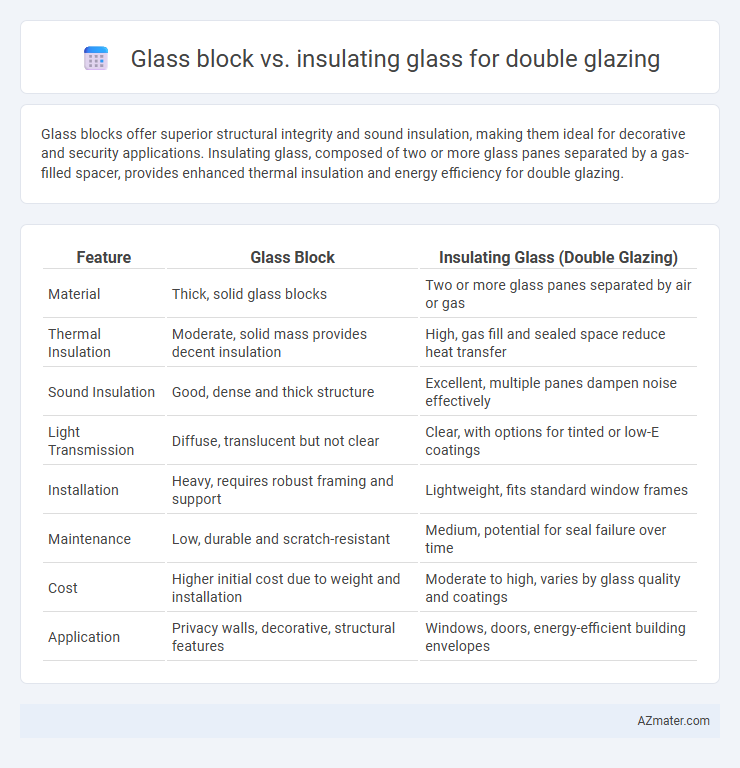
Glass blocks offer superior structural integrity and sound insulation, making them ideal for decorative and security applications. Insulating glass, composed of two or more glass panes separated by a gas-filled spacer, provides enhanced thermal insulation and energy efficiency for double glazing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Block | Insulating Glass (Double Glazing) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thick, solid glass blocks | Two or more glass panes separated by air or gas |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, solid mass provides decent insulation | High, gas fill and sealed space reduce heat transfer |
| Sound Insulation | Good, dense and thick structure | Excellent, multiple panes dampen noise effectively |
| Light Transmission | Diffuse, translucent but not clear | Clear, with options for tinted or low-E coatings |
| Installation | Heavy, requires robust framing and support | Lightweight, fits standard window frames |
| Maintenance | Low, durable and scratch-resistant | Medium, potential for seal failure over time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to weight and installation | Moderate to high, varies by glass quality and coatings |
| Application | Privacy walls, decorative, structural features | Windows, doors, energy-efficient building envelopes |
Introduction to Double Glazing: Glass Block vs Insulating Glass
Double glazing enhances thermal insulation and noise reduction by using two layers of glass separated by a gap filled with air or inert gas. Glass blocks provide structural strength and a distinctive aesthetic with inherent diffusion of light, making them ideal for privacy-focused applications. Insulating glass units (IGUs) feature sealed panes with low-emissivity coatings and gas fills like argon, delivering superior energy efficiency and visibility in modern building designs.
Material Composition and Structure
Glass blocks consist of thick, molded glass with hollow cavities that provide natural insulation through trapped air, whereas insulating glass units (IGUs) use two or more glass panes separated by a sealed spacer filled with air or inert gas like argon. The solid structure of glass blocks offers strength and privacy, but insulating glass maximizes energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer via low-emissivity coatings and gas fills. Both materials contribute to double glazing performance, yet IGUs typically deliver superior thermal insulation due to their advanced multilayer composition and airtight sealing.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Glass block offers superior thermal insulation due to its thick, solid structure and air pockets that reduce heat transfer, making it highly effective in maintaining interior temperature. Insulating glass units (IGUs), composed of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with inert gas like argon, provide improved thermal efficiency by minimizing heat loss and condensation through their sealed air spaces. Both options enhance energy efficiency, but IGUs allow for greater customization in thermal performance with low-emissivity coatings and various gas fills.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Glass blocks provide strong sound insulation due to their thick, solid structure and air-filled cavities, effectively reducing airborne noise transmission in double glazing applications. Insulating glass units (IGUs) typically use two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or inert gas, offering customizable acoustic performance depending on glass thickness, spacer type, and gas fill. While glass blocks excel in blocking low-frequency noise, insulating glass with laminated or thicker panes can achieve superior overall acoustic attenuation, especially for a broader range of frequencies in building facades.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Glass block offers excellent thermal insulation due to its thick, solid structure and air pockets, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in building envelopes. Insulating glass, or double glazing, consists of two or more glass panes separated by a gas-filled space, significantly minimizing heat loss and improving thermal performance by creating an effective barrier against external temperature fluctuations. Both materials contribute to energy savings, but insulating glass typically provides superior thermal resistance and better overall energy efficiency in window applications.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Glass blocks offer rigid design options with limited shapes and sizes, providing a distinct texture and light diffusion ideal for decorative partitions and walls. Insulating glass units (IGUs) provide extensive design flexibility, available in various shapes, sizes, tints, and coatings to enhance energy efficiency while maintaining clear views and modern aesthetics. IGUs enable sleek, minimalist frames for contemporary architecture, whereas glass blocks impart a more vintage or industrial look, influencing the overall visual impact of double-glazed installations.
Installation Processes and Complexity
Glass block installation involves setting heavy, pre-formed units into a mortar framework, requiring precise alignment and skilled masonry work, making it labor-intensive and time-consuming. Insulating glass units (IGUs) used in double glazing are typically factory-sealed, lightweight panels installed within window frames, allowing faster on-site fitting with less specialized labor. The complexity of insulating glass installation is lower, emphasizing frame preparation and sealing, whereas glass block installation demands thorough structural support and moisture-resistant mortar application.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Glass block windows typically cost between $30 to $50 per square foot, making them a budget-friendly option for durable, decorative double glazing. Insulating glass units (IGUs), commonly priced from $40 to $100 per square foot depending on the number of panes and gas fills, offer superior thermal insulation but at a higher initial investment. Budget considerations should factor in long-term energy savings with IGUs, whereas glass blocks provide added structural security and aesthetic appeal for a lower upfront cost.
Durability and Maintenance
Glass block offers exceptional durability due to its thick, solid construction that resists impact, weather, and wear, making it virtually maintenance-free over time. Insulating glass for double glazing, while energy-efficient and offering good thermal insulation, typically requires periodic seal inspections and potential replacements to prevent fogging or moisture buildup between panes. Regular maintenance of insulating glass ensures long-term performance, whereas glass blocks maintain structural integrity and clarity with minimal upkeep.
Best Use Cases and Applications
Glass block offers superior security and decorative appeal, making it ideal for areas requiring privacy and aesthetic enhancement such as bathroom walls and facades. Insulating glass, featuring multiple panes with gas fill and low-emissivity coatings, excels in thermal insulation and energy efficiency, making it the preferred choice for residential and commercial windows. Both options improve soundproofing, but insulating glass is better suited for climate control and energy savings in modern building designs.
Infographic: Glass block vs Insulating glass for Double glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com