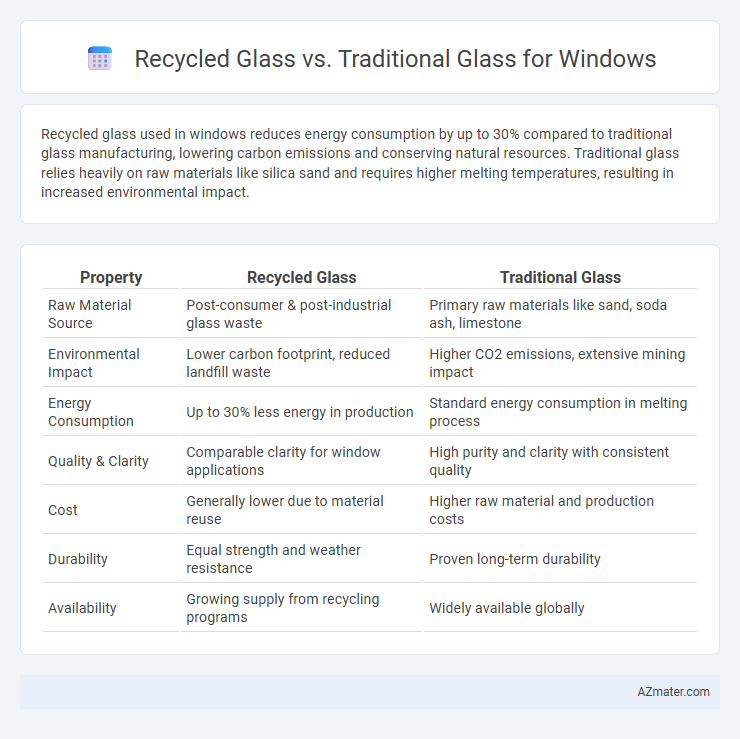
Recycled glass used in windows reduces energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional glass manufacturing, lowering carbon emissions and conserving natural resources. Traditional glass relies heavily on raw materials like silica sand and requires higher melting temperatures, resulting in increased environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Glass | Traditional Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | Post-consumer & post-industrial glass waste | Primary raw materials like sand, soda ash, limestone |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduced landfill waste | Higher CO2 emissions, extensive mining impact |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 30% less energy in production | Standard energy consumption in melting process |
| Quality & Clarity | Comparable clarity for window applications | High purity and clarity with consistent quality |
| Cost | Generally lower due to material reuse | Higher raw material and production costs |
| Durability | Equal strength and weather resistance | Proven long-term durability |
| Availability | Growing supply from recycling programs | Widely available globally |
Introduction: Recycled Glass vs Traditional Glass
Recycled glass for windows offers significant environmental benefits by reducing raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to traditional glass production. It maintains comparable clarity and durability while lowering carbon emissions through efficient reuse of cullet materials. Advances in manufacturing technologies ensure recycled glass matches the thermal insulation and strength standards of conventional glass in architectural applications.
Environmental Impact of Glass Production
Recycled glass significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional glass production, which requires melting raw materials at high temperatures. Using cullet in manufacturing decreases greenhouse gas emissions and conserves natural resources like sand, soda ash, and limestone. Incorporating recycled glass in windows supports sustainable construction by minimizing landfill waste and cutting carbon footprints linked to glass production.
Energy Consumption in Manufacturing
Recycled glass requires significantly less energy to manufacture compared to traditional glass, reducing energy consumption by up to 40%. The melting process for recycled cullet occurs at lower temperatures, cutting down greenhouse gas emissions. Incorporating recycled glass in windows supports sustainable production by minimizing the carbon footprint of manufacturing.
Material Strength and Durability
Recycled glass used in windows maintains comparable material strength to traditional glass, often meeting rigorous building standards for impact resistance and thermal performance. The durability of recycled glass is enhanced by rigorous processing that removes impurities, resulting in an equally robust and long-lasting window material. This sustainable option also resists weathering, abrasion, and UV degradation, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Recycled glass windows offer comparable thermal insulation to traditional glass by maintaining low thermal conductivity, which helps reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. Acoustic insulation in recycled glass is enhanced through its denser composition, effectively dampening sound vibrations and reducing noise pollution. Both glass types can be optimized with double or triple glazing, but recycled glass provides an eco-friendly alternative without compromising thermal and acoustic performance.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Traditional Glass
Recycled glass windows typically cost 10-25% less than traditional glass due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. Traditional glass involves higher manufacturing costs linked to furnace operation and material extraction, driving prices up. Over time, recycled glass products offer better cost efficiency by minimizing waste management fees and supporting sustainable building incentives.
Design and Aesthetic Differences
Recycled glass windows often exhibit a distinctive texture and color variation due to the inclusion of mixed cullet materials, creating a unique, artisanal aesthetic compared to the uniform clarity of traditional glass. The design versatility of recycled glass allows for creative personalization, incorporating subtle hues and patterns that enhance architectural character and sustainability appeal. While traditional glass prioritizes pristine transparency and smoothness, recycled glass emphasizes eco-friendly design innovation paired with visually dynamic effects.
Recycling Process and Availability
Recycled glass for windows is produced by melting crushed post-consumer or industrial glass, reducing energy consumption and raw material usage compared to traditional glass manufacturing, which relies heavily on virgin silica sand and high-temperature furnaces. The availability of recycled glass varies regionally but is increasing due to expanding collection programs and advancements in sorting technologies, enabling higher purity and better quality output. Traditional glass remains widely available with established supply chains, yet the growing demand for sustainable materials is driving a shift towards greater incorporation of recycled content in window production.
Maintenance and Longevity
Recycled glass windows demonstrate superior resistance to scratches and fading, reducing the need for frequent maintenance compared to traditional glass. The non-porous surface of recycled glass minimizes dirt accumulation and staining, ensuring longer-lasting clarity and ease of cleaning. Traditional glass, while durable, often requires more regular upkeep to prevent degradation from environmental factors, impacting its overall longevity.
Sustainability and Future Trends in Glass Windows
Recycled glass window panes significantly reduce energy consumption and raw material extraction compared to traditional glass, lowering the carbon footprint of construction projects. Innovations in recycled glass technology improve durability and clarity, making it a sustainable alternative aligned with green building standards and LEED certifications. Future trends emphasize integrating smart glass capabilities with recycled materials, promoting energy-efficient, eco-friendly windows that support circular economy principles.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Traditional glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com