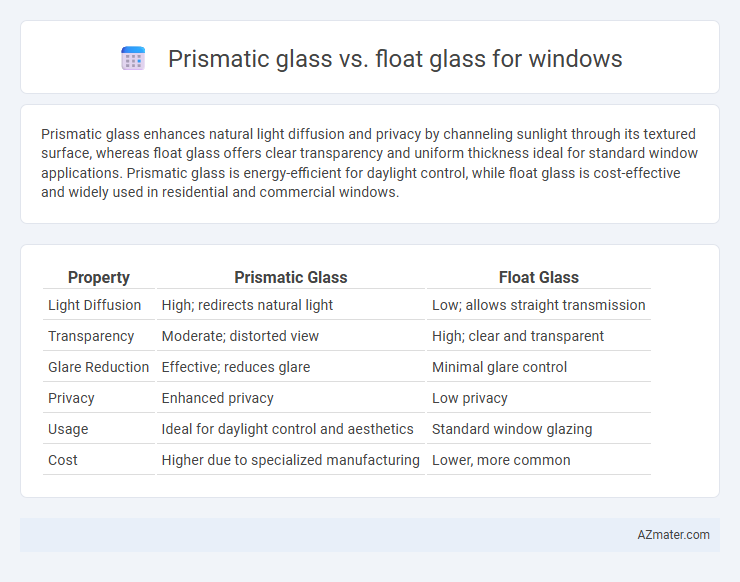
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion and privacy by channeling sunlight through its textured surface, whereas float glass offers clear transparency and uniform thickness ideal for standard window applications. Prismatic glass is energy-efficient for daylight control, while float glass is cost-effective and widely used in residential and commercial windows.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Prismatic Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Diffusion | High; redirects natural light | Low; allows straight transmission |
| Transparency | Moderate; distorted view | High; clear and transparent |
| Glare Reduction | Effective; reduces glare | Minimal glare control |
| Privacy | Enhanced privacy | Low privacy |
| Usage | Ideal for daylight control and aesthetics | Standard window glazing |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized manufacturing | Lower, more common |
Introduction to Prismatic Glass and Float Glass
Prismatic glass contains micro-structured patterns designed to refract and diffuse light evenly, enhancing natural illumination and reducing glare in window applications. Float glass is a flat, uniform sheet created by floating molten glass on a bed of molten tin, widely used for its clarity, strength, and versatility in standard window construction. The choice between prismatic and float glass impacts light distribution, energy efficiency, and visual comfort in architectural designs.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Prismatic glass is composed of molded or patterned glass designed to refract and diffuse light, typically produced through a pressing process that forms specific prism-like textures on the surface, enhancing light control and privacy. Float glass, conversely, consists of clear, flat glass created by floating molten glass on a bed of molten tin, resulting in a smooth, uniform thickness and high optical clarity ideal for windows. The distinct manufacturing methods and compositions define prismatic glass's light-modulating properties versus float glass's clarity and structural simplicity.
Light Transmission and Diffusion Properties
Prismatic glass enhances light transmission through structured surface patterns that refract sunlight, creating uniform diffusion and reducing glare in window applications. Float glass offers high clarity with excellent light transmission but lacks inherent diffusion properties, leading to more direct and potentially harsh light indoors. Opting for prismatic glass improves natural lighting by balancing brightness and glare control, whereas float glass prioritizes transparency over light scattering.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Prismatic glass improves energy efficiency by diffusing natural light and reducing glare, which lowers cooling costs in sunny environments. Float glass offers basic insulation but lacks the light-diffusing properties that enhance thermal performance in prismatic glass. Choosing prismatic glass for windows optimizes indoor temperature regulation and reduces reliance on artificial lighting compared to standard float glass.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Applications
Prismatic glass features a textured surface that refracts light to create dynamic patterns and vibrant color effects, enhancing aesthetic appeal in architectural designs and decorative windows. Float glass offers a smooth, clear finish ideal for minimalist, modern design applications where transparency and unobstructed views are prioritized. Use prismatic glass to add visual interest and diffuse light while float glass provides sleek, clean lines for contemporary window installations.
Privacy and Glare Control Features
Prismatic glass enhances privacy by diffusing light and creating a textured surface that obscures direct visibility, while float glass is clear and offers minimal privacy without additional treatments. The unique surface of prismatic glass significantly reduces glare by redirecting and scattering sunlight, improving indoor comfort compared to the high transparency and glare susceptibility of float glass. For window applications prioritizing both privacy and glare control, prismatic glass provides superior performance through its optical characteristics.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Prismatic glass offers enhanced durability due to its textured surface, which reduces scratches and wear compared to the smooth surface of float glass. Maintenance requirements for prismatic glass are generally lower because its pattern helps mask dirt and minor damage, whereas float glass demands more frequent cleaning to maintain clarity and appearance. Both types are suitable for windows, but prismatic glass provides a longer-lasting, low-maintenance solution in high-traffic or exposed environments.
Cost Comparison: Prismatic vs Float Glass
Prismatic glass typically costs 20-30% more than standard float glass due to its specialized surface pattern designed to control light diffusion and reduce glare. Float glass remains the more budget-friendly option for general window applications, offering basic clarity and strength at a lower price point. The higher upfront cost of prismatic glass can be justified in settings requiring enhanced daylight management and energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Prismatic glass enhances natural daylighting, reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption compared to standard float glass, which has a higher embodied carbon due to energy-intensive manufacturing processes. The manufacturing of prismatic glass often incorporates recycled materials and promotes better thermal performance, contributing to improved building sustainability and reduced carbon footprint. In contrast, float glass production involves higher emissions and less energy efficiency, making prismatic glass a more environmentally friendly option for sustainable window applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windows
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion and reduces glare, making it ideal for energy-efficient windows in commercial and residential buildings. Float glass, known for its smooth surface and clarity, is commonly used in standard window applications where transparency and affordability are priorities. Choosing the right glass depends on factors like light control, insulation, and aesthetic preferences to optimize comfort and energy efficiency in your space.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Float glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com