Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for safety windows in high-risk environments. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with an interlayer, provides enhanced shatter resistance and prevents dangerous shards, ensuring occupant protection during breakage.
Table of Comparison
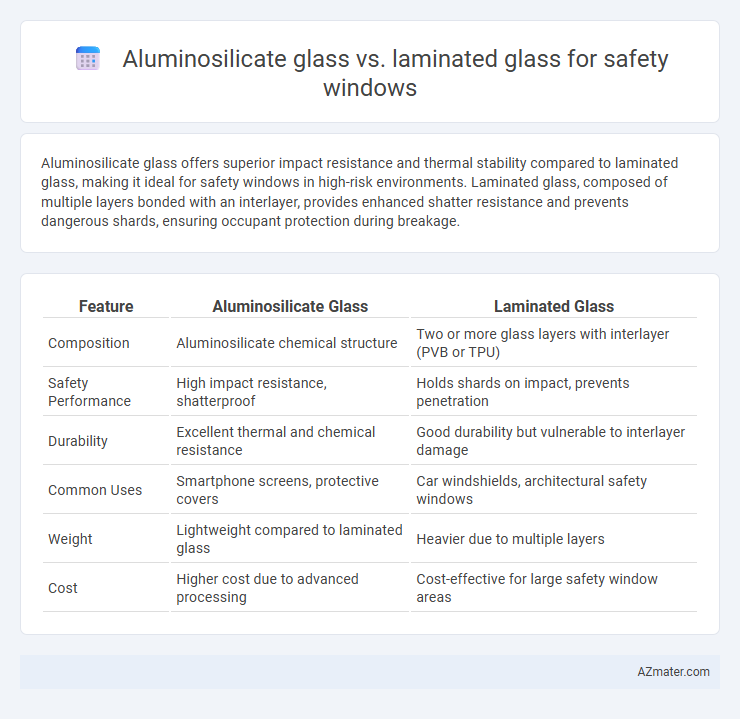
| Feature | Aluminosilicate Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate chemical structure | Two or more glass layers with interlayer (PVB or TPU) |
| Safety Performance | High impact resistance, shatterproof | Holds shards on impact, prevents penetration |
| Durability | Excellent thermal and chemical resistance | Good durability but vulnerable to interlayer damage |
| Common Uses | Smartphone screens, protective covers | Car windshields, architectural safety windows |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to laminated glass | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Cost-effective for large safety window areas |
Introduction to Safety Window Materials
Aluminosilicate glass offers enhanced thermal and mechanical strength, making it highly resistant to impact and suitable for safety window applications in high-stress environments. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing superior shatter resistance by holding fragments together upon breakage. Both materials improve occupant protection, but aluminosilicate glass excels in durability while laminated glass enhances post-impact integrity.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of safety glass known for its high strength and thermal resistance, composed primarily of alumina and silica. It offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to traditional laminated glass, making it ideal for security windows in demanding environments. Its inherent toughness reduces the risk of shattering, enhancing protection in automotive, architectural, and electronic applications.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which holds the glass fragments in place upon impact, enhancing safety. This composition prevents shattering and reduces the risk of injury, making laminated glass ideal for safety windows in vehicles, buildings, and high-security areas. In contrast, aluminosilicate glass offers high thermal and chemical resistance but lacks the layered interlayer structure that provides laminated glass its impact resistance and shatterproof qualities.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength due to its enhanced chemical composition that includes aluminum oxide, making it highly resistant to thermal and mechanical stress. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides exceptional durability by preventing shattering upon impact and maintaining integrity under extreme conditions. For safety windows, aluminosilicate glass excels in scratch resistance and longevity, while laminated glass prioritizes impact resistance and post-breakage safety retention.
Impact Resistance: Aluminosilicate vs Laminated Glass
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance due to its enhanced strength and durability compared to standard laminated glass, making it ideal for high-risk safety window applications. Laminated glass incorporates a plastic interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk but generally absorbing less force before failure than aluminosilicate glass. For environments requiring maximum impact resistance, aluminosilicate glass provides better performance by combining stiffness with energy absorption, whereas laminated glass prioritizes post-breakage safety with controlled fragment retention.
Safety Features and Performance
Aluminosilicate glass offers exceptional impact resistance and thermal durability, making it ideal for safety windows in high-risk environments such as laboratories and industrial settings. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers with interlayers like PVB or EVA, provides superior shatter resistance and maintains structural integrity upon impact, minimizing injury risks from glass shards. Both materials excel in safety performance but laminated glass typically outperforms aluminosilicate glass in preventing glass penetration and enhancing occupant protection during forced entry or accidents.
UV Protection and Optical Clarity
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior UV protection by blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, making it ideal for safety windows exposed to intense sunlight while maintaining high optical clarity without distortion. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with an interlayer, provides effective UV filtering depending on the interlayer material; however, it may exhibit slight reductions in optical clarity due to potential delamination or edge imperfections. The choice between aluminosilicate and laminated glass hinges on balancing maximum UV protection with the required level of optical transparency for specific safety window applications.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Aluminosilicate glass typically offers higher durability and resistance to thermal shock, resulting in lower long-term maintenance costs compared to laminated glass, which requires periodic inspections for delamination and edge seal integrity. Laminated glass, while generally less expensive upfront, may incur higher replacement costs due to potential delamination or adhesive failure over time. Cost analysis should consider both the initial price and lifecycle expenses, with aluminosilicate glass favored in environments demanding minimal maintenance and enhanced longevity.
Applications in Modern Window Design
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-performance safety windows in automotive and aerospace industries, where impact resistance and heat tolerance are critical. Laminated glass combines multiple layers of glass with interlayers, providing enhanced shatter resistance and sound insulation, extensively used in architectural and commercial building windows for occupant protection and noise reduction. Modern window designs leverage aluminosilicate glass for environments demanding extreme durability while laminated glass dominates applications prioritizing impact safety and acoustic comfort.
Choosing the Optimal Safety Glass for Your Needs
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for high-stress environments requiring enhanced safety and durability. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing excellent shatter resistance and preventing dangerous shards, which is essential for security and accident prevention. Selecting the optimal safety glass depends on factors such as impact resistance, thermal performance, and risk mitigation specific to your window application.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Laminated glass for Safety window
 azmater.com
azmater.com