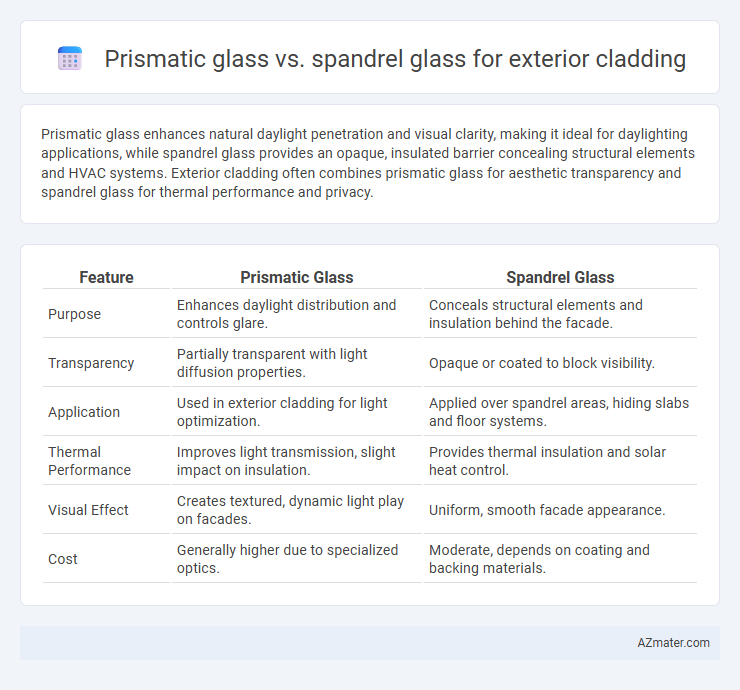
Prismatic glass enhances natural daylight penetration and visual clarity, making it ideal for daylighting applications, while spandrel glass provides an opaque, insulated barrier concealing structural elements and HVAC systems. Exterior cladding often combines prismatic glass for aesthetic transparency and spandrel glass for thermal performance and privacy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Prismatic Glass | Spandrel Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances daylight distribution and controls glare. | Conceals structural elements and insulation behind the facade. |
| Transparency | Partially transparent with light diffusion properties. | Opaque or coated to block visibility. |
| Application | Used in exterior cladding for light optimization. | Applied over spandrel areas, hiding slabs and floor systems. |
| Thermal Performance | Improves light transmission, slight impact on insulation. | Provides thermal insulation and solar heat control. |
| Visual Effect | Creates textured, dynamic light play on facades. | Uniform, smooth facade appearance. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized optics. | Moderate, depends on coating and backing materials. |
Introduction to Exterior Glass Cladding
Exterior glass cladding enhances building aesthetics and performance by using materials such as prismatic glass and spandrel glass, each offering distinct functionality. Prismatic glass optimizes natural light diffusion and energy efficiency through its angular surface design, while spandrel glass conceals structural elements and provides uniform appearance with opaque finishes. Choosing between prismatic and spandrel glass depends on balancing transparency, daylight control, and architectural design requirements for the building facade.
What is Prismatic Glass?
Prismatic glass is a specialized architectural glazing material designed to manipulate light through micro-structured surfaces, enhancing daylight distribution and reducing glare in exterior cladding applications. Unlike spandrel glass, which is typically opaque and used to conceal structural elements, prismatic glass allows natural light diffusion while maintaining privacy and aesthetic appeal. This makes prismatic glass a functional and decorative choice for facade systems seeking energy efficiency and improved visual comfort.
What is Spandrel Glass?
Spandrel glass is an opaque or translucent glass panel used in exterior cladding to conceal structural elements, insulation, and mechanical systems behind a building's facade. Unlike prismatic glass that enhances daylight diffusion and visual aesthetics, spandrel glass primarily serves a functional role in creating a continuous and uniform exterior surface. Its design ensures energy efficiency and maintains the sleek appearance of curtain walls while protecting the building envelope.
Key Differences Between Prismatic and Spandrel Glass
Prismatic glass features a textured surface designed to refract and diffuse light, enhancing natural daylight penetration and reducing glare in building interiors. Spandrel glass is typically opaque or reflective, concealing structural elements and mechanical systems behind the facade while providing a uniform exterior appearance. Unlike prismatic glass, spandrel glass does not contribute to daylighting but serves primarily as an architectural cladding solution for energy efficiency and aesthetic continuity.
Aesthetic Impact: Light and Design Variations
Prismatic glass enhances exterior cladding by creating dynamic visual effects through its unique refraction properties, producing vibrant light patterns and a play of colors that shift with varying sunlight angles. Spandrel glass offers a sleek, uniform appearance that conceals structural elements while providing a consistent opaque surface, ideal for a minimalist and modern facade design. The choice between prismatic and spandrel glass directly influences the aesthetic impact, balancing between kinetic light artistry and streamlined architectural elegance.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Prismatic glass enhances natural daylight penetration while reducing solar heat gain, significantly improving thermal performance and lowering cooling energy demands in exterior cladding applications. Spandrel glass, typically opaque and insulated, offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through building facades, contributing to consistent indoor temperatures and energy savings. Selecting prismatic glass optimizes daylight utilization, whereas spandrel glass prioritizes insulation, making their combined use effective for balanced energy efficiency in building envelopes.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Prismatic glass offers high durability with enhanced impact resistance and better resistance to weathering compared to spandrel glass, which often requires protective coatings to maintain appearance over time. Maintenance for prismatic glass is generally lower due to its surface texture that reduces visible dirt and scratches, while spandrel glass demands more frequent cleaning and coating renewals to prevent fading and surface degradation. Both materials withstand environmental stress well, but prismatic glass provides longer-lasting aesthetics and structural integrity with less upkeep in exterior cladding applications.
Cost Comparison: Prismatic vs Spandrel Glass
Prismatic glass typically costs more than spandrel glass due to its intricate light-diffusing properties and specialized manufacturing process. Spandrel glass, commonly used for concealing building elements like insulation and structural components, offers a more budget-friendly option for exterior cladding. Choosing between the two depends on balancing aesthetic benefits and functional needs against the overall project budget.
Applications in Modern Building Facades
Prismatic glass enhances natural daylighting and glare control, making it ideal for building facades aiming to optimize energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Spandrel glass, often used to conceal structural elements, HVAC systems, and insulation, provides a uniform exterior appearance while maintaining thermal performance. Modern architectural designs frequently combine both materials to balance aesthetics, functionality, and energy performance in exterior cladding systems.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Exterior Cladding
Prismatic glass offers superior light diffusion and energy efficiency, making it ideal for reducing glare and enhancing natural daylight in exterior cladding applications. Spandrel glass provides a smooth, opaque finish that effectively conceals building components while maintaining architectural aesthetics. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing light transmission needs with design requirements and thermal performance for optimal exterior facade functionality.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Spandrel glass for Exterior cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com