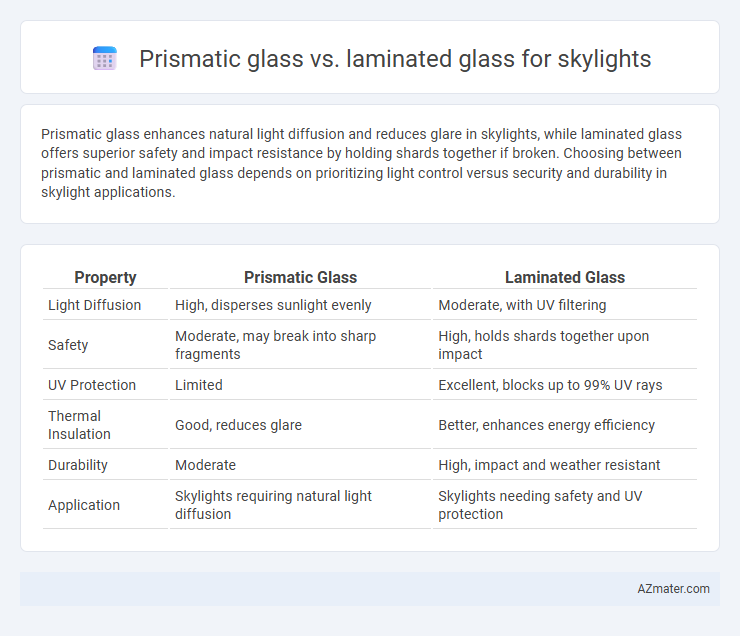
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion and reduces glare in skylights, while laminated glass offers superior safety and impact resistance by holding shards together if broken. Choosing between prismatic and laminated glass depends on prioritizing light control versus security and durability in skylight applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Prismatic Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Diffusion | High, disperses sunlight evenly | Moderate, with UV filtering |
| Safety | Moderate, may break into sharp fragments | High, holds shards together upon impact |
| UV Protection | Limited | Excellent, blocks up to 99% UV rays |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, reduces glare | Better, enhances energy efficiency |
| Durability | Moderate | High, impact and weather resistant |
| Application | Skylights requiring natural light diffusion | Skylights needing safety and UV protection |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion in skylights by refracting sunlight to reduce glare and distribute illumination evenly, improving indoor brightness without increasing heat gain. Laminated glass offers superior safety and noise reduction with its interlayer bonding, ensuring glass fragments remain adhered upon impact while providing UV protection. Both options serve distinct functional benefits for skylights, balancing light quality and building performance.
What is Prismatic Glass?
Prismatic glass, designed with micro-structured surfaces, enhances natural light diffusion and reduces glare in skylight applications. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers bonded together for impact resistance and safety, prismatic glass improves daylight distribution by refracting sunlight more efficiently. This optical property makes prismatic glass ideal for energy-efficient skylights aiming to maximize natural illumination while minimizing heat gain.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass for skylights consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and impact resistance. This construction prevents glass shards from falling if broken, making it ideal for skylights exposed to harsh weather or potential impacts. Laminated glass also offers superior UV protection and noise reduction compared to prismatic glass, enhancing indoor comfort and energy efficiency.
Light Diffusion Capabilities
Prismatic glass offers superior light diffusion for skylights by using micro-structures to redirect and evenly distribute natural sunlight, reducing glare and hotspot formation. Laminated glass provides moderate diffusion while enhancing safety and ultraviolet protection through its interlayer but may result in less uniform light dispersion. Selection between prismatic and laminated glass should consider the desired balance between light diffusion efficiency and structural benefits for optimal daylighting performance.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Prismatic glass enhances solar heat gain control and diffuses natural light, reducing reliance on electric lighting and improving overall energy efficiency in skylights. Laminated glass, with its multiple layers and interlayer, provides superior thermal insulation and solar heat rejection, minimizing heat transfer and lowering HVAC energy consumption. Selecting prismatic glass optimizes daylight harvesting, while laminated glass offers enhanced insulation for energy conservation in different climate conditions.
Safety and Security Aspects
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion while maintaining impact resistance, but laminated glass offers superior safety by holding shattered pieces together upon breakage, significantly reducing injury risks in skylights. Laminated glass provides enhanced security against forced entry and environmental impacts with its durable interlayer, making it the preferred choice for safety-conscious skylight installations. The interlayer in laminated glass also improves resistance to UV radiation and noise, adding to overall protection without compromising visibility.
Durability and Maintenance
Prismatic glass offers enhanced durability due to its resistance to impact and UV radiation, making it less prone to cracking and discoloration over time compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, composed of two or more layers bonded with an interlayer, provides superior safety by holding shards together if broken but may require more frequent inspections to ensure interlayer integrity. Maintenance for prismatic glass is generally lower, as its surface is designed to reduce dirt accumulation and scratching, whereas laminated glass may demand careful cleaning to prevent damage to the interlayer and maintain clarity.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Prismatic glass offers superior light diffusion and vibrant patterns, enhancing skylight aesthetics with dynamic visual effects that reduce glare and distribute daylight evenly. Laminated glass provides design flexibility through its multi-layered construction, allowing customization with tinted, frosted, or textured interlayers for added privacy and unique artistic expressions. Both materials complement modern architectural styles, but prismatic glass excels in creating luminous, decorative skylights while laminated glass prioritizes safety and diverse design options.
Cost Comparison: Prismatic vs Laminated Glass
Prismatic glass for skylights generally costs more upfront than laminated glass due to its specialized optical properties designed to diffuse natural light effectively. Laminated glass offers a more affordable price point while providing enhanced safety through its interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage. When considering long-term investment, prismatic glass may reduce energy costs by improving daylight dispersion, whereas laminated glass excels in impact resistance and security at a lower material cost.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type
Prismatic glass excels in skylight applications requiring enhanced daylight diffusion and glare reduction, making it ideal for office buildings, healthcare facilities, and educational institutions where balanced natural light improves comfort and productivity. Laminated glass offers superior safety, impact resistance, and UV protection, making it the preferred choice for skylights in residential homes, commercial buildings in high-wind areas, and structures needing enhanced security and sound insulation. Selecting prismatic glass optimizes natural light quality, while laminated glass ensures durability and occupant safety under various environmental conditions.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Laminated glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com