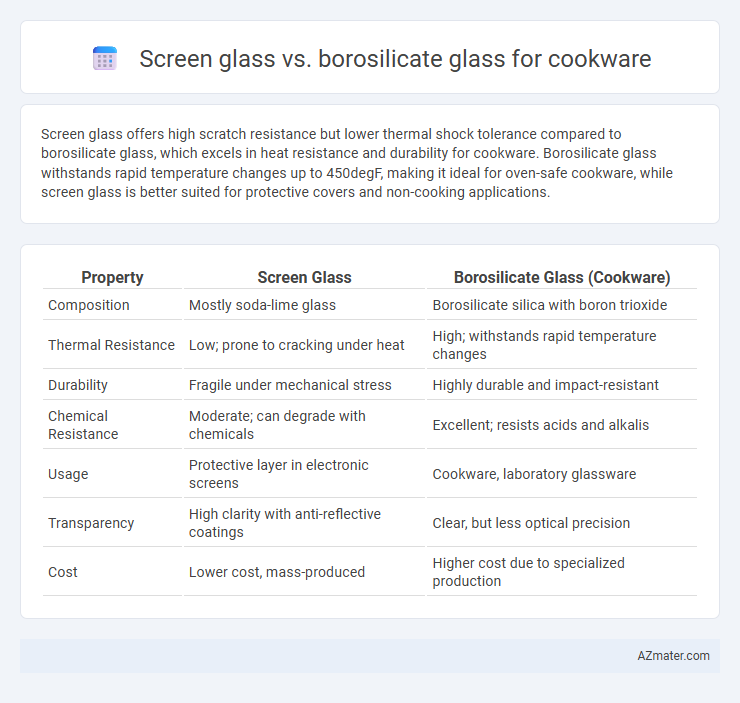
Screen glass offers high scratch resistance but lower thermal shock tolerance compared to borosilicate glass, which excels in heat resistance and durability for cookware. Borosilicate glass withstands rapid temperature changes up to 450degF, making it ideal for oven-safe cookware, while screen glass is better suited for protective covers and non-cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Screen Glass | Borosilicate Glass (Cookware) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mostly soda-lime glass | Borosilicate silica with boron trioxide |
| Thermal Resistance | Low; prone to cracking under heat | High; withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Durability | Fragile under mechanical stress | Highly durable and impact-resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; can degrade with chemicals | Excellent; resists acids and alkalis |
| Usage | Protective layer in electronic screens | Cookware, laboratory glassware |
| Transparency | High clarity with anti-reflective coatings | Clear, but less optical precision |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass-produced | Higher cost due to specialized production |
Introduction to Screen Glass and Borosilicate Glass
Screen glass, typically made from soda-lime composition, offers moderate heat resistance and is commonly used in household items but lacks the thermal durability required for high-temperature cookware. Borosilicate glass, containing boron trioxide, exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand rapid temperature changes up to 450degF (232degC), making it a preferred material for bakeware and cookware. Its low thermal expansion coefficient and enhanced chemical durability ensure reliability and longevity under intense cooking conditions, distinguishing it from conventional screen glass.
What is Screen Glass?
Screen glass, commonly used in electronic displays and protective coverings, is a type of toughened glass designed to resist scratches and impacts, but it lacks the high thermal resistance required for cookware. Borosilicate glass, by contrast, contains boron trioxide, which imparts exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for oven-safe cookware. Unlike screen glass, borosilicate glass can withstand high temperatures without cracking or releasing harmful chemicals, ensuring durability and safety in cooking applications.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, ideal for cookware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Unlike standard screen glass, borosilicate glass offers superior durability and heat resistance, allowing it to withstand direct stovetop or oven heat without cracking. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion and non-porous surface make it safer and more long-lasting for cooking applications.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Screen glass is primarily composed of soda-lime silica, making it less resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress compared to borosilicate glass, which contains a significant amount of boron oxide. Borosilicate glass's unique chemical structure provides superior durability, heat resistance up to 450degF (232degC), and minimal thermal expansion, ideal for cookware exposed to direct flame or sudden temperature changes. In contrast, screen glass is more prone to cracking under high heat, limiting its use in cooking applications.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior heat resistance compared to screen glass, withstanding thermal shock up to 450degF (232degC) without cracking. This makes borosilicate ideal for cookware exposed to direct flame or rapid temperature changes. Screen glass, often used in electronic displays, typically has lower heat tolerance, around 140degF (60degC), making it unsuitable for high-temperature cooking applications.
Durability and Strength Factors
Screen glass, commonly made from soda-lime glass, is less durable and more prone to thermal shock and breakage compared to borosilicate glass, which contains silica and boron oxide to enhance strength and thermal resistance. Borosilicate glass cookware withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking, offering superior durability for stovetop and oven use. The chemical composition of borosilicate glass provides higher impact resistance and longevity, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting, reliable cookware.
Safety Considerations in Cooking
Screen glass lacks the heat resistance and thermal shock durability of borosilicate glass, making it unsafe for cookware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Borosilicate glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and thermal stress, reducing the risk of cracking or shattering during cooking. Its chemical inertness also prevents leaching of harmful substances, ensuring food safety and durability under frequent heating.
Performance in Everyday Use
Screen glass cookware offers moderate thermal resistance and is more prone to scratching and cracking under rapid temperature changes, making it less durable for daily cooking. Borosilicate glass, known for its superior thermal shock resistance and high durability, withstands frequent heating and cooling cycles without compromising structural integrity. Its low thermal expansion allows for even heat distribution, enhancing cooking performance and longevity in everyday use.
Cost and Availability
Screen glass is generally more affordable and widely accessible compared to borosilicate glass, which tends to be pricier due to its enhanced thermal resistance and durability. Borosilicate glass cookware is less common in conventional retail settings but is available through specialized kitchenware suppliers and online platforms. Cost-effectiveness and immediate availability often make screen glass a preferred choice for budget-conscious consumers despite its lower heat tolerance.
Which Glass is Best for Cookware?
Borosilicate glass is considered the best choice for cookware due to its superior thermal resistance and durability, capable of withstanding rapid temperature changes without cracking. Screen glass, typically used for protective covers, lacks the heat tolerance required for cooking applications and may shatter under high temperatures. Borosilicate's low thermal expansion coefficient ensures long-lasting performance and safety in ovens and stovetops.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Borosilicate glass for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com