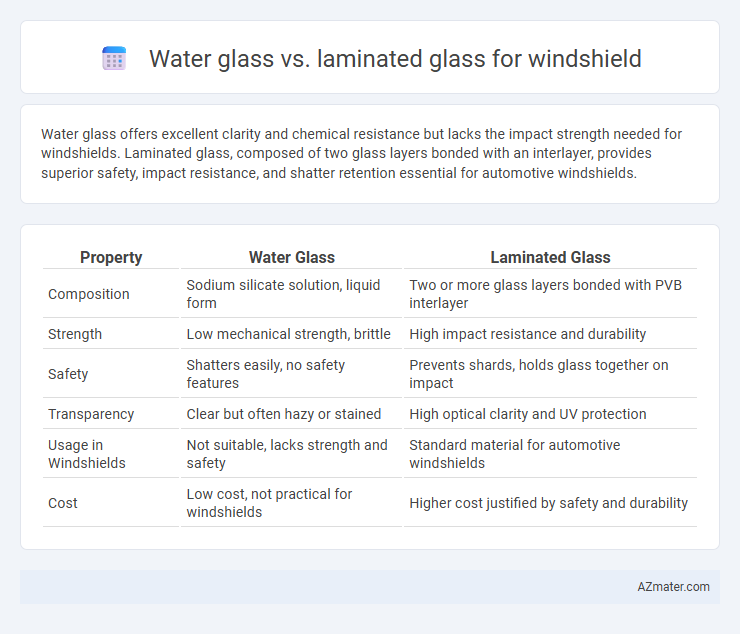
Water glass offers excellent clarity and chemical resistance but lacks the impact strength needed for windshields. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with an interlayer, provides superior safety, impact resistance, and shatter retention essential for automotive windshields.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate solution, liquid form | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer |
| Strength | Low mechanical strength, brittle | High impact resistance and durability |
| Safety | Shatters easily, no safety features | Prevents shards, holds glass together on impact |
| Transparency | Clear but often hazy or stained | High optical clarity and UV protection |
| Usage in Windshields | Not suitable, lacks strength and safety | Standard material for automotive windshields |
| Cost | Low cost, not practical for windshields | Higher cost justified by safety and durability |
Introduction to Automotive Windshield Glass Types
Automotive windshields primarily use laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer for enhanced safety and impact resistance, preventing shattering upon collision. Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is not typically used as a windshield material but serves in other automotive applications such as sealing or texturizing glass surfaces. Laminated glass remains the industry standard for windshields due to its durability, clarity, and ability to maintain structural integrity during accidents.
What is Water Glass?
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is a liquid solution that forms a durable, transparent coating when applied to glass surfaces. It enhances windshield strength by filling microscopic cracks and providing a protective barrier against moisture and impact damage. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers including a plastic interlayer for safety, water glass serves as a treatment to extend windshield durability rather than a structural glass type.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety by preventing shattering upon impact. This structure offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to standard water glass, which lacks the layered, bonded composition. Laminated glass also provides better sound insulation and UV protection, making it the preferred choice for vehicle windshields.
Structural Differences: Water Glass vs Laminated Glass
Water glass, often referring to chemically strengthened glass, has undergone an ion-exchange process to enhance surface compressive stress, resulting in increased strength and resistance to shattering. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shards upon breakage. The key structural difference lies in water glass being a single strengthened pane, while laminated glass integrates multiple layers to improve safety and durability in windshields.
Safety Performance Comparison
Laminated glass offers superior safety performance compared to water glass for windshields due to its construction, which includes a plastic interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact, reducing the risk of injury from sharp glass shards. Water glass, lacking this interlayer, is more prone to breaking into dangerous fragments, compromising occupant protection during collisions. Moreover, laminated glass maintains structural integrity under high stress and impact, enhancing overall vehicle safety.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to water glass for windshields due to its multi-layer construction, which includes a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds the glass together upon impact. Water glass, typically referring to glass treated with a protective coating, lacks the structural reinforcement provided by lamination, making it more susceptible to shattering. The enhanced toughness of laminated glass ensures better protection against road debris and collision forces, significantly improving vehicle safety.
Optical Clarity and UV Protection
Water glass offers superior optical clarity due to its uniform surface and minimal distortion, enhancing driver visibility compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides excellent UV protection by incorporating a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer, blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays. While water glass prioritizes clear vision, laminated glass balances clarity with essential UV shielding for safer windshield performance.
Cost Analysis: Water Glass and Laminated Glass
Water glass windshields generally offer a lower initial cost compared to laminated glass, making them a budget-friendly option for vehicle owners. Laminated glass, while more expensive upfront, provides enhanced durability and safety features, often reducing long-term expenses related to repairs and replacements. Factoring in lifespan and impact resistance, laminated glass tends to offer better value despite higher initial investment.
Legal Requirements for Windshield Glass
Laminated glass is typically mandated by legal regulations for windshield use due to its safety features, including shatter resistance and impact absorption. Water glass, often used in industrial applications, does not meet stringent automotive safety standards for windshields, lacking the necessary durability and clarity requirements. Compliance with vehicle safety standards such as FMVSS 205 in the US ensures laminated windshields provide adequate protection and visibility under legal guidelines.
Choosing the Right Windshield: Expert Recommendations
Water glass windshields offer moderate impact resistance but lack the durability and shatter protection found in laminated glass, which consists of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer for enhanced safety. Experts recommend laminated glass for windshields due to its superior ability to absorb impact, prevent shattering, and maintain structural integrity during accidents. Choosing laminated glass ensures compliance with automotive safety standards and provides better protection against debris and collision-related injuries.
Infographic: Water glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com