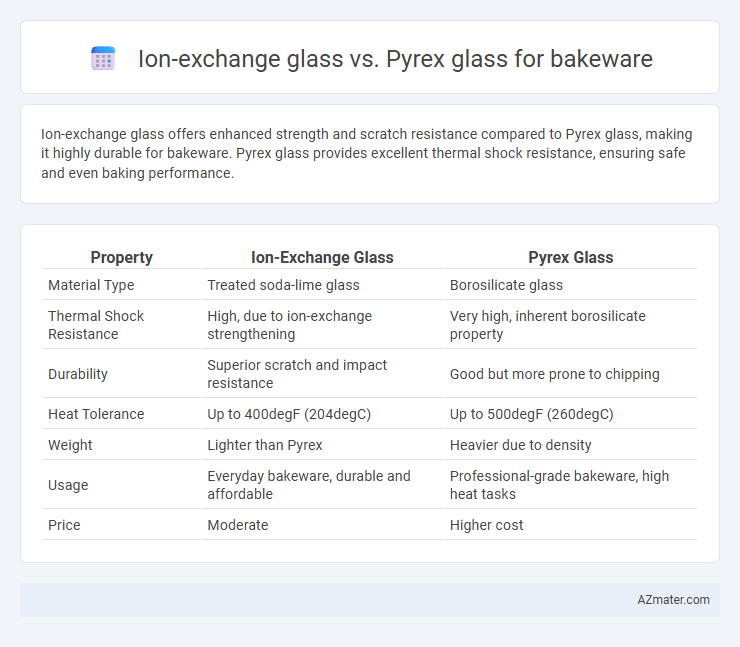
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced strength and scratch resistance compared to Pyrex glass, making it highly durable for bakeware. Pyrex glass provides excellent thermal shock resistance, ensuring safe and even baking performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | Pyrex Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Treated soda-lime glass | Borosilicate glass |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High, due to ion-exchange strengthening | Very high, inherent borosilicate property |
| Durability | Superior scratch and impact resistance | Good but more prone to chipping |
| Heat Tolerance | Up to 400degF (204degC) | Up to 500degF (260degC) |
| Weight | Lighter than Pyrex | Heavier due to density |
| Usage | Everyday bakeware, durable and affordable | Professional-grade bakeware, high heat tasks |
| Price | Moderate | Higher cost |
Introduction to Bakeware Glass Types
Ion-exchange glass used in bakeware undergoes a chemical strengthening process that enhances its durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature baking applications. Pyrex glass, traditionally made from borosilicate, offers exceptional heat resistance and thermal stability, preventing cracking during rapid temperature changes. Understanding the distinct properties of ion-exchange and Pyrex glass helps consumers select bakeware that suits specific cooking needs and ensures long-lasting performance.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a type of strengthened glass created through an ion-exchange process where smaller sodium ions in the glass surface are replaced by larger potassium ions, resulting in increased compressive stress and enhanced durability. This process significantly improves resistance to thermal shock and mechanical breakage compared to standard glass types like Pyrex, which is primarily borosilicate glass. Ion-exchange glass bakeware offers superior toughness and longevity, making it ideal for frequent heating and cooling cycles in baking applications.
What is Pyrex Glass?
Pyrex glass is a brand of borosilicate glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability in bakeware applications. Unlike ion-exchange glass, which gains strength through surface compression by swapping smaller ions with larger ones, Pyrex's borosilicate composition provides natural resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. This makes Pyrex ideal for high-temperature cooking and is favored in kitchens for its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Ion-exchange glass for bakeware is manufactured using a chemical strengthening process where smaller sodium ions in the glass surface are replaced by larger potassium ions, enhancing durability and resistance to thermal shock. Pyrex glass is produced through a borosilicate composition with a low coefficient of thermal expansion, formed and annealed at high temperatures to ensure thermal stability. The ion-exchange manufacturing process results in a tougher surface layer, while Pyrex relies on the intrinsic chemical composition to withstand baking conditions.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior strength compared to Pyrex glass due to its enhanced surface compression achieved through ion-exchange processes, resulting in increased resistance to mechanical impacts and thermal stress. Pyrex glass, while durable and resistant to thermal shock, typically lacks the enhanced surface compression and hardness found in ion-exchange glass, making it more prone to chips and cracks under sudden temperature changes. The durability of ion-exchange glass bakeware surpasses Pyrex, offering longer lifespan and improved resistance to daily wear and tear in high-temperature baking environments.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Ion-exchange glass offers superior thermal shock resistance compared to Pyrex glass due to its surface compression layer, which significantly reduces the risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes. Pyrex glass, traditionally made from borosilicate, is known for its moderate thermal shock resistance but can be more susceptible to sudden temperature shifts in bakeware applications. The engineered strength of ion-exchange glass makes it a preferred choice for bakeware that requires durability and reliable performance under extreme heating and cooling cycles.
Performance in Everyday Baking
Ion-exchange glass offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to Pyrex glass, making it ideal for everyday baking where frequent use and cleaning occur. Pyrex glass, known for its excellent thermal shock resistance, performs well under rapid temperature changes, reducing the risk of cracking during oven-to-counter transitions. Both materials provide reliable heat distribution, but ion-exchange glass tends to maintain its structural integrity longer, enhancing longevity in routine baking tasks.
Safety Considerations
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to thermal shock, reducing the risk of cracking and shattering during baking. Pyrex glass, typically made from borosilicate or tempered soda-lime glass, provides reliable heat resistance but may be more susceptible to sudden temperature changes. Safety considerations prioritize ion-exchange glass for its superior strength and longevity, minimizing potential hazards from breakage in bakeware applications.
Cost and Availability
Ion-exchange glass bakeware typically costs more due to the specialized manufacturing process that enhances strength and durability, making it less commonly available in general retail stores compared to Pyrex glass. Pyrex glass is widely produced and distributed, offering a more affordable and readily accessible option for most consumers. The broader market presence of Pyrex also ensures a larger variety of sizes and styles, contributing to its popularity in bakeware.
Which is Better for Bakeware?
Ion-exchange glass offers superior strength and chip resistance compared to Pyrex glass, making it more durable for bakeware applications that involve frequent temperature changes and rough handling. Pyrex glass, traditionally made from borosilicate, provides excellent thermal shock resistance but is more prone to surface scratches and chips over time. For bakeware, ion-exchange glass is generally better due to its enhanced durability and long-lasting clarity under regular oven use.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Pyrex glass for Bakeware
 azmater.com
azmater.com