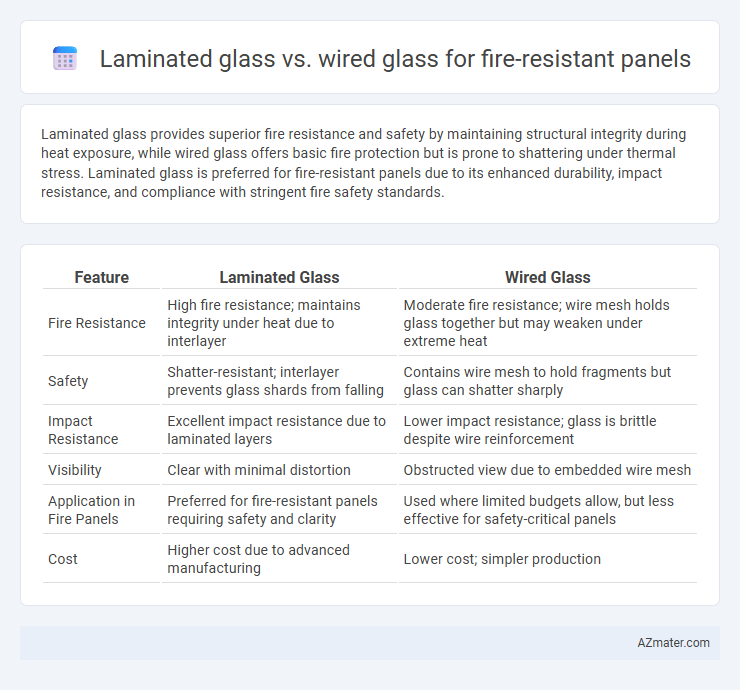
Laminated glass provides superior fire resistance and safety by maintaining structural integrity during heat exposure, while wired glass offers basic fire protection but is prone to shattering under thermal stress. Laminated glass is preferred for fire-resistant panels due to its enhanced durability, impact resistance, and compliance with stringent fire safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High fire resistance; maintains integrity under heat due to interlayer | Moderate fire resistance; wire mesh holds glass together but may weaken under extreme heat |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant; interlayer prevents glass shards from falling | Contains wire mesh to hold fragments but glass can shatter sharply |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent impact resistance due to laminated layers | Lower impact resistance; glass is brittle despite wire reinforcement |
| Visibility | Clear with minimal distortion | Obstructed view due to embedded wire mesh |
| Application in Fire Panels | Preferred for fire-resistant panels requiring safety and clarity | Used where limited budgets allow, but less effective for safety-critical panels |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced manufacturing | Lower cost; simpler production |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Glass Panels
Fire-resistant glass panels play a critical role in preventing the spread of flames and smoke during fire emergencies, ensuring safety and structural integrity. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded with a durable interlayer that enhances impact resistance and maintains glass cohesion under heat exposure. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh that provides additional strength and heat resistance but may compromise clarity and safety during impact.
Understanding Laminated Glass Technology
Laminated glass technology for fire-resistant panels involves bonding multiple glass layers with interlayers such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) to enhance impact resistance and maintain integrity under heat exposure. This construction allows laminated glass to prevent fire and smoke from spreading while offering superior clarity and safety compared to wired glass, which contains embedded wire mesh that can weaken under extreme temperatures. Fire-rated laminated glass panels meet stringent building codes and standards like UL 972 and NFPA 257, ensuring reliable performance in fire containment applications.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of fire-resistant glass that contains an embedded metal wire mesh, designed to hold the glass together during high heat exposure and prevent shattering. This mesh reinforcement ensures structural integrity and fire containment by resisting thermal stress and limiting the spread of flames and smoke. Unlike laminated glass, wired glass offers enhanced safety in fire-rated panels due to its ability to maintain a barrier even when cracked.
Fire Resistance Capabilities Compared
Laminated glass for fire-resistant panels offers enhanced fire resistance by combining multiple layers of glass with a durable interlayer that maintains integrity under extreme heat, preventing glass shattering and reducing smoke penetration. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh that holds the glass in place during fire exposure but is more prone to brittle fracture under thermal stress. Fire resistance tests show laminated glass can achieve longer integrity and insulation ratings than wired glass, making it a superior choice for critical fire containment applications.
Impact and Safety Performance
Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance due to its interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage, reducing injury risks during fire emergencies. Wired glass, while providing fire resistance through embedded wire mesh, tends to shatter into sharp fragments, posing higher safety hazards. For fire-resistant panels, laminated glass enhances safety performance by maintaining structural integrity and minimizing dangerous debris in impact incidents.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetics
Laminated glass offers superior visual clarity and aesthetic appeal compared to wired glass, as it lacks the mesh that disrupts transparency and distorts views. The smooth, clear surface of laminated glass enhances natural light transmission, making it ideal for modern fire-resistant panels where design and visibility are critical. Wired glass, while fire-resistant, compromises aesthetics due to its embedded wire mesh that creates a grid pattern, reducing clarity and diminishing the overall appearance.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Laminated glass for fire-resistant panels offers straightforward installation due to its uniform thickness and flexibility, reducing labor time and minimizing fitting errors compared to wired glass, which often requires precise handling to ensure wire integrity. Maintenance of laminated glass is simpler, as it resists cracking and does not require frequent inspections for wire corrosion or breakage, unlike wired glass that may degrade over time due to wire oxidation affecting fire resistance. Choosing laminated glass enhances long-term performance with less frequent replacement, while wired glass demands ongoing maintenance to uphold safety standards in fire-rated applications.
Building Codes and Certification Standards
Laminated glass and wired glass both meet fire-resistant panel requirements but differ significantly in building codes and certification standards. Laminated glass complies with NFPA 257 and UL 10C standards, offering enhanced safety by holding shards in place during breakage, while wired glass meets ASTM E119 and NFPA 80 codes, valued for its fire containment but prone to shattering hazards. Certification for laminated glass often includes fire ratings of 20 to 90 minutes, whereas wired glass is certified primarily for 45 to 60 minutes, influencing their selection based on specific fire protection and safety regulations.
Cost Comparison and Lifespan
Laminated glass typically incurs higher initial costs than wired glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and enhanced fire-resistant properties. Despite the greater upfront investment, laminated glass offers a longer lifespan, maintaining structural integrity and clarity under fire exposure better than wired glass. Wired glass, while more cost-effective initially, tends to have a shorter service life due to potential wire corrosion and reduced thermal stability in fire conditions.
Best Applications for Laminated vs Wired Glass
Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels in high-visibility areas such as office partitions, storefronts, and skylights where aesthetics and safety are critical. Wired glass provides robust fire containment with enhanced thermal stability, suitable for industrial settings, stairwells, and fire doors where maximum fire protection and code compliance are paramount. Selecting laminated glass ensures better sound insulation and UV protection, while wired glass excels in fire-rated assemblies requiring structural integrity under extreme heat.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com