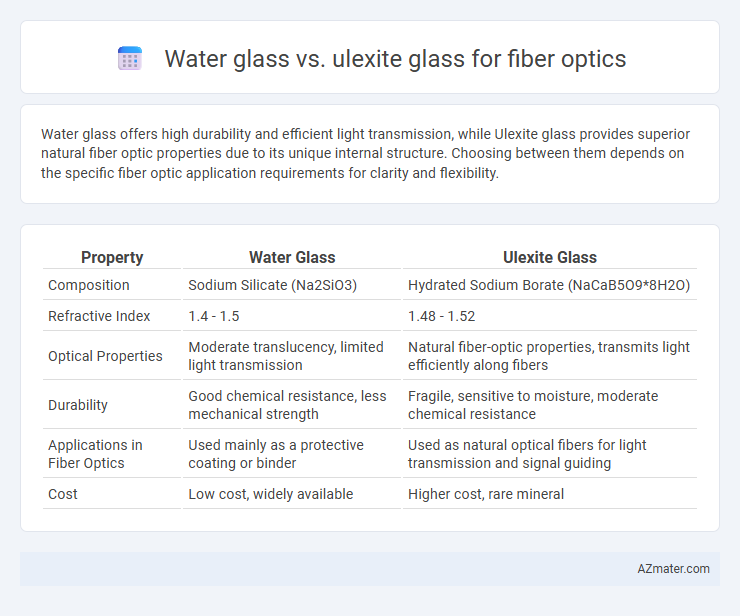
Water glass offers high durability and efficient light transmission, while Ulexite glass provides superior natural fiber optic properties due to its unique internal structure. Choosing between them depends on the specific fiber optic application requirements for clarity and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass | Ulexite Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium Silicate (Na2SiO3) | Hydrated Sodium Borate (NaCaB5O9*8H2O) |
| Refractive Index | 1.4 - 1.5 | 1.48 - 1.52 |
| Optical Properties | Moderate translucency, limited light transmission | Natural fiber-optic properties, transmits light efficiently along fibers |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, less mechanical strength | Fragile, sensitive to moisture, moderate chemical resistance |
| Applications in Fiber Optics | Used mainly as a protective coating or binder | Used as natural optical fibers for light transmission and signal guiding |
| Cost | Low cost, widely available | Higher cost, rare mineral |
Introduction to Fiber Optic Glass Types
Water glass and Ulexite glass are key materials in fiber optic technology, each offering unique properties for light transmission. Water glass, known chemically as sodium silicate, provides cost-effective optical clarity but has limitations in tensile strength and durability compared to Ulexite glass. Ulexite, a naturally occurring borate mineral with inherent fiber optic characteristics, excels in light refraction and internal reflection, making it highly effective for specialized fiber optic applications.
Overview of Water Glass in Fiber Optics
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, serves as a critical bonding and protective agent in fiber optic manufacturing due to its excellent adhesive properties and transparency. Its chemical stability and resistance to moisture make it ideal for creating durable fiber optic components, ensuring signal integrity and long-term performance. Compared to Ulexite glass, water glass offers superior flexibility in forming protective coatings and improving fiber optic cable resilience.
Ulexite Glass: Properties and Origins
Ulexite glass, also known as TV rock, features high natural fiber optic properties due to its unique fibrous crystal structure that channels light effectively. Originating primarily from borate mineral deposits in regions like California and Turkey, ulexite exhibits excellent transparency, low refractive index, and high thermal stability, making it suitable for specialized fiber optic applications. Compared to conventional water glass, ulexite glass offers superior light guidance and durability, crucial for enhancing signal transmission efficiency in fiber optic systems.
Optical Transmission Efficiency Comparison
Water glass and ulexite glass exhibit distinct optical transmission efficiencies crucial for fiber optic applications. Ulexite glass, with its natural fiber-like tubular structures, offers superior light channeling and minimal scattering, resulting in higher transmission efficiency compared to conventional water glass. In contrast, water glass tends to have increased optical losses due to its homogeneous amorphous composition, making ulexite glass a more efficient medium for fiber optic signal transmission.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Water glass exhibits moderate mechanical strength with good resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for certain fiber optic applications requiring durability. Ulexite glass, characterized by enhanced hardness and higher tensile strength, offers superior mechanical stability and long-term durability under stress. Comparative analysis reveals Ulexite glass outperforms water glass in resisting physical wear and maintaining structural integrity in fiber optic systems.
Light Scattering Characteristics
Water glass exhibits low light scattering properties, making it suitable for clear fiber optic transmission with minimal signal loss. Ulexite glass contains natural fibers that cause higher light scattering due to its unique microstructure, resulting in diffused light propagation. For fiber optic applications requiring sharp signal clarity and minimal attenuation, water glass is preferred over ulexite glass.
Cost and Availability Factors
Water glass, or sodium silicate, is widely available and cost-effective for use as a cladding material in fiber optics due to its low price and abundant supply. Ulexite glass, though offering superior natural fiber optic properties, tends to be more expensive and less readily available, limiting its use primarily to specialized or high-performance applications. Cost efficiency and easy procurement make water glass the preferred choice for large-scale fiber optic manufacturing and installation projects.
Application Suitability: Water Glass vs Ulexite Glass
Water glass offers superior durability and thermal resistance, making it ideal for fiber optic applications requiring long-term stability and protection in harsh environments. Ulexite glass features excellent light transmission and natural fiber-optic properties, which enhance signal clarity and minimize loss in optical communication systems. Selecting between water glass and ulexite glass depends on the specific demands for mechanical strength versus optical performance in fiber optic technology.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate, offers eco-friendly benefits due to its abundant natural raw materials and low-energy production process, resulting in reduced carbon emissions. Ulexite glass, containing boron minerals, requires more intensive mining and energy consumption, which can increase environmental degradation and a larger carbon footprint. Fiber optic components using water glass demonstrate greater sustainability through recyclability and lower ecological impact compared to those made from ulexite glass.
Future Trends in Fiber Optic Glass Materials
Future trends in fiber optic glass materials emphasize the advancement of water glass and ulexite glass due to their unique optical properties and environmental resilience. Water glass offers enhanced durability and cost-effectiveness, while ulexite glass provides superior light transmission and natural fiber optic capabilities, making it ideal for high-precision applications. Innovations in doping techniques and hybrid composites are set to improve signal clarity and expand the functionality of these glasses in next-generation fiber optic technologies.
Infographic: Water glass vs Ulexite glass for Fiber optic
 azmater.com
azmater.com