Patterned glass offers decorative textures that enhance privacy and diffuse light, while tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare by absorbing visible light for improved energy efficiency. Choosing between patterned and tinted glass depends on balancing aesthetic appeal with thermal performance requirements for the facade.
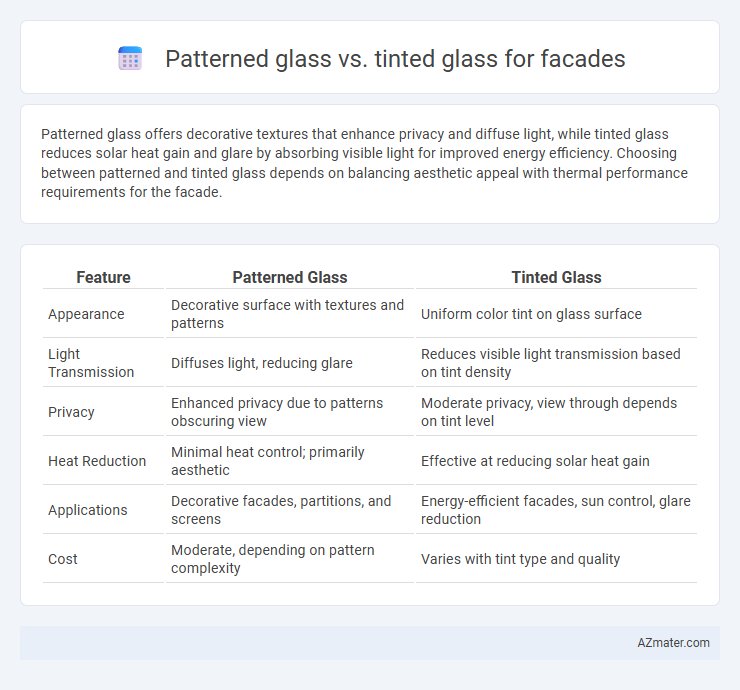
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Patterned Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Decorative surface with textures and patterns | Uniform color tint on glass surface |
| Light Transmission | Diffuses light, reducing glare | Reduces visible light transmission based on tint density |
| Privacy | Enhanced privacy due to patterns obscuring view | Moderate privacy, view through depends on tint level |
| Heat Reduction | Minimal heat control; primarily aesthetic | Effective at reducing solar heat gain |
| Applications | Decorative facades, partitions, and screens | Energy-efficient facades, sun control, glare reduction |
| Cost | Moderate, depending on pattern complexity | Varies with tint type and quality |
Introduction to Facade Glass Solutions
Patterned glass enhances facade aesthetics by offering unique textures and privacy while diffusing natural light, making it ideal for architectural creativity and occupant comfort. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare through various shades and coatings, improving energy efficiency and maintaining clear outward views. Both options serve distinct purposes in facade glass solutions, balancing visual appeal with functional performance in modern building design.
What is Patterned Glass?
Patterned glass features textured or embossed surface designs that enhance privacy and diffuse light while maintaining transparency, making it ideal for commercial facades requiring both aesthetic appeal and functionality. Unlike tinted glass, which reduces solar heat gain and glare by adding color, patterned glass emphasizes visual interest and surface variation without significantly altering light transmission. This type of glass improves natural daylight distribution and can obscure views, offering both decorative and practical benefits in architectural facades.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass for facades is designed with added metal oxides or chemicals during manufacturing to absorb solar radiation, reducing glare and heat transmission. This glass enhances energy efficiency by lowering cooling costs while maintaining visibility and natural daylight. Compared to patterned glass, which features etched or textured designs for privacy and aesthetic purposes, tinted glass primarily targets thermal control and comfort in building exteriors.
Aesthetic Differences: Patterned vs Tinted Glass
Patterned glass offers intricate designs and textures that create visual interest and diffuse natural light, enhancing facade aesthetics with depth and artistic expression. Tinted glass provides a uniform coloration that reduces glare and solar heat gain while giving the facade a sleek, modern appearance with consistent shading. Both options impact building energy performance, but patterned glass emphasizes decorative appeal, whereas tinted glass prioritizes functional shading and exterior uniformity.
Daylighting and Privacy Considerations
Patterned glass enhances daylight diffusion by scattering light evenly, reducing glare while maintaining high privacy levels due to its textured surface that obscures visibility. Tinted glass lowers solar heat gain and controls daylight intensity by filtering light, but it offers less privacy since it remains relatively transparent. Choosing patterned glass maximizes privacy without sacrificing natural light, whereas tinted glass prioritizes solar control with moderate privacy.
Energy Efficiency and Solar Control
Patterned glass enhances facade aesthetics while diffusing natural light, reducing glare and improving daylight penetration without compromising energy efficiency. Tinted glass significantly lowers solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting infrared radiation, leading to better solar control and reduced cooling loads in buildings. Combining patterned designs with tinted coatings can optimize both energy efficiency and solar control, making facades more sustainable and comfortable.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Patterned glass offers high durability with enhanced surface treatments that resist scratches and impacts, making it suitable for long-lasting facade applications. Tinted glass, while effective in reducing solar heat gain and glare, may face challenges with color fading and requires regular cleaning to maintain its appearance. Maintenance demands for patterned glass are generally lower due to its textured surface that conceals dirt and minor imperfections, whereas tinted glass requires more frequent upkeep to prevent streaks and preserve tint uniformity.
Cost Implications for Facade Projects
Patterned glass generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized manufacturing processes and custom designs, impacting total facade project budgets more significantly than standard alternatives. Tinted glass offers cost savings through simpler production and energy efficiency benefits that can reduce long-term operational expenses in facade applications. Choosing between patterned and tinted glass requires balancing upfront investment against potential energy savings and aesthetic value in facade projects.
Application Scenarios: Matching Glass to Building Needs
Patterned glass enhances privacy and diffuses light, making it ideal for office partitions, bathrooms, and facades requiring soft illumination without compromising natural light. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare, improving energy efficiency in commercial buildings with large south-facing facades or residences in hot climates. Selecting glass based on thermal performance, privacy needs, and aesthetic goals ensures optimal building comfort and energy savings.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade
Patterned glass enhances facade design by providing texture, privacy, and diffused natural light, ideal for areas requiring both aesthetics and moderation of visibility. Tinted glass offers solar control benefits, reducing glare and heat gain, making it suitable for facades in sunny climates aiming to improve energy efficiency. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing privacy needs, light transmission, thermal performance, and aesthetic goals specific to the building's location and function.
Infographic: Patterned glass vs Tinted glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com