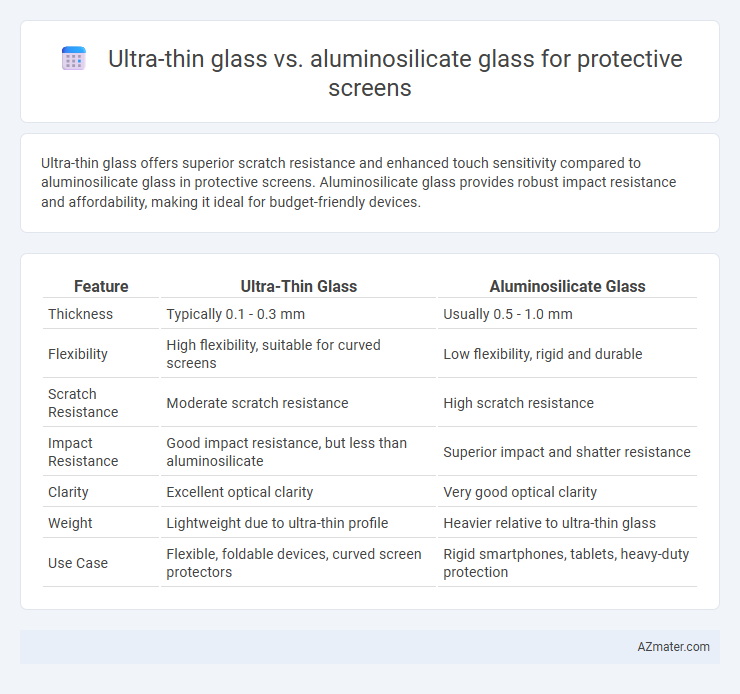
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced touch sensitivity compared to aluminosilicate glass in protective screens. Aluminosilicate glass provides robust impact resistance and affordability, making it ideal for budget-friendly devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Thin Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 0.1 - 0.3 mm | Usually 0.5 - 1.0 mm |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, suitable for curved screens | Low flexibility, rigid and durable |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate scratch resistance | High scratch resistance |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance, but less than aluminosilicate | Superior impact and shatter resistance |
| Clarity | Excellent optical clarity | Very good optical clarity |
| Weight | Lightweight due to ultra-thin profile | Heavier relative to ultra-thin glass |
| Use Case | Flexible, foldable devices, curved screen protectors | Rigid smartphones, tablets, heavy-duty protection |
Introduction to Modern Protective Screen Materials
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional clarity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for high-end electronic device screens. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its superior toughness and impact resistance, is widely used in smartphones and tablets to prevent shattering. Both materials leverage advanced chemical strengthening processes to enhance durability while maintaining touch sensitivity and optical performance.
What is Ultra-thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass, typically less than 100 microns thick, offers exceptional flexibility and durability for protective screens while maintaining high transparency and scratch resistance. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, which is chemically strengthened and thicker, ultra-thin glass provides a lightweight solution ideal for foldable and curved devices. Its unique composition and manufacturing process enable superior impact absorption and enhanced touch sensitivity compared to traditional aluminosilicate glass screens.
Overview of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass is a chemically strengthened material characterized by high scratch resistance and exceptional impact durability, making it ideal for protective screens in smartphones and tablets. Its robust atomic structure, enhanced through ion-exchange processes, provides superior thermal stability and resistance to cracking compared to ultra-thin glass. Manufacturers favor aluminosilicate glass for its balance of thinness and toughness, ensuring reliable protection without compromising touch sensitivity or clarity.
Key Material Differences: Ultra-thin Glass vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Ultra-thin glass features high flexibility and superior optical clarity due to its reduced thickness, making it ideal for foldable and curved protective screens, while aluminosilicate glass offers exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, commonly used in rigid smartphone displays. Chemically, ultra-thin glass is typically soda-lime or low-alkali glass enhanced through precise thermal treatment, whereas aluminosilicate glass contains aluminum oxide, providing enhanced chemical durability and impact resistance. Mechanical properties highlight ultra-thin glass's flexibility under bending stress, contrasting with aluminosilicate glass's rigidity and higher modulus, influencing device design and durability in protective screen applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass due to its higher modulus of elasticity and denser molecular structure, providing superior protection against everyday abrasions. Aluminosilicate glass, while highly durable with impressive impact resistance, tends to show more surface wear over time in high-friction environments. Both materials excel in durability, but ultra-thin glass delivers a better balance of lightweight protection and long-term scratch resistance for premium protective screen applications.
Flexibility and Design Capabilities
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility compared to aluminosilicate glass, enabling curved and foldable screen designs without compromising durability. Its ultra-thin profile allows for sleeker, lighter devices with enhanced aesthetic appeal and innovative form factors. Aluminosilicate glass, while highly scratch-resistant and robust, is more rigid, limiting design adaptability in flexible and foldable applications.
Impact on Touch Sensitivity and Display Clarity
Ultra-thin glass offers superior display clarity with higher light transmittance compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing screen brightness and color accuracy. Aluminosilicate glass provides robust impact resistance but may slightly reduce touch sensitivity due to its thicker construction and lower capacitive response. For applications prioritizing touch responsiveness and visual sharpness, ultra-thin glass is typically preferred despite a compromise in impact durability.
Real-world Applications in Consumer Electronics
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced touch sensitivity, making it ideal for foldable smartphones and wearable devices where flexibility and durability are critical. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its exceptional impact resistance and high hardness, is widely used in traditional smartphone displays and tablets, providing robust protection against drops and everyday wear. In consumer electronics, the choice between ultra-thin and aluminosilicate glass depends on device design requirements, with ultra-thin glass favored for innovative form factors and aluminosilicate glass preferred for standard rigid screens.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and scratch resistance but comes at a higher manufacturing cost due to complex processes and specialized equipment. Aluminosilicate glass is more cost-effective and easier to mass-produce, making it a popular choice for protective screens with balanced durability and affordability. Manufacturing ultra-thin glass requires stringent control and precision, while aluminosilicate glass benefits from established production lines that reduce lead times and expenses.
Future Trends in Protective Screen Technologies
Ultra-thin glass is gaining traction in protective screen technologies due to its superior scratch resistance, flexibility, and optical clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass, which remains valued for its chemical strength and impact resistance. Innovations in ultra-thin glass manufacturing, such as enhanced chemical strengthening and hybrid layering techniques, are pushing the material toward widespread adoption in foldable and wearable devices. Future trends emphasize integrating ultra-thin glass with advanced coatings for oleophobic and antimicrobial properties, positioning it as a leading solution in next-generation protective screens.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Protective screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com