Glass ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and shatterproof properties compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for high-safety applications. Laminated glass enhances impact resistance and prevents glass fragmentation by holding shards together with an interlayer, providing effective protection against breakage.
Table of Comparison
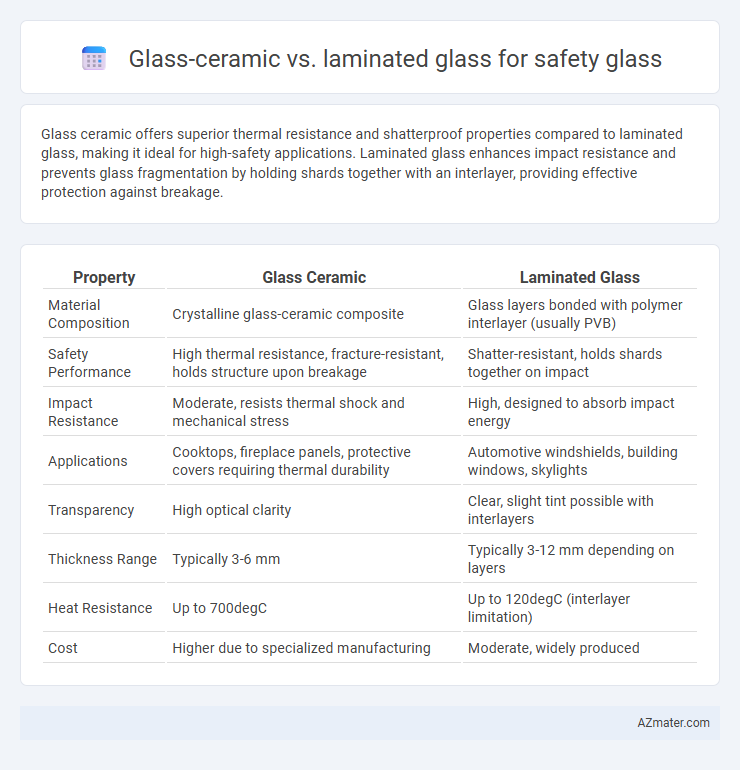
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Crystalline glass-ceramic composite | Glass layers bonded with polymer interlayer (usually PVB) |
| Safety Performance | High thermal resistance, fracture-resistant, holds structure upon breakage | Shatter-resistant, holds shards together on impact |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, resists thermal shock and mechanical stress | High, designed to absorb impact energy |
| Applications | Cooktops, fireplace panels, protective covers requiring thermal durability | Automotive windshields, building windows, skylights |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Clear, slight tint possible with interlayers |
| Thickness Range | Typically 3-6 mm | Typically 3-12 mm depending on layers |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 700degC | Up to 120degC (interlayer limitation) |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized manufacturing | Moderate, widely produced |
Introduction to Safety Glass: Glass Ceramic vs Laminated Glass
Glass ceramic and laminated glass serve distinct roles in safety glass applications, with glass ceramic offering high thermal resistance and structural stability under rapid temperature changes. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, enhancing impact resistance and ensuring shards remain adhered upon breakage. Selecting between glass ceramic and laminated glass depends on specific safety requirements such as heat tolerance and shatterproof performance.
Defining Glass Ceramic: Composition and Properties
Glass ceramic safety glass is composed of fine-grained crystalline phases embedded in a glassy matrix, offering high thermal stability and resistance to impact. Its unique microstructure provides exceptional strength, low thermal expansion, and enhanced fracture toughness compared to laminated glass. This makes glass ceramic ideal for safety applications requiring durability under extreme temperature changes and mechanical stress.
What is Laminated Glass? Structure and Features
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together by an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering. Its structure provides superior safety by holding glass fragments in place upon breakage, reducing the risk of injury and maintaining structural integrity. Laminated glass also offers sound insulation, UV protection, and durability, making it ideal for automotive windshields, architectural applications, and safety glass requirements.
Key Differences: Glass Ceramic vs Laminated Glass
Glass ceramic offers exceptional thermal resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for high-temperature and heavy-duty safety applications. Laminated glass, composed of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, excels in shatter resistance and retaining glass fragments upon impact. The primary difference lies in glass ceramic's durability under extreme heat versus laminated glass's superior ability to prevent injury by holding broken glass together.
Impact Resistance and Strength Comparison
Glass ceramic offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for environments with high stress or rapid temperature changes. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety by holding shattered pieces together due to its interlayer, but generally has lower impact strength than glass ceramic. The choice depends on specific safety requirements, with glass ceramic favored for high-impact resistance and laminated glass preferred for controlled breakage and occupant protection.
Thermal Performance: Heat Resistance and Expansion
Glass ceramic demonstrates superior thermal performance compared to laminated glass due to its exceptional heat resistance and minimal thermal expansion, maintaining structural integrity under rapid temperature changes. Laminated glass, while providing safety through its interlayer bonding, typically exhibits higher thermal expansion rates that may lead to stress and potential failure under extreme heat. This makes glass ceramic a preferred choice in applications requiring durability against thermal shock and sustained high temperatures.
Safety and Security: Shatter Resistance Analysis
Glass ceramic offers superior shatter resistance due to its crystalline structure, which enhances impact tolerance and prevents fragmentation into sharp shards, ensuring higher safety in hazardous situations. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, which holds broken glass pieces together, reducing injury risk and improving security against forced entry. Both materials provide safety advantages, but glass ceramic excels in maintaining structural integrity upon impact, while laminated glass offers reliable containment of glass fragments.
Applications in Building and Automotive Industries
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and impact durability, making it ideal for high-temperature architectural applications like skylights and facades in the building industry. Laminated glass provides excellent shatter resistance and sound insulation, commonly used in automotive windshields and building windows to enhance passenger safety and reduce noise pollution. Both materials meet stringent safety standards, but glass ceramic is preferred for heat-intensive environments, while laminated glass dominates in impact protection and fracture containment.
Cost Considerations and Longevity
Glass ceramic offers higher durability and thermal resistance compared to laminated glass, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced replacement frequency, which can offset its initially higher cost. Laminated glass typically presents a more affordable upfront expense but may require more frequent maintenance or replacement due to susceptibility to delamination and impact damage. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and durability, often positions glass ceramic as more cost-effective over time for safety glass applications.
Choosing the Best Safety Glass: Factors to Consider
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for environments prone to rapid temperature changes or high stress. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety by holding shards together upon breakage, reducing injury risks. When choosing the best safety glass, consider factors like application type, impact resistance, thermal performance, and compliance with safety standards such as ANSI Z97.1 or EN 356 for optimal protection.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Laminated glass for Safety glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com