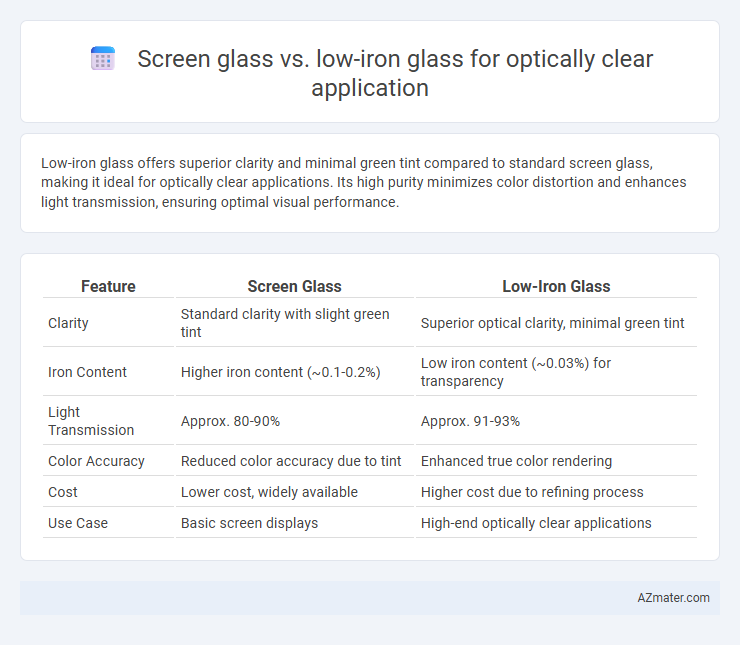
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and minimal green tint compared to standard screen glass, making it ideal for optically clear applications. Its high purity minimizes color distortion and enhances light transmission, ensuring optimal visual performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screen Glass | Low-Iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Clarity | Standard clarity with slight green tint | Superior optical clarity, minimal green tint |
| Iron Content | Higher iron content (~0.1-0.2%) | Low iron content (~0.03%) for transparency |
| Light Transmission | Approx. 80-90% | Approx. 91-93% |
| Color Accuracy | Reduced color accuracy due to tint | Enhanced true color rendering |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to refining process |
| Use Case | Basic screen displays | High-end optically clear applications |
Introduction to Optically Clear Glass Applications
Optically clear glass applications demand materials with minimal distortion and high transparency to ensure accurate visual representation and performance. Screen glass provides standard clarity suitable for general display uses, while low-iron glass offers superior optical purity by significantly reducing the green tint inherent in regular glass, enhancing color fidelity and light transmission. Low-iron glass is preferred in high-precision fields such as optical instruments, display screens, and architectural glazing where utmost clarity and true-color rendition are critical.
What is Screen Glass?
Screen glass is a type of glass specifically designed to minimize light reflection and enhance clarity, making it ideal for optically clear applications such as display screens, touch panels, and optical lenses. It usually incorporates anti-reflective coatings or treatments to reduce glare and preserve color accuracy, ensuring sharp and vivid visuals. Compared to low-iron glass, which offers superior transparency by reducing iron content, screen glass prioritizes optical performance through surface treatments that enhance user visibility and interaction.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of architectural glass specially formulated to reduce the iron content typically found in standard glass, resulting in higher clarity and transparency crucial for optically clear applications. This glass exhibits minimal greenish tint, allowing for true color representation and enhanced light transmission, making it ideal for display cases, aquariums, and solar panels. Compared to screen glass, low-iron glass offers superior optical performance by maximizing visual fidelity and reducing distortion in high-precision environments.
Key Differences: Screen Glass vs Low-Iron Glass
Screen glass typically features a standard iron content resulting in a slight greenish tint, which can affect color clarity and transparency in optically clear applications. Low-iron glass is specially manufactured with reduced iron levels, enhancing light transmission up to 91% and delivering superior color neutrality and visual clarity for high-precision optical uses. The key difference lies in low-iron glass providing enhanced optical performance with minimal distortion, making it ideal for applications demanding true transparency and minimal color cast compared to screen glass.
Optical Clarity: Light Transmission and Color Accuracy
Screen glass offers high optical clarity with light transmission rates typically around 90-92%, but low-iron glass surpasses this with transmission rates up to 96%, enhancing brightness and color accuracy. Low-iron glass's reduced iron content minimizes the greenish tint common in standard screen glass, resulting in more precise color rendering critical for optically clear applications such as display screens and museum exhibits. The superior optical performance of low-iron glass makes it the preferred choice where maximum light transmission and true color fidelity are essential.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Screen glass typically offers enhanced impact resistance due to its chemical and thermal tempering processes, making it more durable for high-touch applications. Low-iron glass provides superior optical clarity with reduced green tint but generally has lower strength compared to tempered screen glass. For optically clear applications requiring both durability and clarity, screen glass is preferred for strength, while low-iron glass excels in visual performance but may require additional strengthening treatments.
Cost Analysis: Screen Glass vs Low-Iron Glass
Screen glass offers a cost-effective solution for optically clear applications with moderate clarity and durability, typically priced 20-30% lower than low-iron glass. Low-iron glass provides superior transparency and minimal greenish tint, essential for high-end displays, but its manufacturing complexity results in a 25-40% higher cost compared to standard screen glass. Selecting between screen glass and low-iron glass requires balancing budget constraints with the demand for optical purity in the final application.
Common Uses in Optically Clear Applications
Screen glass is commonly used in optically clear applications such as display screens for smartphones, tablets, and televisions due to its anti-reflective properties and durability. Low-iron glass is preferred for high-clarity projects like aquarium panels, picture framing, and solar panels because it offers superior transparency and minimal green tint. Both types maximize visual clarity but are selected based on specific needs for strength, color neutrality, and edge finish.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Screen glass offers standard clarity suitable for general display applications but can introduce slight color distortion due to its iron content, which may affect the true color rendition of visuals. Low-iron glass provides superior optical clarity with enhanced light transmission and minimal green tint, making it ideal for projects demanding precise color accuracy and transparency. Selecting low-iron glass ensures the highest visual fidelity for critical design, museum displays, or high-end electronic screens where clear, true-to-life images are essential.
Conclusion: Which Glass is Best for Optical Clarity?
Low-iron glass outperforms screen glass in optical clarity due to its reduced iron content, resulting in higher light transmittance and minimal green tint. Screen glass, while durable and suitable for certain touchscreen applications, typically exhibits lower light transmission and slight color distortion. For applications demanding maximum optical clarity and true color representation, low-iron glass is the superior choice.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Low-iron glass for Optically clear application
 azmater.com
azmater.com