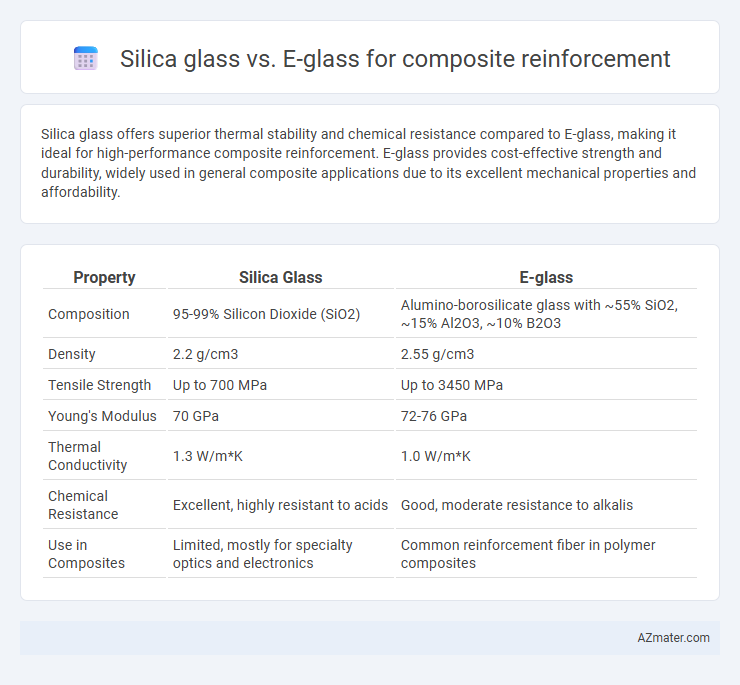
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-performance composite reinforcement. E-glass provides cost-effective strength and durability, widely used in general composite applications due to its excellent mechanical properties and affordability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | E-glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 95-99% Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) | Alumino-borosilicate glass with ~55% SiO2, ~15% Al2O3, ~10% B2O3 |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | 2.55 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 700 MPa | Up to 3450 MPa |
| Young's Modulus | 70 GPa | 72-76 GPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.3 W/m*K | 1.0 W/m*K |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to acids | Good, moderate resistance to alkalis |
| Use in Composites | Limited, mostly for specialty optics and electronics | Common reinforcement fiber in polymer composites |
Introduction to Composite Reinforcement Materials
Silica glass and E-glass are prominent composite reinforcement materials known for enhancing mechanical strength and durability in fiber-reinforced composites. Silica glass fibers exhibit superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. E-glass fibers, composed mainly of alumino-borosilicate, offer excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, widely used in automotive and marine composites.
Overview of Silica Glass and E-glass
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), offers exceptional thermal stability, high chemical resistance, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. E-glass, an alumino-borosilicate glass containing calcium oxide, provides a cost-effective balance of high tensile strength, good electrical insulation, and moisture resistance, widely used in composite reinforcements like fiberglass. The choice between silica glass and E-glass hinges on the specific mechanical properties, environmental resistance, and cost requirements of the composite material application.
Chemical Composition Differences
Silica glass primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with high purity levels, offering superior thermal and chemical resistance. E-glass contains approximately 54-56% SiO2, along with significant amounts of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), calcium oxide (CaO), and boron oxide (B2O3), which enhance mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties. The distinct chemical compositions influence their performance in composites: silica glass provides enhanced heat resistance, whereas E-glass delivers improved structural reinforcement due to its balanced oxide mixture.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Silica glass exhibits superior tensile strength and higher modulus of elasticity compared to E-glass, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced stiffness and durability in composite reinforcement. E-glass offers better impact resistance and flexibility, providing a balance between strength and toughness for versatile composite structures. The mechanical performance of silica glass significantly improves composite hardness and thermal stability, whereas E-glass ensures cost-effective reinforcement with satisfactory mechanical properties for general use.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Silica glass exhibits superior thermal stability compared to E-glass, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, whereas E-glass typically degrades above 600degC. This enhanced thermal resistance makes silica glass ideal for high-performance composite reinforcements exposed to extreme heat environments in aerospace and industrial applications. E-glass, while offering good mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness, underperforms in high-temperature stability, limiting its use in advanced thermal management systems.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Silica glass offers superior electrical insulation properties compared to E-glass, with higher dielectric strength and lower dielectric losses, making it ideal for high-voltage composite applications. The low electrical conductivity of silica glass fibers enhances their performance in environments requiring excellent insulating capabilities. In contrast, E-glass provides good insulation but exhibits higher moisture absorption, which can degrade its electrical properties over time.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
E-glass is significantly more cost-effective than silica glass, making it the preferred choice for large-scale composite reinforcement applications due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Market availability of E-glass fibers is widespread globally, supported by extensive production infrastructure, whereas silica glass fibers, despite superior thermal properties, have limited availability and higher prices due to more complex fabrication processes. Cost analysis reveals that E-glass offers a balanced performance-to-price ratio, driving its dominance in industries like automotive and construction.
Applications in Modern Composites
Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-performance composites in aerospace and electronics. E-glass provides excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, widely used in automotive parts, marine structures, and wind turbine blades. Both materials enhance composite durability, with silica glass favored for extreme environments and E-glass preferred for versatile structural applications.
Long-Term Durability and Environmental Resistance
Silica glass fibers exhibit superior long-term durability and environmental resistance compared to E-glass, maintaining mechanical properties under prolonged exposure to moisture, UV radiation, and chemical agents. The high silica content in silica glass imparts enhanced thermal stability and corrosion resistance, reducing degradation in hostile environments such as marine or industrial applications. E-glass, while cost-effective and widely used, tends to absorb moisture leading to matrix-fiber interface weakening and reduced lifespan under harsh conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Composite Reinforcement
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications requiring durability in extreme environments. E-glass provides a cost-effective solution with excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, suitable for general-purpose composites. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints specific to the composite application.
Infographic: Silica glass vs E-glass for Composite reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com