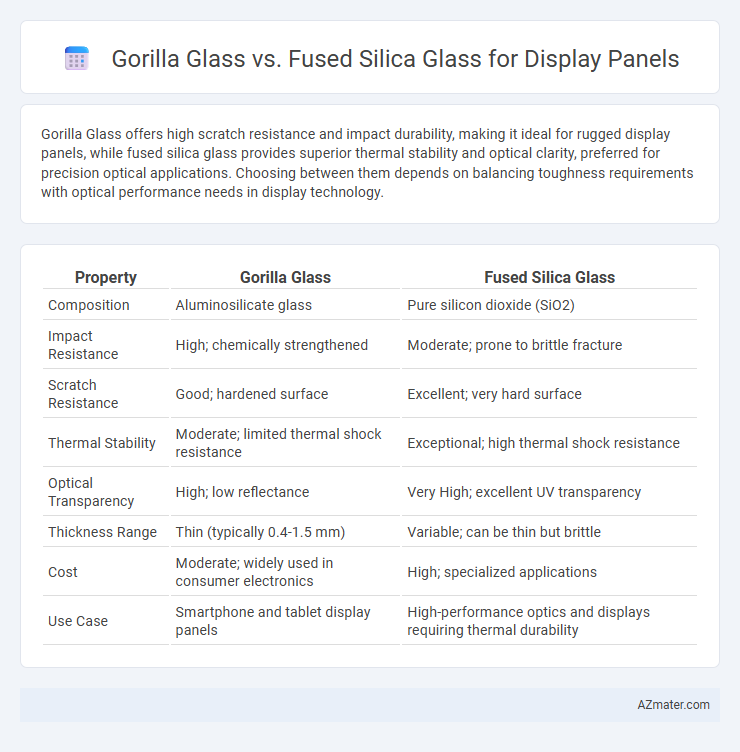
Gorilla Glass offers high scratch resistance and impact durability, making it ideal for rugged display panels, while fused silica glass provides superior thermal stability and optical clarity, preferred for precision optical applications. Choosing between them depends on balancing toughness requirements with optical performance needs in display technology.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gorilla Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate glass | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) |
| Impact Resistance | High; chemically strengthened | Moderate; prone to brittle fracture |
| Scratch Resistance | Good; hardened surface | Excellent; very hard surface |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate; limited thermal shock resistance | Exceptional; high thermal shock resistance |
| Optical Transparency | High; low reflectance | Very High; excellent UV transparency |
| Thickness Range | Thin (typically 0.4-1.5 mm) | Variable; can be thin but brittle |
| Cost | Moderate; widely used in consumer electronics | High; specialized applications |
| Use Case | Smartphone and tablet display panels | High-performance optics and displays requiring thermal durability |
Introduction to Gorilla Glass and Fused Silica Glass
Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet designed for high strength, scratch resistance, and durability, making it ideal for smartphone and tablet display panels. Fused silica glass, composed primarily of silicon dioxide, offers exceptional thermal stability, high optical clarity, and resistance to thermal shock, which benefits precision display applications. The choice between Gorilla Glass and fused silica glass depends on specific requirements such as impact resistance versus thermal performance in display panel manufacturing.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Gorilla Glass, primarily composed of aluminosilicate, undergoes a chemical strengthening process called ion exchange, where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions to create a compressive stress layer that enhances durability and scratch resistance. In contrast, Fused silica glass consists almost entirely of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with an amorphous structure, produced through melting high-purity quartz sand followed by rapid cooling, resulting in exceptional thermal stability and optical clarity. The manufacturing process of Gorilla Glass targets high impact resistance and flexibility for touchscreens, while fused silica glass manufacturing emphasizes low thermal expansion and chemical inertness for precision displays.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Gorilla Glass exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than fused silica glass, with a compressive strength often exceeding 1.5 GPa due to its chemically strengthened surface. Fused silica glass, while highly resistant to thermal shock and possessing exceptional hardness, generally has a lower fracture toughness and tensile strength compared to Gorilla Glass. This makes Gorilla Glass more suitable for display panels requiring superior resistance to scratches, impacts, and bending stresses in consumer electronics.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it highly durable against everyday abrasions on display panels. Fused silica glass, while having excellent thermal stability and optical clarity, generally exhibits lower impact resistance and is more prone to chipping under mechanical stress compared to Gorilla Glass. The enhanced tensile strength and toughness of Gorilla Glass provide better protection for devices subjected to drops and impacts.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Gorilla Glass offers high optical clarity with excellent light transmission rates around 90%, ensuring vibrant and sharp display visibility under various lighting conditions. Fused silica glass surpasses Gorilla Glass in optical purity due to its ultra-low iron content, yielding light transmission rates exceeding 92%, which reduces color distortion and increases display brightness. While both materials provide durable display protection, fused silica glass excels in maintaining superior light transmission and minimal optical absorption, crucial for high-performance display panels.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Gorilla Glass, engineered with alkali-aluminosilicate composition, exhibits superior thermal stability and higher heat resistance up to approximately 500degC, making it suitable for devices exposed to rapid temperature changes. Fused silica glass, composed of pure silicon dioxide, offers exceptional thermal stability with a melting point near 1,600degC and minimal thermal expansion, ideal for high-temperature applications requiring dimensional stability. However, Gorilla Glass provides better mechanical strength and scratch resistance, while fused silica glass excels in maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat without deformation.
Chemical Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Gorilla Glass exhibits high chemical durability due to its aluminosilicate composition, offering superior resistance to alkali and acid corrosion compared to traditional glass types. Fused silica glass provides exceptional corrosion resistance and chemical inertness because of its pure silicon dioxide structure, making it highly stable in harsh chemical environments. While Gorilla Glass balances strength and chemical resistance for touchscreen applications, fused silica glass is preferred in environments demanding extreme chemical durability and minimal degradation.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Gorilla Glass offers a competitive cost advantage due to large-scale manufacturing and widespread commercial availability, making it a preferred choice for consumer electronic display panels. Fused silica glass, while providing superior thermal and optical properties, commands higher prices and faces limited commercial availability in display panel applications. The cost-effectiveness and established supply chain of Gorilla Glass drive its dominance in the smartphone and tablet market.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gorilla Glass, made from aluminosilicate, features enhanced durability and scratch resistance, reducing device replacement frequency and e-waste generation. Fused silica glass, composed primarily of high-purity silicon dioxide, offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, promoting longer device lifespans and recycling potential. The production of Gorilla Glass typically involves higher energy consumption than fused silica, yet its robust performance can contribute to sustainable device usage by minimizing resource depletion and landfill accumulation over time.
Best Use Cases for Display Panels
Gorilla Glass offers exceptional scratch resistance and impact durability, making it ideal for smartphones, tablets, and ruggedized laptops where mobility and daily wear are common. Fused silica glass provides superior thermal stability and optical clarity, suitable for high-precision displays such as medical imaging devices and industrial touchscreens requiring extreme temperature resistance. For consumer electronics, Gorilla Glass excels in durability and lightweight design, while fused silica is preferred in specialized environments demanding high-temperature tolerance and chemical inertness.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Fused silica glass for Display panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com