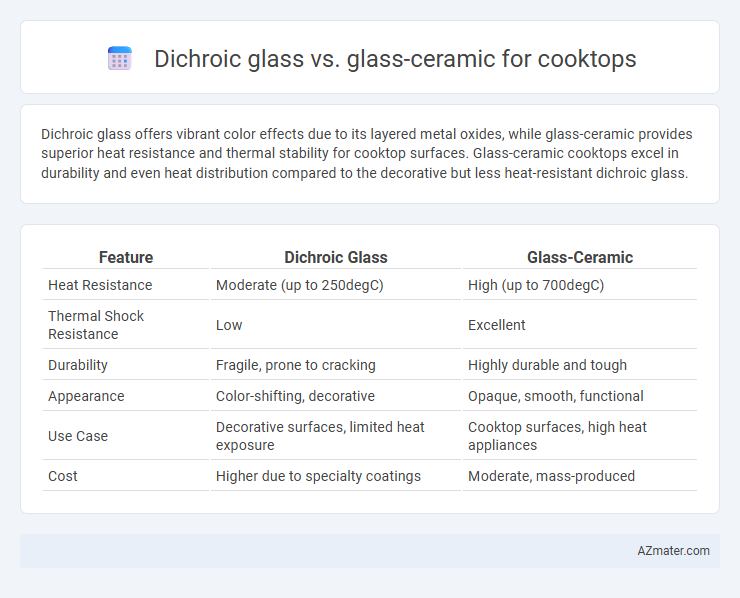
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color effects due to its layered metal oxides, while glass-ceramic provides superior heat resistance and thermal stability for cooktop surfaces. Glass-ceramic cooktops excel in durability and even heat distribution compared to the decorative but less heat-resistant dichroic glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dichroic Glass | Glass-Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 250degC) | High (up to 700degC) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | Excellent |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to cracking | Highly durable and tough |
| Appearance | Color-shifting, decorative | Opaque, smooth, functional |
| Use Case | Decorative surfaces, limited heat exposure | Cooktop surfaces, high heat appliances |
| Cost | Higher due to specialty coatings | Moderate, mass-produced |
Introduction to Cooktop Materials
Dichroic glass and glass-ceramic are two common materials used in cooktop surfaces, each offering unique thermal and aesthetic properties. Dichroic glass features multiple micro-layers of metal oxides, providing vibrant color shifts and excellent heat resistance, suitable for decorative yet functional kitchen designs. Glass-ceramic is engineered for superior thermal shock resistance and durability, with low thermal conductivity that ensures efficient heat transfer and safety during cooking processes.
What is Dichroic Glass?
Dichroic glass is a material composed of multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides deposited on glass, creating a unique optical effect that changes color based on the angle of light. Unlike glass-ceramic cooktops, which are known for their heat resistance and durability, dichroic glass prioritizes aesthetic appeal and light manipulation. This makes dichroic glass less common in cooktop applications where thermal performance and scratch resistance are critical.
What is Glass-Ceramic?
Glass-ceramic is a specialized material engineered for cooktops, combining the aesthetic clarity of glass with the heat resistance and durability of ceramics. It features a crystalline structure formed through controlled crystallization, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking. Unlike dichroic glass, which is primarily decorative and relies on thin film interference to produce shifting colors, glass-ceramic is specifically designed to provide a robust, heat-resistant cooking surface with excellent thermal shock resistance.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Dichroic glass offers moderate heat resistance suitable for decorative applications but is generally less effective in withstanding high cooking temperatures compared to glass-ceramic cooktops. Glass-ceramic cooktops feature exceptional thermal stability and can endure rapid temperature fluctuations up to 700degC, making them ideal for high-heat cooking environments. The crystalline structure in glass-ceramic enhances heat resistance and prevents cracking, setting it apart from dichroic glass in durable cookware surfaces.
Durability and Strength
Dichroic glass, composed of multiple ultra-thin layers, offers moderate durability with vibrant color shifts but is more prone to scratching and chipping compared to glass-ceramic. Glass-ceramic cooktop surfaces, engineered through controlled crystallization, provide superior thermal shock resistance, high mechanical strength, and enhanced durability under continuous high heat exposure. The inherent toughness and fracture resistance of glass-ceramic materials make them the preferred choice for long-lasting cooktop applications.
Aesthetic Differences
Dichroic glass cooktops exhibit a vibrant, iridescent appearance due to their multi-layered coatings that reflect varying colors depending on the light and angle, creating a dynamic visual effect. In contrast, glass-ceramic cooktops offer a smooth, matte or glossy finish with consistent coloration, often in neutral tones, emphasizing sleek modernity and understated elegance. The aesthetic choice between these materials influences kitchen ambiance, with dichroic glass providing a bold, artistic statement and glass-ceramic ensuring timeless, minimalist design.
Cost Considerations
Dichroic glass cooktops typically incur higher costs due to their complex manufacturing process and specialized coatings that enhance aesthetic appeal and heat distribution. Glass-ceramic cooktops offer a more budget-friendly option with durable heat resistance and efficient cooking performance, making them cost-effective for everyday use. Long-term expenses also favor glass-ceramic models, which generally require less maintenance and have greater scratch resistance compared to the delicate dichroic glass surfaces.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Dichroic glass cooktops require gentle, non-abrasive cleaning products to prevent damage to their delicate, colorful surface, ensuring longevity and vibrant aesthetics. Glass-ceramic cooktops allow for more robust cleaning techniques, including specialized scrapers for burnt-on residues, offering ease of maintenance without compromising surface integrity. Regular use of pH-neutral cleaners and avoiding harsh chemicals extends the lifespan and performance of both materials while maintaining a pristine cooking surface.
Suitability for Various Cooking Styles
Dichroic glass cooktops offer excellent heat resistance and vibrant aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for rapid heating and precision cooking styles like stir-frying and sauteing. Glass-ceramic cooktops provide superior thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution, ideal for diverse cooking methods such as simmering, boiling, and slow cooking with heavy pots. Both materials support induction heating technology, but glass-ceramic is generally preferred for its durability and compatibility with a wider range of cookware in various culinary applications.
Conclusion: Which Material is Better for Cooktops?
Dichroic glass offers superior aesthetic appeal with vibrant color reflections but lacks the heat resistance and durability required for cooktops. Glass-ceramic provides exceptional thermal shock resistance, high heat tolerance, and scratch resistance, making it the optimal choice for cooktop surfaces. For longevity and performance under high temperatures, glass-ceramic outperforms dichroic glass in kitchen applications.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Glass-ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com