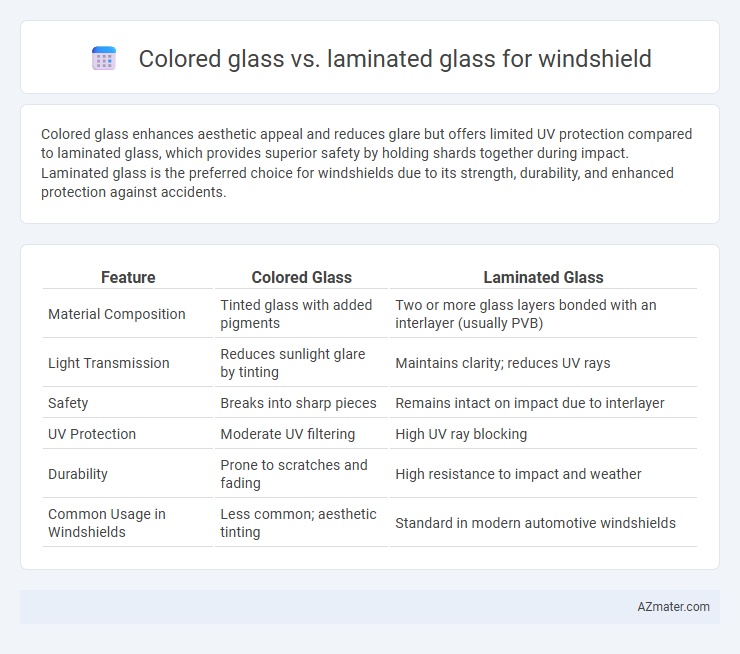
Colored glass enhances aesthetic appeal and reduces glare but offers limited UV protection compared to laminated glass, which provides superior safety by holding shards together during impact. Laminated glass is the preferred choice for windshields due to its strength, durability, and enhanced protection against accidents.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Tinted glass with added pigments | Two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer (usually PVB) |
| Light Transmission | Reduces sunlight glare by tinting | Maintains clarity; reduces UV rays |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp pieces | Remains intact on impact due to interlayer |
| UV Protection | Moderate UV filtering | High UV ray blocking |
| Durability | Prone to scratches and fading | High resistance to impact and weather |
| Common Usage in Windshields | Less common; aesthetic tinting | Standard in modern automotive windshields |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Types
Windshield glass primarily includes laminated glass and colored glass, each offering unique benefits for automotive safety and aesthetics. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon impact. Colored glass incorporates tints or dyes to reduce glare and UV exposure, improving driver comfort without compromising visibility or structural integrity.
What is Colored Glass?
Colored glass for windshields is manufactured by adding metal oxides or dyes during the glass-making process, resulting in a tinted surface that reduces glare and enhances UV protection. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers including a plastic interlayer for impact resistance and safety, colored glass focuses primarily on aesthetic appeal and light filtration. This type of glass helps in improving driver comfort by minimizing eye strain while maintaining structural integrity depending on the base glass type used.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is a safety glass composed of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an inner layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon impact. Unlike colored glass, which mainly offers aesthetic appeal and UV protection, laminated glass is designed to maintain windshield integrity and occupant safety during collisions. This makes laminated glass the industry standard for automotive windshields due to its superior durability and protective properties.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Colored glass for windshields involves adding metal oxide particles during the molten glass phase, creating a uniform tint that reduces glare and UV exposure. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer through heat and pressure, enhancing impact resistance and preventing shattering. The manufacturing process of laminates requires precise lamination and curing stages, whereas colored glass relies primarily on controlled chemical infusion during melting.
Optical Clarity: Colored vs Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for windshields offers superior optical clarity compared to colored glass due to its structure, which includes a plastic interlayer that minimizes distortion and reduces glare. Colored glass can alter the perception of colors and reduce visibility, especially under low light conditions, potentially affecting driver safety. The consistent transparency of laminated glass ensures clearer vision and better protection against UV rays without compromising optical performance.
Safety and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass is engineered with a PVB interlayer that holds shards together during impact, significantly enhancing windshield safety by preventing glass from shattering and causing injury. Colored glass, while helpful in reducing glare and UV penetration, lacks the multiple layers found in laminated glass and does not provide the same level of impact resistance. For optimal protection against collisions and debris, laminated glass remains the industry standard in windshield safety performance.
UV and Heat Protection
Colored glass reduces visible light transmission and blocks some UV rays but offers limited heat protection compared to laminated glass, which contains an interlayer that significantly enhances UV blocking up to 99% and reduces solar heat by filtering infrared radiation. Laminated glass's polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ionoplast interlayer provides superior thermal insulation, keeping the vehicle interior cooler and protecting occupants from harmful UV exposure. For optimal windshield performance, laminated glass is preferred for its combined safety features and enhanced UV and heat rejection capabilities.
Durability and Longevity
Colored glass windshields offer enhanced UV protection but generally have lower impact resistance compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass features a PVB interlayer that improves durability by preventing shattering on impact, significantly extending windshield longevity. This structural design makes laminated glass the preferred choice for windshield safety and long-term performance.
Cost Effectiveness
Colored glass windshields often incur higher costs due to specialized tinting processes and materials, whereas laminated glass provides superior cost-effectiveness by combining two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, enhancing durability and safety. Laminated glass reduces long-term expenses by minimizing the need for frequent replacements and repairs caused by cracks or shattering. The energy efficiency and UV protection of laminated glass further contribute to lower maintenance and cooling costs, making it a more economical choice for vehicle windshields.
Which is Better: Colored or Laminated Glass for Windshields?
Laminated glass is generally better for windshields due to its enhanced safety features, as it consists of two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact. Colored glass primarily offers aesthetic appeal and UV protection but lacks the structural integrity and safety benefits provided by laminated glass. For optimal windshield performance, durability, and occupant protection, laminated glass is the preferred choice over colored glass.
Infographic: Colored glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com