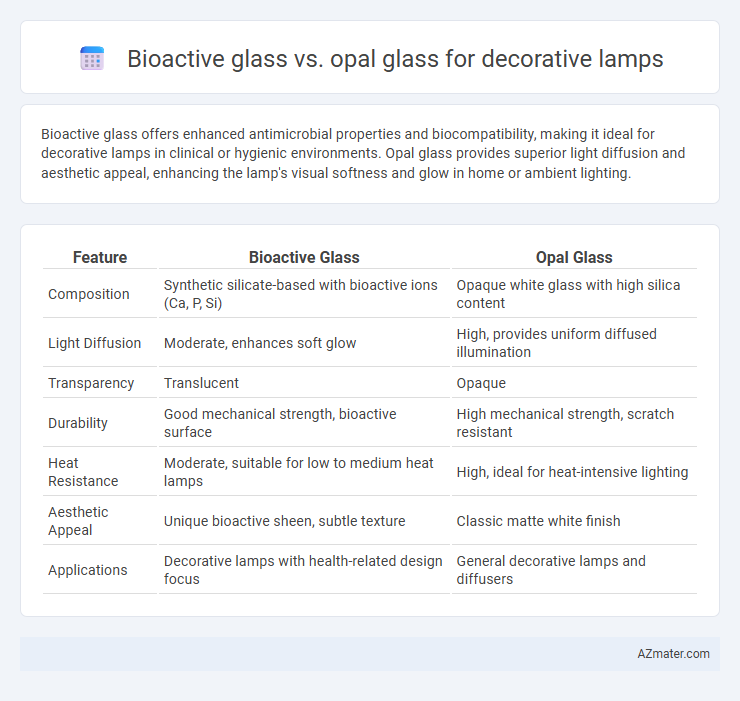
Bioactive glass offers enhanced antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility, making it ideal for decorative lamps in clinical or hygienic environments. Opal glass provides superior light diffusion and aesthetic appeal, enhancing the lamp's visual softness and glow in home or ambient lighting.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioactive Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic silicate-based with bioactive ions (Ca, P, Si) | Opaque white glass with high silica content |
| Light Diffusion | Moderate, enhances soft glow | High, provides uniform diffused illumination |
| Transparency | Translucent | Opaque |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, bioactive surface | High mechanical strength, scratch resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, suitable for low to medium heat lamps | High, ideal for heat-intensive lighting |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Unique bioactive sheen, subtle texture | Classic matte white finish |
| Applications | Decorative lamps with health-related design focus | General decorative lamps and diffusers |
Introduction to Bioactive Glass and Opal Glass
Bioactive glass is a type of material composed primarily of silica, calcium oxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, known for its ability to bond with biological tissues, making it ideal for medical and decorative applications due to its bioactivity and translucent appearance. Opal glass, characterized by its milky, opaque finish achieved through the incorporation of phosphates or fluorides, provides a diffuse light effect that enhances decorative lamp aesthetics by softening illumination. Both materials offer unique optical properties; bioactive glass allows light transmission with subtle color variations, while opal glass ensures uniform brightness and privacy in lighting design.
Chemical Composition: Bioactive vs Opal Glass
Bioactive glass primarily consists of silica (SiO2), calcium oxide (CaO), sodium oxide (Na2O), and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), designed to interact biologically with tissues for medical applications. Opal glass is composed mainly of silica (SiO2) with added opacifying agents such as tin oxide (SnO2) or bone ash (Ca3(PO4)2), which create its characteristic translucent white appearance ideal for decorative lamps. The key chemical difference lies in bioactive glass's bio-interactive components versus opal glass's opaque modifiers, influencing their functionality and aesthetic properties in lighting design.
Aesthetic Properties for Decorative Lamps
Bioactive glass offers a unique translucency with subtle, natural hues that enhance the aesthetic appeal of decorative lamps, creating a soft, ambient glow. Opal glass provides a smooth, uniform surface and diffused light output, making it ideal for achieving a consistent and elegant illumination effect. The choice between bioactive and opal glass depends on the desired visual texture and light diffusion characteristics for decorative lighting designs.
Light Diffusion and Clarity Comparison
Bioactive glass offers superior light diffusion for decorative lamps due to its porous microstructure, which scatters light evenly and reduces glare. Opal glass provides higher clarity with a smooth, opaque surface that produces a soft, uniform glow but less light dispersion. When prioritizing even light spread, bioactive glass excels, while opal glass is ideal for applications requiring clear, diffused illumination with minimal haze.
Durability and Longevity of Both Glass Types
Bioactive glass exhibits superior durability due to its enhanced chemical stability and resistance to surface degradation compared to Opal glass, making it a more long-lasting choice for decorative lamps. Opal glass, while aesthetically appealing with its diffuse light properties, is generally more prone to micro-cracking and surface wear over time, reducing its longevity. The bioactive glass's ability to maintain structural integrity under varied environmental conditions ensures extended lifespan and sustained visual appeal in decorative applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass enhances sustainability through its non-toxic, biodegradable properties, contributing to reduced environmental footprint in decorative lamps. Opal glass, while offering superior light diffusion, commonly relies on energy-intensive production processes and contains materials that are less eco-friendly. Prioritizing bioactive glass in decorative lamp manufacturing supports circular economy principles and aligns with green building standards.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Bioactive glass offers superior customization and design flexibility for decorative lamps, enabling intricate shapes and vibrant color variations through precise composition adjustments. Opal glass provides consistent matte diffusion and smooth finishes but limits complex geometric customization due to its manufacturing constraints. Designers seeking tailored aesthetics and innovative forms typically prefer bioactive glass for its adaptability in lamp design.
Cost Analysis: Bioactive vs Opal Glass
Bioactive glass typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to its specialized composition and processing requirements compared to opal glass, which is more readily produced at scale. Opal glass offers a cost-effective solution for decorative lamps, benefiting from abundant raw materials and established production techniques that reduce overall expenses. When evaluating cost efficiency for decorative lamp applications, opal glass generally provides a more budget-friendly option, while bioactive glass may justify its premium price through added functional benefits.
Market Trends in Decorative Lamp Materials
Bioactive glass is gaining traction in decorative lamp markets due to its eco-friendly properties and ability to enhance aesthetic appeal through natural translucency and biocompatibility. Opal glass remains popular for its consistent diffusion of light and affordability, maintaining strong demand in traditional and mass-market decorative lighting segments. Current market trends indicate a growing preference for sustainable, innovative materials like bioactive glass, driven by increasing consumer awareness and regulatory pressures on environmental impact.
Choosing the Ideal Glass for Your Decorative Lamp
Bioactive glass offers enhanced durability and biocompatibility, making it suitable for decorative lamps that require long-lasting, safe materials resistant to environmental wear. Opal glass provides a soft, diffused light effect with excellent translucency, ideal for lamps designed to create a gentle, ambient glow in interior spaces. Selecting between bioactive glass and opal glass depends on prioritizing either structural resilience and health benefits or aesthetic light diffusion and visual softness.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Opal glass for Decorative lamp
 azmater.com
azmater.com