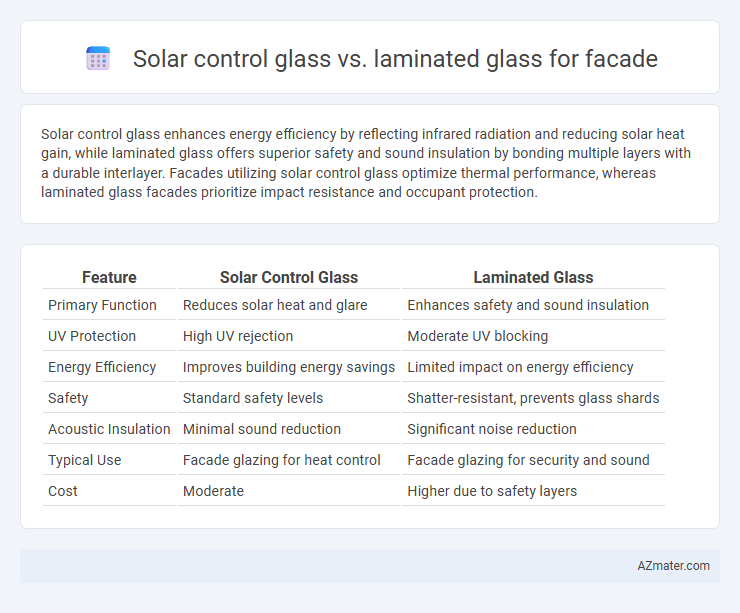
Solar control glass enhances energy efficiency by reflecting infrared radiation and reducing solar heat gain, while laminated glass offers superior safety and sound insulation by bonding multiple layers with a durable interlayer. Facades utilizing solar control glass optimize thermal performance, whereas laminated glass facades prioritize impact resistance and occupant protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solar Control Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces solar heat and glare | Enhances safety and sound insulation |
| UV Protection | High UV rejection | Moderate UV blocking |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves building energy savings | Limited impact on energy efficiency |
| Safety | Standard safety levels | Shatter-resistant, prevents glass shards |
| Acoustic Insulation | Minimal sound reduction | Significant noise reduction |
| Typical Use | Facade glazing for heat control | Facade glazing for security and sound |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to safety layers |
Introduction to Facade Glass Technologies
Facade glass technologies include solar control glass and laminated glass, each designed to enhance building performance and aesthetics. Solar control glass reduces heat gain by reflecting infrared radiation while allowing visible light, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Laminated glass combines layers of glass with interlayers for enhanced safety, noise reduction, and UV protection, providing structural integrity and occupant safety in facade applications.
What is Solar Control Glass?
Solar control glass is designed to limit the amount of solar heat entering a building while allowing natural light to pass through, improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort for facade applications. It typically features a special coating that reflects infrared and ultraviolet rays, reducing cooling costs and protecting interior furnishings from sun damage. Unlike laminated glass, which primarily offers safety and sound insulation benefits through layers of glass and interlayers, solar control glass focuses on thermal regulation and glare reduction.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is a safety glass consisting of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the glass pieces in place upon impact. Solar control glass, unlike laminated glass, is primarily designed to reduce solar heat gain and glare while maintaining transparency. Laminated glass offers enhanced security, sound insulation, and UV protection, making it ideal for facades requiring both safety and durability.
Key Performance Differences
Solar control glass significantly reduces solar heat gain by reflecting and absorbing infrared radiation, enhancing energy efficiency in building facades. Laminated glass primarily provides safety and security benefits through its interlayer, which holds glass shards together upon impact, but offers limited solar heat reduction. The key performance difference lies in solar control glass's ability to improve thermal comfort and lower cooling costs, whereas laminated glass prioritizes structural integrity and sound insulation.
Light Transmission and Glare Reduction
Solar control glass offers superior glare reduction by reflecting and absorbing a significant portion of solar radiation while maintaining moderate to high light transmission levels, typically ranging from 40% to 70%. Laminated glass primarily enhances safety and sound insulation with only marginal impact on light transmission and glare reduction, usually allowing 75% to 90% light transmission but minimal solar heat and glare control. For facade applications prioritizing daylighting with reduced glare, solar control glass provides better performance in managing solar heat gain and visual comfort compared to laminated glass.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Solar control glass significantly improves thermal insulation by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, reducing heat gain inside buildings and enhancing energy efficiency. Laminated glass, while providing safety benefits, offers moderate thermal insulation primarily through its interlayer, which limits heat transfer but is less effective than solar control coatings. Combining solar control glass with laminated layers optimizes facade performance by maximizing energy savings and maintaining occupant comfort.
Safety and Security Benefits
Solar control glass enhances facade safety by reducing heat transmission and glare, lowering the risk of thermal stress and glass breakage while improving occupant comfort. Laminated glass offers superior security benefits through its interlayer that holds shattered glass fragments together, preventing penetration and reducing injury risk during impact or forced entry. Combining solar control and laminated glass in facades maximizes protection against environmental hazards and intrusion, ensuring both occupant safety and building security.
Acoustic Insulation Comparison
Solar control glass enhances facade efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare, while its acoustic insulation performance varies depending on thickness and coating. Laminated glass provides superior acoustic insulation due to its interlayer design that dampens sound vibrations, significantly lowering noise transmission in urban environments. For facades prioritizing noise reduction, laminated glass typically outperforms solar control glass, offering enhanced soundproofing alongside safety benefits.
Cost Implications and Long-term Value
Solar control glass typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to laminated glass due to its advanced coatings that reduce heat gain and increase energy efficiency in building facades. Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and sound insulation benefits but may require additional treatments to achieve comparable solar control, potentially increasing overall expenses. Evaluating long-term value, solar control glass reduces HVAC energy consumption leading to lower operational costs, whereas laminated glass adds durability and impact resistance, decreasing maintenance and replacement frequency.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade
Solar control glass offers superior energy efficiency by reducing heat gain and glare, making it ideal for facades in hot climates seeking to minimize cooling costs. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and sound insulation, combining multiple layers that hold together upon impact, suitable for facades prioritizing security and noise reduction. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing thermal performance, safety requirements, and aesthetic preferences specific to the building's environment and design goals.
Infographic: Solar control glass vs Laminated glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com