Anti-reflective glass enhances natural daylight transmission and reduces glare in curtain wall facades, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Tinted glass decreases solar heat gain and glare by absorbing sunlight, optimizing thermal performance but potentially reducing visible light levels.
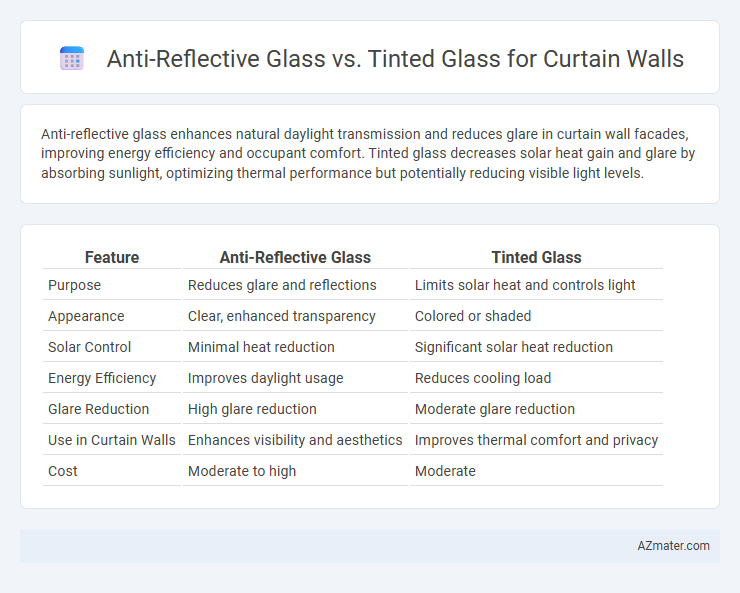
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces glare and reflections | Limits solar heat and controls light |
| Appearance | Clear, enhanced transparency | Colored or shaded |
| Solar Control | Minimal heat reduction | Significant solar heat reduction |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves daylight usage | Reduces cooling load |
| Glare Reduction | High glare reduction | Moderate glare reduction |
| Use in Curtain Walls | Enhances visibility and aesthetics | Improves thermal comfort and privacy |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Solutions
Curtain wall glazing solutions primarily involve materials like anti-reflective glass and tinted glass, each offering unique performance benefits for building facades. Anti-reflective glass enhances natural daylight penetration while minimizing glare, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, contributing to thermal regulation and aesthetic customization of curtain walls.
What is Anti-reflective Glass?
Anti-reflective glass is specially treated to reduce glare and reflections on curtain walls, enhancing natural light transmission while maintaining clear visibility. This type of glass improves energy efficiency by minimizing solar heat gain and optimizing daylight, making building interiors more comfortable. Compared to tinted glass, which reduces light transmission by darkening the glass, anti-reflective glass preserves transparency without compromising aesthetic appeal or natural illumination.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass for curtain walls contains additives like metal oxides that absorb solar radiation, reducing glare and heat gain while enhancing energy efficiency. Unlike anti-reflective glass, which minimizes surface reflections to improve clarity, tinted glass provides a colored or shaded appearance that controls daylight and improves occupant comfort. This type of glass is especially beneficial for buildings in hot climates or urban settings where reducing solar heat and glare is critical.
Visual Clarity: Anti-reflective vs Tinted Glass
Anti-reflective glass enhances visual clarity by minimizing surface reflections, allowing more natural light to penetrate and providing unobstructed views through curtain walls. Tinted glass reduces glare by filtering sunlight, but often compromises clarity with a colored hue that can distort external views and reduce overall brightness. For projects prioritizing transparency and maximum daylight, anti-reflective glass delivers superior optical performance compared to tinted glass for curtain wall applications.
Light Transmission and Glare Control
Anti-reflective glass for curtain walls enhances light transmission rates up to 90%, minimizing surface reflections and ensuring clear, unobstructed natural daylight. Tinted glass reduces light transmission by 30-70%, depending on the tint intensity, effectively controlling glare and solar heat gain but at the expense of interior brightness. Both types optimize energy efficiency, yet anti-reflective glass is ideal for maximizing visibility, while tinted glass excels in glare reduction and thermal comfort.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Anti-reflective glass enhances energy efficiency in curtain walls by reducing glare and improving solar heat control, which lowers cooling costs and maintains natural daylight. Tinted glass decreases solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting solar radiation, reducing the need for artificial cooling but can also reduce visible light transmission. Comparing energy performance, anti-reflective glass often provides better balance between light transmission and heat reduction, optimizing both daylighting and thermal insulation.
Aesthetic Differences in Facade Design
Anti-reflective glass enhances curtain wall facades by minimizing glare and reflections, resulting in a clearer, more transparent appearance that highlights interior design and architectural details. Tinted glass offers varying color tones that modify the building's external look, adding depth and visual interest while controlling light and heat, but can reduce transparency. The choice influences facade aesthetics significantly: anti-reflective glass emphasizes openness and clarity, while tinted glass provides a distinctive coloration and shading effect.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Anti-reflective glass for curtain walls typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced coating technologies but offers reduced glare and improved visibility, leading to lower maintenance in cleaning and replacement over time. Tinted glass generally presents a more cost-effective upfront option with simpler production processes, though it may require more frequent cleaning to prevent visible dirt accumulation and can experience fading, increasing maintenance efforts. Long-term cost efficiency favors anti-reflective glass as its durability and performance reduce labor and replacement expenses compared to tinted glass.
Application Suitability for Different Projects
Anti-reflective glass is ideal for curtain walls in commercial buildings where maximizing natural light and improving visibility without glare is crucial, such as office towers and retail spaces. Tinted glass suits projects requiring enhanced solar control and privacy, making it preferred for residential high-rises and buildings in hot climates. Selecting between the two depends on the project's specific needs for light transmission, energy efficiency, and aesthetic goals.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall
When selecting glass for curtain walls, anti-reflective glass offers enhanced transparency and minimizes glare by reducing surface reflections, making it ideal for maximizing natural light and maintaining clear views. Tinted glass, on the other hand, provides superior solar control by absorbing and reflecting solar radiation, which reduces heat gain and enhances energy efficiency in buildings exposed to intense sunlight. Evaluating factors such as building orientation, climate, and aesthetic preferences is crucial to determine whether anti-reflective or tinted glass best meets the performance requirements of your curtain wall system.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Tinted glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com