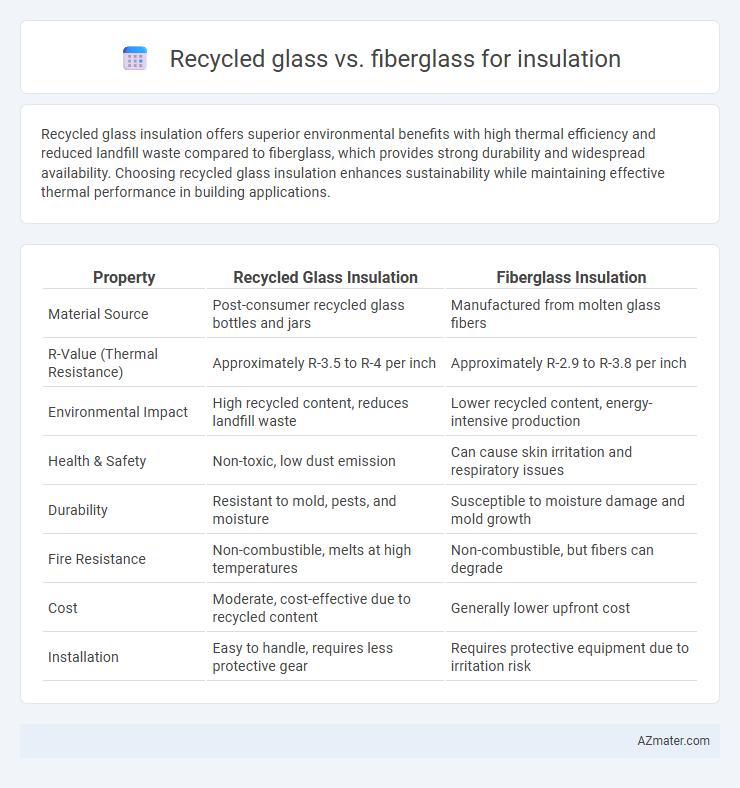
Recycled glass insulation offers superior environmental benefits with high thermal efficiency and reduced landfill waste compared to fiberglass, which provides strong durability and widespread availability. Choosing recycled glass insulation enhances sustainability while maintaining effective thermal performance in building applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Glass Insulation | Fiberglass Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer recycled glass bottles and jars | Manufactured from molten glass fibers |
| R-Value (Thermal Resistance) | Approximately R-3.5 to R-4 per inch | Approximately R-2.9 to R-3.8 per inch |
| Environmental Impact | High recycled content, reduces landfill waste | Lower recycled content, energy-intensive production |
| Health & Safety | Non-toxic, low dust emission | Can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues |
| Durability | Resistant to mold, pests, and moisture | Susceptible to moisture damage and mold growth |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, melts at high temperatures | Non-combustible, but fibers can degrade |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective due to recycled content | Generally lower upfront cost |
| Installation | Easy to handle, requires less protective gear | Requires protective equipment due to irritation risk |
Introduction to Recycled Glass and Fiberglass Insulation
Recycled glass insulation utilizes crushed post-consumer or industrial glass transformed into loose-fill or rigid board materials, offering sustainable thermal and acoustic benefits with reduced environmental impact. Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers spun from molten glass, valued for its widespread availability, high R-value per inch, and fire resistance. Both materials serve as effective insulators, but recycled glass insulation emphasizes eco-friendliness while fiberglass prioritizes cost efficiency and ease of installation.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Recycled glass insulation primarily consists of cullet, melted and reformed into glass fibers, utilizing less energy and reducing landfill waste compared to fiberglass. Fiberglass insulation is manufactured by melting silica sand and other raw materials at high temperatures, then spun into fine fibers, which requires more raw resources and energy. The eco-friendly production of recycled glass offers lower carbon emissions, while fiberglass remains a widely used synthetic material in thermal insulation.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Recycled glass insulation offers excellent thermal performance due to its dense composition and ability to trap air, resulting in an R-value typically ranging from 3.5 to 4.0 per inch. Fiberglass insulation provides comparable thermal resistance with R-values between 2.9 and 3.8 per inch, but it is often less effective at preventing air infiltration unless properly installed. Choosing recycled glass insulation can enhance energy efficiency by providing superior heat retention and minimizing temperature fluctuations in buildings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled glass insulation significantly reduces landfill waste and lowers energy consumption during production compared to conventional fiberglass, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Fiberglass insulation relies on energy-intensive manufacturing processes and incorporates non-renewable materials, resulting in a higher carbon footprint over its lifecycle. Selecting recycled glass insulation promotes circular economy principles and reduces resource depletion, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable building projects.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Recycled glass insulation offers cost efficiency due to its lower production expenses and abundant supply from post-consumer waste, making it a sustainable choice for budget-conscious projects. Fiberglass insulation, widely available in various forms, tends to have moderate upfront costs but may require more frequent replacement over time, impacting long-term expenses. Availability of recycled glass varies regionally, while fiberglass remains consistently accessible in most markets, influencing project planning and material sourcing decisions.
Installation and Handling Differences
Recycled glass insulation typically requires careful handling due to its brittleness and potential for sharp edges, necessitating gloves and protective equipment during installation. Fiberglass insulation, composed of fine glass fibers, can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues if proper protective gear like masks and long sleeves are not used. Installation of recycled glass panels is often more rigid and requires precise fitting, while fiberglass batts offer more flexibility and easier cutting for various spaces.
Health and Safety Considerations
Recycled glass insulation is non-toxic, free from formaldehyde, and less likely to cause respiratory irritation compared to fiberglass, which contains tiny glass fibers that can irritate skin, eyes, and lungs during installation. Recycled glass products are often mold-resistant and do not off-gas harmful chemicals, improving indoor air quality and reducing long-term health risks. Fiberglass requires careful handling with protective gear to mitigate inhalation and skin contact hazards, while recycled glass insulation offers a safer alternative with minimal health concerns.
Durability and Longevity
Recycled glass insulation offers excellent durability due to its resistance to moisture, mold, and pests, maintaining its thermal properties over time. Fiberglass insulation, while widely used, can degrade when exposed to moisture and may settle, reducing its effectiveness and lifespan. Both materials provide significant longevity, but recycled glass often outperforms fiberglass in maintaining insulation integrity in harsh environments.
Acoustic Insulation Properties
Recycled glass insulation offers superior acoustic absorption due to its porous structure that effectively dampens sound waves, making it ideal for noise reduction in residential and commercial buildings. Fiberglass insulation, while also providing soundproofing benefits, tends to have less density, resulting in moderate sound attenuation compared to recycled glass. Evaluations show recycled glass materials can reduce airborne noise by up to 50% more than standard fiberglass batts, enhancing overall acoustic comfort.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Recycled glass insulation offers excellent thermal and acoustic properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly residential and commercial buildings aiming to reduce environmental impact. Fiberglass insulation provides superior fire resistance and moisture control, thus best suited for industrial settings and areas with high humidity or stringent fire codes. For optimal performance, choose recycled glass for sustainable, low-impact construction and fiberglass for durability and safety in demanding environments.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com