Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight durability compared to Opal glass, which provides excellent light diffusion and a smooth, opaque finish ideal for decorative light fixtures. Selecting foam glass enhances energy efficiency in lighting design, while Opal glass maximizes aesthetic appeal through uniform, soft illumination.
Table of Comparison
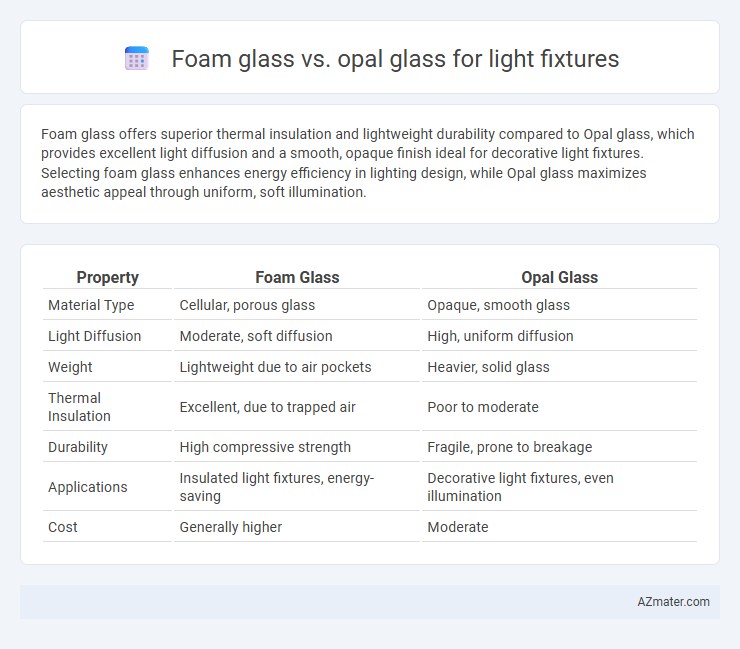
| Property | Foam Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Cellular, porous glass | Opaque, smooth glass |
| Light Diffusion | Moderate, soft diffusion | High, uniform diffusion |
| Weight | Lightweight due to air pockets | Heavier, solid glass |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, due to trapped air | Poor to moderate |
| Durability | High compressive strength | Fragile, prone to breakage |
| Applications | Insulated light fixtures, energy-saving | Decorative light fixtures, even illumination |
| Cost | Generally higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Foam Glass and Opal Glass
Foam glass is a lightweight, durable material composed of crushed glass fused into a cellular structure, providing excellent thermal insulation and high resistance to moisture, making it ideal for light fixture bases and thermal barriers. Opal glass, characterized by its milky white, translucent appearance, diffuses light evenly to reduce glare and enhance aesthetic appeal in light fixtures, often used for lamp shades and decorative covers. Both materials optimize light fixture performance but serve distinct functions: foam glass offers structural and insulating benefits, while opal glass focuses on light diffusion and visual enhancement.
What is Foam Glass? Key Properties
Foam glass is a lightweight, highly insulative material composed of crushed glass fused with gas bubbles, providing excellent thermal resistance and durability ideal for light fixture diffusers. Its key properties include high compressive strength, low water absorption, and resistance to fire and chemicals, ensuring long-lasting performance and safety. Foam glass offers superior insulation and structural integrity compared to opal glass, making it suitable for energy-efficient lighting solutions.
What is Opal Glass? Key Properties
Opal glass is a type of translucent glass characterized by its milky white appearance, achieved through the inclusion of small amounts of opacifying agents like tin oxide or bone ash. Its key properties include excellent light diffusion, resistance to ultraviolet radiation, and a smooth, uniform surface that reduces glare in light fixtures. Compared to foam glass, opal glass offers superior optical clarity and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for decorative and functional lighting applications.
Comparing Light Diffusion: Foam vs Opal
Foam glass fixtures provide a unique light diffusion by incorporating tiny air bubbles that scatter light softly, resulting in a matte, frosted effect that reduces glare and creates a calming ambiance. Opal glass, known for its milky white translucency, offers more uniform and even light diffusion, producing a brighter and cleaner illumination ideal for enhancing color accuracy and minimizing harsh shadows. When comparing light diffusion, foam glass excels in creating textured, subtle luminance, while opal glass delivers consistent brightness and clarity suitable for task lighting and decorative applications.
Durability and Strength Differences
Foam glass offers superior durability and strength in light fixtures due to its closed-cell structure, providing excellent resistance to impact, compression, and moisture penetration. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing and diffusing light evenly, tends to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking or shattering under mechanical stress. The lightweight yet robust composition of foam glass makes it a preferred choice for long-lasting, resilient lighting applications where durability is critical.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Foam glass offers a unique textured appearance with a porous, matte finish that enhances modern and industrial light fixture designs, while Opal glass provides a smooth, translucent surface that diffuses light evenly, creating a soft, elegant ambiance. Opal glass excels in design flexibility due to its ability to be molded into various shapes and thicknesses without compromising light diffusion, whereas foam glass is more rigid and limited in form but adds a distinctive aesthetic with its frosted, crystalline look. Choosing between foam glass and opal glass depends on the desired visual effect and the level of versatility required for custom lighting applications.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.04 W/m*K, significantly reducing heat loss in light fixtures and enhancing energy efficiency by maintaining stable internal temperatures. Opal glass, while providing excellent light diffusion and aesthetic appeal, has a higher thermal conductivity around 1.0 W/m*K, resulting in less effective thermal performance compared to foam glass. Choosing foam glass for light fixtures optimizes energy savings by minimizing heat transfer, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced thermal management and insulation.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Foam glass offers superior resistance to moisture and staining, making maintenance straightforward with occasional wiping using mild detergents, whereas opal glass, being more porous, requires gentler cleaning to avoid surface abrasions and discoloration. Foam glass's closed-cell structure prevents dirt accumulation, reducing the frequency of cleaning, while opal glass necessitates more regular upkeep to maintain its translucency and aesthetic appeal. Both materials benefit from non-abrasive cleaning tools, but foam glass generally withstands harsh environmental conditions better, enhancing longevity in light fixture applications.
Cost Comparison: Foam Glass vs Opal Glass
Foam glass typically costs less than opal glass, offering a budget-friendly option for light fixtures while providing excellent insulation and durability. Opal glass commands a higher price due to its superior translucency and aesthetic appeal, enhancing light diffusion and fixture elegance. Choosing foam glass reduces initial expenses without compromising performance, whereas opal glass represents an investment in premium visual quality and design.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type in Lighting
Foam glass, with its excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, is ideal for exterior or industrial light fixtures where durability and energy efficiency are critical. Opal glass, known for its smooth, diffused light output and aesthetic appeal, suits indoor decorative lighting, providing soft, glare-free illumination for residential and commercial spaces. Each glass type optimizes light fixture performance based on environmental exposure and desired light quality.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Opal glass for Light fixture
 azmater.com
azmater.com