Screen glass offers high scratch resistance and clarity but lacks thermal shock resistance, making it less suitable for cookware. Glass ceramic cookware provides superior heat tolerance and thermal shock resistance, ensuring durability and safety during cooking.
Table of Comparison
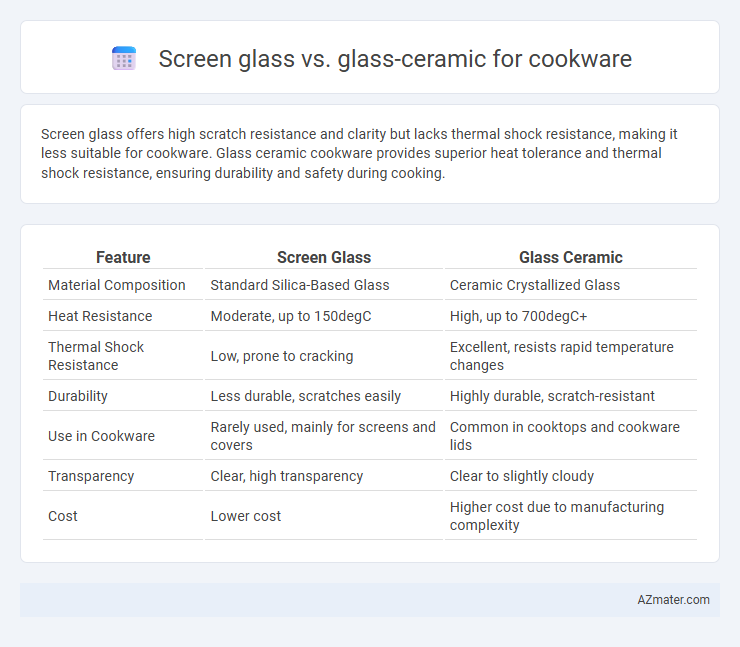
| Feature | Screen Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Standard Silica-Based Glass | Ceramic Crystallized Glass |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, up to 150degC | High, up to 700degC+ |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low, prone to cracking | Excellent, resists rapid temperature changes |
| Durability | Less durable, scratches easily | Highly durable, scratch-resistant |
| Use in Cookware | Rarely used, mainly for screens and covers | Common in cooktops and cookware lids |
| Transparency | Clear, high transparency | Clear to slightly cloudy |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity |
Introduction to Cookware Materials
Screen glass and glass ceramic differ significantly in cookware applications due to their thermal properties and durability. Glass ceramic cookware offers exceptional resistance to thermal shock and high temperatures, making it ideal for direct stovetop use. In contrast, screen glass, typically used in electronic displays, lacks the heat tolerance and strength necessary for effective cookware materials.
What is Screen Glass?
Screen glass is a type of transparent, tempered glass commonly used in electronic displays but also applied in cookware lids for its durability and heat resistance. Unlike glass ceramic, screen glass offers high impact resistance but lacks the exceptional thermal shock resistance that glass ceramic provides. Screen glass is less prone to shattering under physical stress but may not withstand rapid temperature changes as effectively as glass ceramic cookware.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a specialized material engineered through controlled crystallization of glass, resulting in a durable, heat-resistant surface ideal for cookware and stovetops. Unlike traditional screen glass, glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and maintains strength under rapid temperature changes up to 1000degF (537degC). Its low coefficient of thermal expansion prevents cracking and warping, making it the preferred choice for induction cooktops and high-performance cooking environments.
Heat Resistance: Screen Glass vs Glass Ceramic
Screen glass typically exhibits lower heat resistance compared to glass ceramic, making it less suitable for high-temperature cooking applications. Glass ceramic cookware can withstand sudden temperature changes up to 800degC (1472degF) without cracking or shattering, providing enhanced durability and thermal shock resistance. This superior heat resistance makes glass ceramic the preferred choice for cookware used on stovetops and in ovens.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Glass ceramic cookware offers superior durability and strength compared to screen glass, as it is engineered to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without cracking or breaking. Screen glass, while visually clear and smooth, is more prone to scratches and thermal shock, making it less reliable for high-heat cooking applications. The molecular structure of glass ceramic provides enhanced resistance to deformation and impact, ensuring longer-lasting performance in demanding kitchen environments.
Thermal Shock Performance
Screen glass typically exhibits lower thermal shock resistance compared to glass ceramic, making it more prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic cookware is engineered to withstand sudden temperature fluctuations, offering superior durability and minimizing the risk of breakage during stovetop to oven transitions. Its crystalline structure provides enhanced thermal stability, ensuring safe and efficient performance in high-heat cooking applications.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Screen glass in cookware is typically lighter and thinner compared to glass ceramic, making it easier to handle and store. Glass ceramic cookware offers greater thickness and durability, ensuring higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical impact. The increased weight and robust structure of glass ceramic contribute to enhanced heat retention and even cooking performance.
Cooking Performance and Versatility
Screen glass cookware offers excellent heat retention and even distribution, making it suitable for slow cooking and simmering dishes with consistent temperature control. Glass ceramic cookware excels in rapid heat response and thermal shock resistance, enabling quick temperature changes ideal for versatile cooking techniques like sauteing and frying. Both materials are non-porous and easy to clean, but glass ceramic's durability under high heat provides greater flexibility for stovetop and oven use.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Screen glass cookware requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent scratches, while glass ceramic cookware offers greater resistance to stains and heat marks, making maintenance simpler. Both materials respond well to using mild detergents and avoiding harsh chemicals, but glass ceramic surfaces typically tolerate scrubbing more effectively without damage. Regular wiping after use helps preserve clarity and performance in screen glass, whereas glass ceramic is less prone to discoloration from food residue.
Which is Better: Screen Glass or Glass Ceramic?
Screen glass offers excellent scratch resistance and durability, making it suitable for protective covers but less ideal for cookware due to its lower heat tolerance. Glass ceramic cookware, composed of crystalline and glass elements, withstands rapid temperature changes and high heat without cracking or deforming, making it the superior choice for cooking applications. For cookware, glass ceramic provides optimal thermal shock resistance and consistent heat distribution, outperforming screen glass in durability and safety during cooking.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com