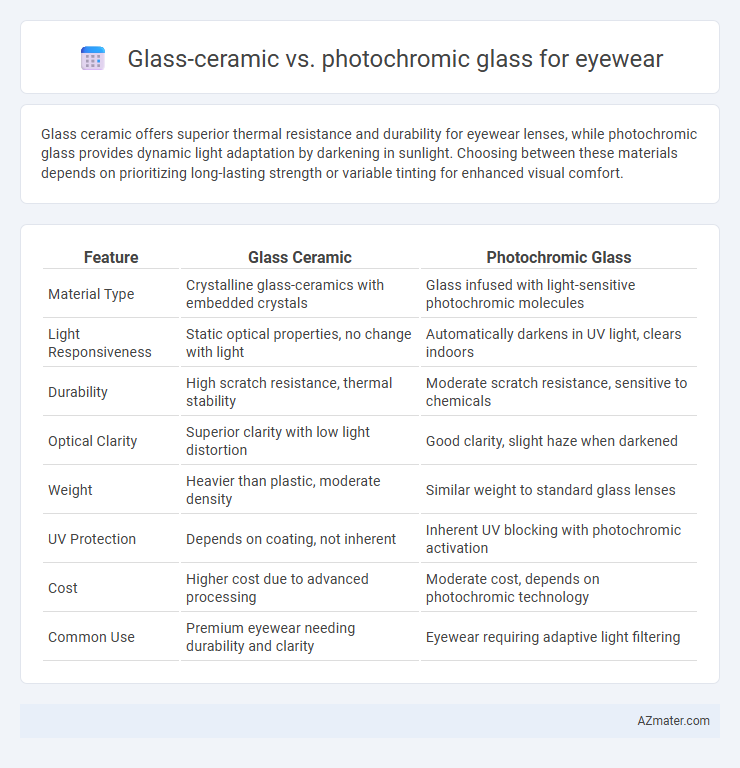
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and durability for eyewear lenses, while photochromic glass provides dynamic light adaptation by darkening in sunlight. Choosing between these materials depends on prioritizing long-lasting strength or variable tinting for enhanced visual comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Ceramic | Photochromic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Crystalline glass-ceramics with embedded crystals | Glass infused with light-sensitive photochromic molecules |
| Light Responsiveness | Static optical properties, no change with light | Automatically darkens in UV light, clears indoors |
| Durability | High scratch resistance, thermal stability | Moderate scratch resistance, sensitive to chemicals |
| Optical Clarity | Superior clarity with low light distortion | Good clarity, slight haze when darkened |
| Weight | Heavier than plastic, moderate density | Similar weight to standard glass lenses |
| UV Protection | Depends on coating, not inherent | Inherent UV blocking with photochromic activation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Moderate cost, depends on photochromic technology |
| Common Use | Premium eyewear needing durability and clarity | Eyewear requiring adaptive light filtering |
Introduction to Glass Ceramic and Photochromic Glass
Glass ceramic eyewear combines the strength and thermal stability of ceramic materials with the transparency of glass, offering superior scratch resistance and durability. Photochromic glass, embedded with light-sensitive molecules, dynamically adjusts its tint based on UV exposure, enhancing visual comfort by darkening in sunlight and clearing indoors. Both materials optimize eyewear performance but serve distinct functional needs--glass ceramics prioritize durability, while photochromic glass emphasizes adaptive light modulation.
Composition and Material Differences
Glass ceramic eyewear lenses consist primarily of crystalline structures embedded within a glass matrix, offering high thermal stability and durability. Photochromic glass incorporates silver halide or silver chloride compounds within the glass that react to ultraviolet light, causing reversible darkening. The key compositional difference lies in glass ceramic's varied crystalline phases versus photochromic glass's embedded light-sensitive molecules, impacting weight, reactivity, and optical clarity.
How Glass Ceramic Works in Eyewear
Glass ceramic in eyewear utilizes a unique crystalline structure embedded within the glass matrix, enabling precise control of light transmission and enhanced durability. This material undergoes a high-temperature treatment that creates microscopic crystals, which contribute to superior thermal stability and scratch resistance compared to traditional glass lenses. The combination of strength and optical clarity makes glass ceramic ideal for eyewear requiring both resilience and high visual performance.
Functionality of Photochromic Glass Lenses
Photochromic glass lenses automatically adjust their tint based on UV light exposure, providing optimal vision clarity both indoors and outdoors. This transition functionality enhances eye protection by reducing glare and blocking harmful UV rays without compromising visual acuity. When compared to glass ceramic lenses, photochromic lenses offer dynamic adaptability that improves comfort and convenience for various lighting conditions.
Optical Performance Comparison
Glass ceramic lenses exhibit superior scratch resistance and thermal stability, maintaining consistent optical clarity under varying temperatures. Photochromic glass lenses dynamically adjust tint based on UV exposure, providing adaptive light transmission but may reduce visual sharpness in low-light conditions. Both materials offer high optical precision, yet glass ceramics deliver more stable refractive properties, enhancing visual acuity during prolonged wear.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Glass ceramic eyewear lenses offer superior durability and exceptional scratch resistance due to their hard, dense molecular structure, making them highly resistant to impacts and abrasions. Photochromic glass, while providing the added benefit of adaptive light filtering, generally has lower scratch resistance and may be more prone to surface damage over time without specialized coatings. Opting for glass ceramic lenses ensures long-lasting clarity and strength, especially for users prioritizing rugged wear and minimal lens degradation.
UV Protection Capabilities
Glass ceramic lenses offer outstanding UV protection by blocking nearly 100% of harmful ultraviolet rays, ensuring enhanced eye safety in various lighting conditions. Photochromic glass lenses dynamically adjust their tint based on UV exposure, providing adaptive protection by darkening outdoors and remaining clear indoors while still filtering UV radiation effectively. Both materials are engineered for optimal UV defense, with glass ceramic providing consistent protection and photochromic glass delivering variable shade to improve comfort and vision clarity.
User Comfort and Style Options
Glass ceramic lenses provide exceptional durability and resistance to scratches, enhancing long-term user comfort by maintaining clear vision without frequent replacements. Photochromic glass lenses adapt to changing light conditions, reducing eye strain and increasing comfort during outdoor activities while offering a sleek, modern style that seamlessly transitions from indoor to outdoor settings. Style options for glass ceramic focus on classic, polished looks, whereas photochromic glass enables dynamic aesthetics with lenses that darken and lighten, catering to fashion-conscious users seeking both functionality and trendiness.
Cost and Affordability Considerations
Glass ceramic lenses typically cost more due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior durability, making them a premium choice for eyewear. Photochromic glass lenses offer moderate pricing but include the added convenience of automatic tint adjustment to light conditions, providing value through multifunctionality. When considering cost and affordability, photochromic lenses generally present a more budget-friendly option, especially for everyday use, while glass ceramic suits users prioritizing longevity and resistance to scratches.
Which is Better: Glass Ceramic or Photochromic Glass?
Glass ceramic lenses offer superior scratch resistance and durability, making them ideal for long-term use in eyewear, while photochromic glass provides the advantage of automatic tint adjustment based on light exposure, enhancing comfort and eye protection. Photochromic glass lenses excel in versatility for outdoor activities, responding quickly to changing light conditions, whereas glass ceramic lenses maintain clear vision without tint changes and resist breakage better. Choosing between them depends on lifestyle needs: glass ceramic suits those prioritizing toughness and optical clarity, while photochromic glass benefits users seeking convenience and adaptive vision.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Photochromic glass for Eyewear
 azmater.com
azmater.com