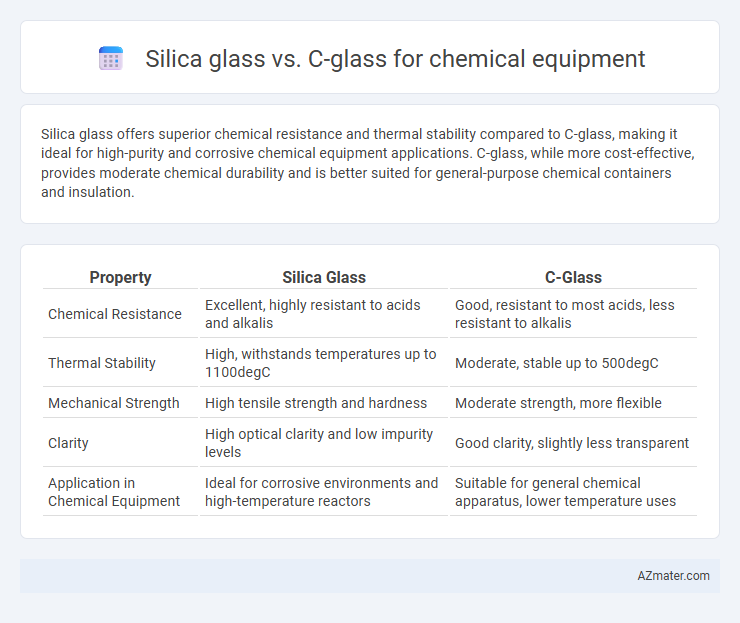
Silica glass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to C-glass, making it ideal for high-purity and corrosive chemical equipment applications. C-glass, while more cost-effective, provides moderate chemical durability and is better suited for general-purpose chemical containers and insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | C-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to acids and alkalis | Good, resistant to most acids, less resistant to alkalis |
| Thermal Stability | High, withstands temperatures up to 1100degC | Moderate, stable up to 500degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and hardness | Moderate strength, more flexible |
| Clarity | High optical clarity and low impurity levels | Good clarity, slightly less transparent |
| Application in Chemical Equipment | Ideal for corrosive environments and high-temperature reactors | Suitable for general chemical apparatus, lower temperature uses |
Introduction to Silica Glass and C-Glass
Silica glass, composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2), offers exceptional thermal stability, high chemical resistance, and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for demanding chemical equipment applications. C-glass, a type of glass fiber rich in calcium oxide and alumina, provides strong alkali resistance and mechanical strength but lower thermal tolerance compared to silica glass. Selecting between silica glass and C-glass depends on factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress in industrial chemical processing environments.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Silica glass primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with a highly ordered, amorphous network structure that provides exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive reagents. C-glass, composed mainly of calcium aluminosilicate with added boron oxides, has a less pure silica content and a more complex structure, offering good chemical durability but lower resistance to alkali environments compared to silica glass. The higher purity and uniform network of silica glass translate into superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength in demanding chemical processing applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Silica glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and high thermal resistance, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. C-glass offers good chemical durability but generally lower mechanical strength compared to silica glass, limiting its use in applications demanding high structural integrity. Silica glass's enhanced durability against thermal shock and corrosion ensures longer service life and reliability in harsh chemical environments.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Silica glass exhibits superior thermal resistance with a melting point around 1713degC, significantly outperforming C-glass which melts near 1050degC, making silica glass ideal for high-temperature chemical equipment. The low thermal expansion coefficient of silica glass (about 0.5 x 10^-6 /degC) enhances its thermal shock resistance, whereas C-glass has higher thermal expansion, limiting its use under rapid temperature changes. Silica glass also offers excellent chemical stability and optical clarity, ensuring reliable performance in corrosive environments and precise process monitoring.
Chemical Resistance in Corrosive Environments
Silica glass exhibits superior chemical resistance in highly corrosive environments due to its high purity and low alkali content, making it ideal for handling aggressive acids and alkalis. C-glass, while offering good resistance to aqueous solutions and mild acids, demonstrates lower durability against strong alkaline substances and hydrofluoric acid. Therefore, silica glass is preferred for long-term chemical equipment applications requiring robust corrosion resistance and minimal reactivity.
Applications in Chemical Equipment
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature reactors, flow tubes, and analytical instruments in chemical processing plants. C-glass, with its enhanced alkali resistance and cost-effectiveness, suits general-purpose chemical containers, tubing, and insulation components where extreme heat resistance is less critical. Both materials are selected based on specific chemical compatibility, thermal requirements, and mechanical durability in chemical equipment applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Silica glass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability but comes at a significantly higher cost and limited availability compared to C-glass. C-glass provides adequate corrosion resistance at a lower price point and is more readily accessible for large-scale chemical equipment applications. Budget constraints and supply chain considerations often make C-glass the preferred choice despite silica glass's enhanced performance characteristics.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Silica glass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and extended lifespan in harsh chemical environments compared to C-glass. C-glass, while more cost-effective, is prone to chemical degradation and frequent surface corrosion, leading to increased maintenance and shorter operational life. Choosing silica glass enhances durability and reduces downtime, making it ideal for long-term chemical equipment applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Silica glass demonstrates superior environmental sustainability compared to C-glass due to its higher thermal stability and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. It is more easily recyclable through processes like re-melting without significant degradation, whereas C-glass contains additives that complicate recycling and increase environmental toxicity. Utilizing silica glass in chemical equipment minimizes ecological footprint and enhances end-of-life material recovery.
Choosing the Right Glass for Chemical Equipment
Silica glass offers exceptional chemical resistance and thermal durability, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments and high-temperature reactions in chemical equipment. C-glass, with good alkali resistance and moderate thermal stability, suits applications requiring cost-effectiveness and resistance to attack by most acids. Selecting the right glass depends on specific chemical exposure, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Infographic: Silica glass vs C-glass for Chemical equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com