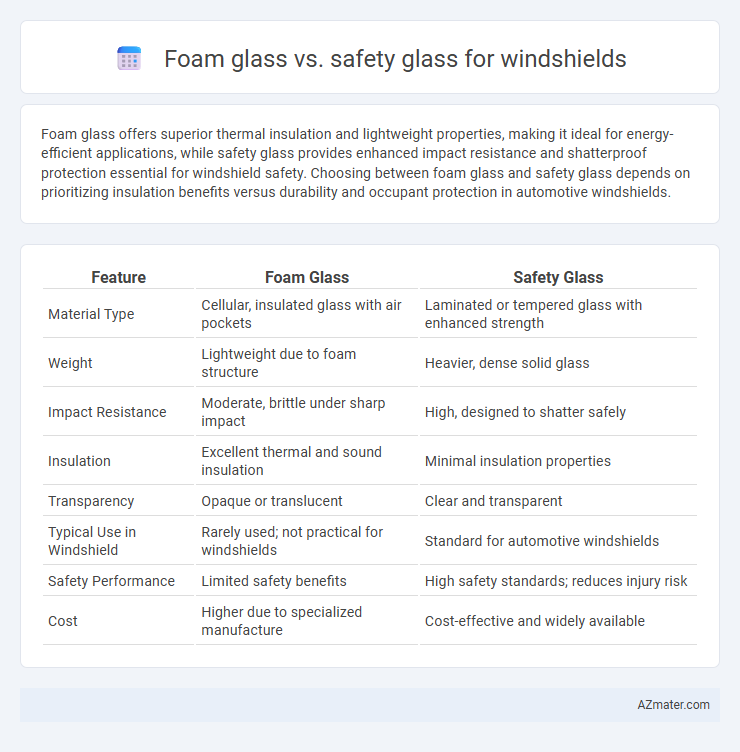
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient applications, while safety glass provides enhanced impact resistance and shatterproof protection essential for windshield safety. Choosing between foam glass and safety glass depends on prioritizing insulation benefits versus durability and occupant protection in automotive windshields.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Glass | Safety Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Cellular, insulated glass with air pockets | Laminated or tempered glass with enhanced strength |
| Weight | Lightweight due to foam structure | Heavier, dense solid glass |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, brittle under sharp impact | High, designed to shatter safely |
| Insulation | Excellent thermal and sound insulation | Minimal insulation properties |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Typical Use in Windshield | Rarely used; not practical for windshields | Standard for automotive windshields |
| Safety Performance | Limited safety benefits | High safety standards; reduces injury risk |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized manufacture | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Automotive Windshield Technologies
Foam glass offers exceptional thermal insulation and lightweight properties but lacks the transparency and impact resistance essential for automotive windshields. Safety glass, including laminated and tempered types, is engineered to withstand collisions by preventing shattering and protecting passengers through controlled fracture patterns. Advances in windshield technologies prioritize safety glass innovations due to their optical clarity, durability, and regulatory compliance in automotive applications.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a lightweight, insulating material made from crushed glass that is heated to form a porous structure, offering excellent thermal and sound insulation properties. Unlike safety glass used in windshields, which is laminated or tempered to resist impact and shattering, foam glass is primarily utilized in construction and industrial applications rather than automotive safety. Foam glass's unique cellular composition makes it unsuitable for windshield use but valuable for insulation and lightweight structural purposes.
What is Safety Glass?
Safety glass is a specially treated glass designed to reduce injury upon impact, commonly used in windshields to enhance passenger protection. It consists of laminated or tempered glass layers that prevent shattering into sharp shards, ensuring durability and safety during collisions. Unlike foam glass, which is primarily used for insulation and structural applications, safety glass prioritizes impact resistance and visibility for automotive use.
Manufacturing Processes: Foam Glass vs Safety Glass
Foam glass is produced through a process of melting glass cullet combined with a foaming agent, which creates a lightweight, porous material ideal for insulation but unsuitable for windshields. Safety glass manufacturing involves a lamination or tempering process, where layers of glass are either heat-treated or bonded with plastic interlayers to enhance impact resistance and shatterproof properties essential for automotive windshields. The significant differences in manufacturing processes result in foam glass's application primarily in construction insulation, while safety glass is specifically engineered to meet stringent safety standards in windshield production.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation, lightweight characteristics, and high compressive strength, making it suitable for sound absorption but lacks transparency and flexibility needed for windshields. Safety glass, composed of laminated or tempered layers, provides superior impact resistance, optical clarity, and shatterproof properties essential for vehicle windshields. The key material properties distinguishing safety glass for windshields include high tensile strength, transparency, and ability to prevent injury upon glass breakage, unlike foam glass which is primarily rigid and opaque.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Foam glass offers exceptional impact resistance due to its cellular structure that absorbs energy and prevents shattering, making it highly durable under stress. Safety glass, typically laminated or tempered, combines multiple layers to enhance impact resistance by holding shards together, thus reducing injury risk during collisions. While safety glass is specifically engineered for vehicle windshields, foam glass provides superior durability in applications requiring lightweight, insulating, and impact-absorbing materials.
Safety Performance in Accidents
Safety glass, commonly used in windshields, offers superior impact resistance and shatters into small, less harmful pieces, significantly reducing injury risk in accidents. Foam glass lacks the structural integrity and controlled breakage properties required for windshield safety, making it unsuitable for automotive collision protection. The specialized lamination and tempered properties of safety glass ensure enhanced occupant protection compared to foam glass during crashes.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Foam glass is rarely used for windshields due to its high cost and limited availability, making it impractical for automotive applications. Safety glass, such as laminated or tempered glass, is widely available and cost-effective, offering essential impact resistance and optical clarity required for vehicle windshields. Automotive manufacturers prioritize safety glass because it meets stringent safety standards and maintains affordability for mass production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam glass offers superior environmental benefits compared to safety glass for windshields due to its high recyclability and production from recycled glass materials, reducing landfill waste and raw resource extraction. Safety glass, primarily made from laminated or tempered glass combined with plastic interlayers, poses challenges in recycling and results in higher energy consumption during manufacturing. The sustainable advantage of foam glass lies in its lower carbon footprint and contribution to circular economy principles, making it a more eco-friendly choice for automotive applications.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Windshield
Foam glass offers excellent insulation and impact resistance but lacks the transparency required for windshields, making safety glass the optimal choice due to its laminated structure that prevents shattering and enhances driver protection. Safety glass, typically made from two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, provides superior visibility and durability under various impact conditions. Selecting safety glass ensures compliance with automotive safety standards while maintaining clear vision and occupant safety during collisions.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Safety glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com