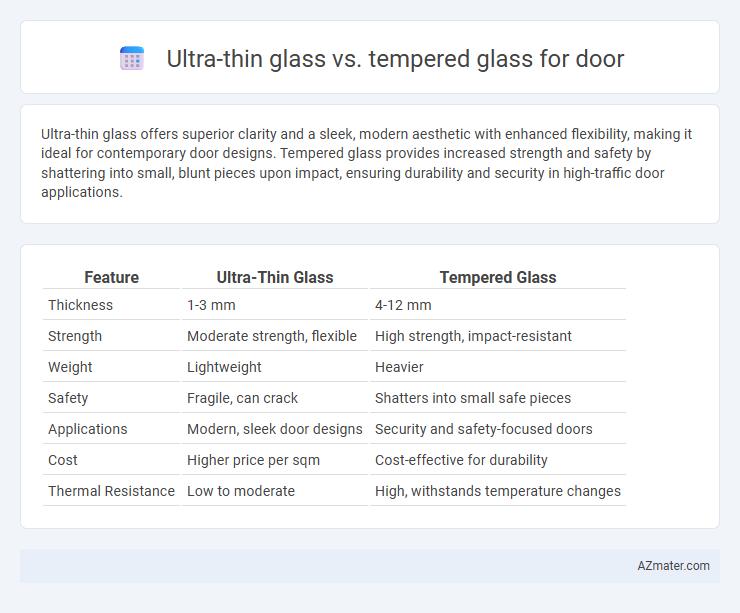
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and a sleek, modern aesthetic with enhanced flexibility, making it ideal for contemporary door designs. Tempered glass provides increased strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, ensuring durability and security in high-traffic door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Thin Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 1-3 mm | 4-12 mm |
| Strength | Moderate strength, flexible | High strength, impact-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Safety | Fragile, can crack | Shatters into small safe pieces |
| Applications | Modern, sleek door designs | Security and safety-focused doors |
| Cost | Higher price per sqm | Cost-effective for durability |
| Thermal Resistance | Low to moderate | High, withstands temperature changes |
Introduction to Glass Options for Doors
Ultra-thin glass for doors offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with enhanced transparency and lightweight properties, making it ideal for minimalist designs and spaces where natural light is prioritized. Tempered glass, however, provides superior strength and safety by undergoing a heat-treatment process that increases its resistance to impact and thermal stress, making it suitable for high-traffic or security-focused door applications. Choosing between these glass types depends on balancing design preferences with functional requirements such as durability, safety standards, and maintenance considerations.
What is Ultra-Thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass is a high-performance, lightweight glass with a thickness typically below 2 mm, designed for enhanced flexibility and durability in door applications. It offers superior clarity and impact resistance compared to standard tempered glass, making it ideal for modern, minimalist door designs requiring both aesthetics and safety. Its ultra-thin profile allows for slimmer frames and innovative architectural solutions without compromising strength or security.
Understanding Tempered Glass
Tempered glass for doors offers enhanced strength and safety by undergoing a heat treatment process that increases its resistance to impact and thermal stress. Unlike ultra-thin glass, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces when broken, reducing the risk of injury. Its durability and safety features make tempered glass a preferred choice for high-traffic areas and exterior doors requiring robust protection.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Ultra-thin glass offers lightweight flexibility with moderate strength, making it ideal for sleek door designs where minimal weight is critical, but it is more prone to scratches and impact damage compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass undergoes a heat-treatment process that significantly enhances its strength and durability, making it highly resistant to shattering and suitable for high-traffic door applications requiring robust safety features. While ultra-thin glass excels in aesthetic and design adaptability, tempered glass provides superior longevity and impact resistance for secure and durable door installations.
Thickness and Design Flexibility
Ultra-thin glass ranges from 0.1mm to 0.5mm in thickness, offering exceptional design flexibility for sleek, modern door applications where minimal weight and translucency are critical. Tempered glass typically measures between 4mm and 12mm, providing superior strength and safety but limiting customization due to its rigid thickness standards. The ultra-thin glass enables innovative architectural designs with curved or layered surfaces, whereas tempered glass is preferred for traditional flat-panel doors requiring robust impact resistance.
Safety Features and Breakage Patterns
Ultra-thin glass for doors offers high flexibility and resistance to shattering, minimizing sharp edges upon breakage and enhancing safety in impact scenarios. Tempered glass is engineered to crumble into small, blunt granules when broken, significantly reducing injury risk compared to traditional glass. The breakage pattern of ultra-thin glass prevents large shards, while tempered glass ensures rapid disintegration into harmless pieces, both prioritizing occupant protection.
Aesthetic Appeal and Transparency
Ultra-thin glass offers superior aesthetic appeal with its sleek, minimalist profile and higher transparency, allowing maximum natural light to pass through and enhancing the visual openness of door designs. Tempered glass, while robust and safe, typically has a thicker appearance and may slightly reduce clarity due to its manufacturing process, impacting the overall sleekness of the door. Choosing ultra-thin glass prioritizes elegance and a modern look, making it ideal for contemporary interiors that emphasize light and unobstructed views.
Cost Comparison: Ultra-Thin vs. Tempered Glass
Ultra-thin glass generally costs 20-30% more than tempered glass due to its advanced manufacturing process and specialized materials. Tempered glass remains more budget-friendly, making it a popular choice for door applications requiring safety and durability. Long-term investment in ultra-thin glass can offer aesthetic advantages and lighter weight but often comes with higher upfront expenses compared to tempered glass.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional lightweight properties and high transparency, making it ideal for sleek modern interior doors and partitions where minimal visual intrusion and design flexibility are prioritized. Tempered glass provides superior strength and safety, suited for exterior doors and high-traffic areas requiring enhanced durability and impact resistance. Choosing between ultra-thin and tempered glass depends on balancing aesthetic demands with safety and structural requirements for specific door applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Doors
Ultra-thin glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with lightweight properties ideal for minimalist door designs, yet tempered glass provides superior strength, safety, and impact resistance essential for high-traffic or security-focused doors. Prioritizing tempered glass ensures compliance with safety standards and durability in commercial or residential entryways. Selecting between ultra-thin and tempered glass depends on balancing design preferences with required structural performance and safety regulations.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com