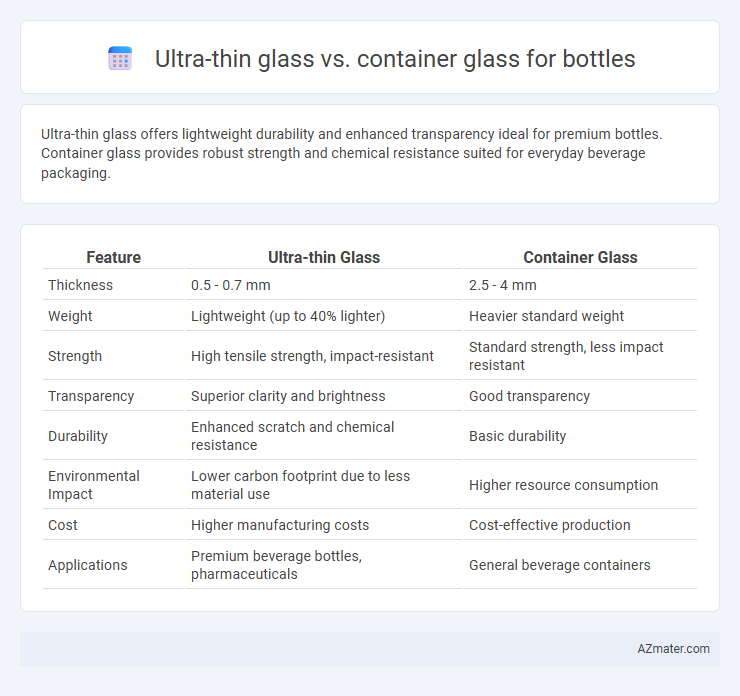
Ultra-thin glass offers lightweight durability and enhanced transparency ideal for premium bottles. Container glass provides robust strength and chemical resistance suited for everyday beverage packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-thin Glass | Container Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.5 - 0.7 mm | 2.5 - 4 mm |
| Weight | Lightweight (up to 40% lighter) | Heavier standard weight |
| Strength | High tensile strength, impact-resistant | Standard strength, less impact resistant |
| Transparency | Superior clarity and brightness | Good transparency |
| Durability | Enhanced scratch and chemical resistance | Basic durability |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to less material use | Higher resource consumption |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing costs | Cost-effective production |
| Applications | Premium beverage bottles, pharmaceuticals | General beverage containers |
Introduction: Ultra-thin Glass vs. Container Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers significantly reduced weight and enhanced durability compared to traditional container glass, making it ideal for lightweight bottle applications. This innovative material maintains high strength and fracture resistance despite its minimal thickness, optimizing sustainability by lowering raw material use and transportation emissions. In contrast, container glass provides robust protection but typically involves heavier, thicker walls that increase overall bottle weight and environmental impact.
Defining Ultra-thin Glass and Container Glass
Ultra-thin glass is engineered with a reduced thickness, typically less than 1 millimeter, offering enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and increased sustainability by lowering raw material usage and transportation emissions. Container glass, commonly used for bottles and jars, is thicker, generally ranging from 2 to 5 millimeters, designed to provide durability, thermal resistance, and protection for contents during storage and transport. Comparing ultra-thin glass to container glass reveals trade-offs between lightweight efficiency and mechanical robustness in packaging applications.
Manufacturing Processes Overview
Ultra-thin glass bottles are produced using advanced forming techniques like precision press-and-blow or narrow-neck pressing, enabling wall thicknesses as low as 0.6 mm, which reduces material usage and weight compared to traditional container glass. Container glass manufacturing typically involves the standard blow-and-blow or press-and-blow processes with thicker walls averaging 2.5-3.5 mm to ensure durability and resistance to impact and thermal stress. Innovations in ultra-thin glass production incorporate stringent quality control through real-time inspection and tailored annealing cycles to maintain mechanical integrity despite reduced thickness.
Physical Properties and Thickness Comparison
Ultra-thin glass for bottles exhibits a significantly reduced thickness, often ranging between 0.2 to 0.5 millimeters, compared to standard container glass, which typically measures 1.5 to 3 millimeters. Despite its thinner profile, ultra-thin glass maintains high mechanical strength and enhanced impact resistance due to advanced manufacturing techniques like chemical strengthening and precision annealing. Container glass tends to have higher weight and rigidity, but ultra-thin glass offers improved lightweight properties and increased sustainability through reduced material usage without compromising durability.
Weight and Durability for Bottles
Ultra-thin glass offers a significant weight reduction compared to traditional container glass, enhancing portability and reducing shipping costs for bottles. Despite its reduced thickness, ultra-thin glass maintains impressive durability by leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques and material composition. Container glass, although thicker and heavier, provides reliable strength and impact resistance, making it a preferred choice for heavier or high-stress applications.
Chemical Resistance and Safety Considerations
Ultra-thin glass bottles demonstrate superior chemical resistance compared to conventional container glass, offering enhanced protection against corrosion and chemical interactions with stored liquids. The reduced thickness of ultra-thin glass minimizes the exposure to contaminants while maintaining structural integrity, which is critical for safety in packaging sensitive substances like pharmaceuticals and beverages. Safety considerations also favor ultra-thin glass due to its lower breakage potential and improved recyclability, contributing to a safer handling and environmental profile in comparison to traditional container glass.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Ultra-thin glass offers superior design flexibility for bottle manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and ability to achieve intricate shapes and smooth finishes while maintaining strength. Container glass, typically thicker and heavier, limits design options but provides excellent durability and chemical resistance, essential for preserving contents. The enhanced transparency and sleek appearance of ultra-thin glass elevate the aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for premium and luxury packaging.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Ultra-thin glass bottles significantly reduce raw material usage and lower carbon emissions in production compared to traditional container glass, enhancing environmental sustainability. Their lighter weight decreases transportation fuel consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions during distribution. Both ultra-thin and container glass are highly recyclable, but ultra-thin glass offers improved recyclability efficiency by using less energy in melting and remanufacturing processes.
Applications in the Bottling Industry
Ultra-thin glass offers significant weight reduction and improved sustainability compared to traditional container glass, making it ideal for premium beverage bottles and reducing transportation costs in the bottling industry. Its enhanced strength and lower thickness allow manufacturers to produce lightweight bottles without compromising durability, catering to consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging. Container glass remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility for diverse beverage types, including carbonated drinks, spirits, and juices.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
Ultra-thin glass for bottles is gaining significant traction in the packaging industry due to its lightweight properties and sustainability benefits, driving demand in premium beverage markets. Container glass continues to dominate due to its durability and cost-effectiveness but faces challenges from shifting consumer preferences towards eco-friendly and innovative materials. Market forecasts predict accelerated adoption of ultra-thin glass in the next decade, supported by advancements in manufacturing technology and heightened regulatory emphasis on reducing carbon footprints.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Container glass for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com