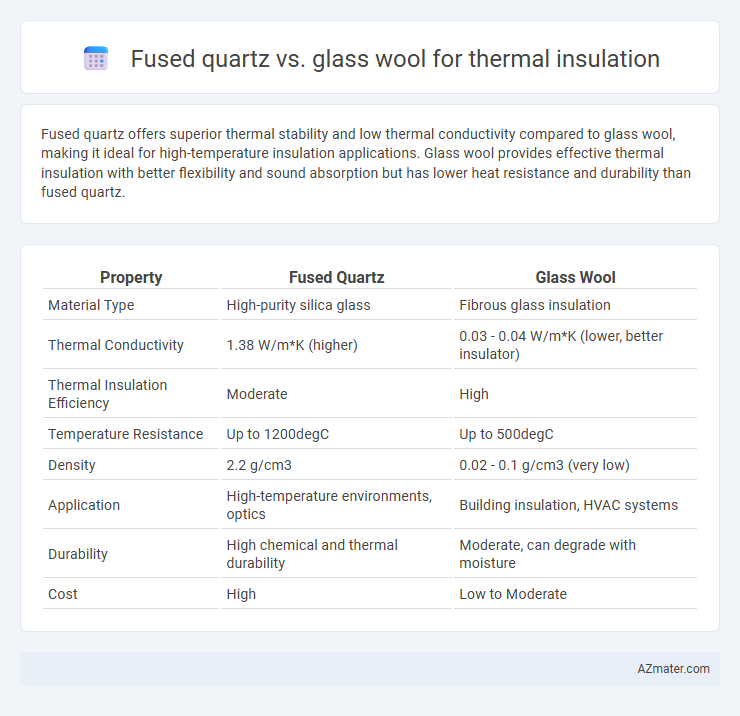
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and low thermal conductivity compared to glass wool, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Glass wool provides effective thermal insulation with better flexibility and sound absorption but has lower heat resistance and durability than fused quartz.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Glass Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-purity silica glass | Fibrous glass insulation |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.38 W/m*K (higher) | 0.03 - 0.04 W/m*K (lower, better insulator) |
| Thermal Insulation Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 500degC |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | 0.02 - 0.1 g/cm3 (very low) |
| Application | High-temperature environments, optics | Building insulation, HVAC systems |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal durability | Moderate, can degrade with moisture |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity and high temperature resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring stability in extreme heat. Glass wool, composed of fine glass fibers, provides superior thermal insulation by trapping air within its structure, resulting in excellent heat retention and soundproofing properties. Both materials are widely used in construction and industrial settings, with fused quartz preferred for high-temperature environments and glass wool favored for cost-effective, general-purpose insulation.
What is Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is a high-purity, non-crystalline form of silicon dioxide characterized by exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Unlike glass wool, which consists of fibrous materials designed primarily for thermal and acoustic insulation, fused quartz provides superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Its microscopic structure also contributes to minimal heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency in insulating environments exposed to extreme temperatures.
What is Glass Wool?
Glass wool is a fibrous material made from molten glass spun into fine fibers, widely used for thermal insulation due to its excellent heat resistance and sound-absorbing properties. Unlike fused quartz, which is a dense, crystalline form of silicon dioxide with high thermal stability, glass wool offers superior flexibility and ease of installation in building insulation. Its porous structure traps air, reducing heat transfer and making it a cost-effective solution for residential and commercial insulation applications.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Fused quartz exhibits a much lower thermal conductivity typically around 1.4 W/m*K, making it an excellent material for high-temperature insulation and applications requiring minimal heat transfer. Glass wool, on the other hand, has a thermal conductivity ranging from 0.03 to 0.04 W/m*K, which is significantly lower than fused quartz, providing superior insulation performance in building and industrial contexts. The porous structure of glass wool traps air effectively, reducing heat flow, whereas fused quartz's dense composition results in higher conductivity but greater thermal stability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fused quartz offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to glass wool due to its dense, non-porous structure and high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Glass wool, while effective for thermal insulation, exhibits lower mechanical strength and can degrade over time when exposed to moisture or physical stress. The enhanced durability of fused quartz makes it ideal for high-performance insulation applications requiring long-term structural integrity.
Temperature Resistance and Stability
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional temperature resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, whereas glass wool typically withstands up to 600degC before degrading. The thermal stability of fused quartz is superior due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Glass wool, while effective for moderate temperature insulation, tends to lose insulating properties and structural stability under prolonged high heat exposure.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Fused quartz exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to glass wool, as it is non-porous and does not absorb water, preventing degradation and loss of insulating properties even in humid environments. Chemically, fused quartz is highly inert, resisting acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, whereas glass wool can degrade or lose effectiveness when exposed to certain chemical contaminants. These properties make fused quartz a more durable choice for long-term thermal insulation in moisture-prone or chemically aggressive settings.
Application Fields: Fused Quartz vs Glass Wool
Fused quartz excels in high-temperature applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace, and laboratory equipment due to its exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion. Glass wool is widely used in building insulation, HVAC systems, and industrial pipe insulation because of its cost-effectiveness, excellent thermal resistance, and soundproofing qualities. The choice between fused quartz and glass wool depends on specific thermal requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints in their respective application fields.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Fused quartz offers superior chemical purity and minimal off-gassing, reducing indoor air pollutants compared to glass wool, which may release respirable fibers posing respiratory health risks. Glass wool often contains binders and formaldehyde, potentially affecting indoor air quality and contributing to environmental toxicity during production and disposal. Fused quartz's inert composition enhances environmental sustainability by minimizing hazardous waste and promoting safer handling without respiratory protection.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Fused quartz offers superior thermal insulation with high-temperature resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost and limited availability compared to glass wool, making it less feasible for large-scale applications. Glass wool is widely available, cost-effective, and commonly used in residential and commercial insulation projects due to its balance of thermal performance and affordability. Evaluating project scale and budget is crucial, as glass wool provides more practical insulation solutions for most cost-sensitive applications.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Glass wool for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com