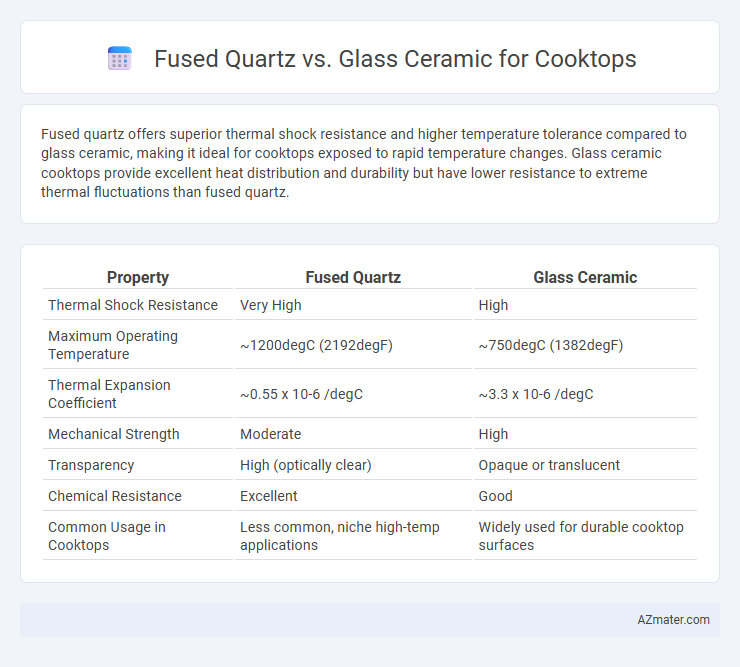
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to glass ceramic, making it ideal for cooktops exposed to rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic cooktops provide excellent heat distribution and durability but have lower resistance to extreme thermal fluctuations than fused quartz.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Very High | High |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | ~1200degC (2192degF) | ~750degC (1382degF) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ~0.55 x 10-6 /degC | ~3.3 x 10-6 /degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Transparency | High (optically clear) | Opaque or translucent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Common Usage in Cooktops | Less common, niche high-temp applications | Widely used for durable cooktop surfaces |
Introduction to Cooktop Surface Materials
Fused quartz and glass ceramic are prominent materials used for cooktop surfaces due to their exceptional thermal resistance and durability. Fused quartz offers superior heat tolerance and minimal thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to cracking under sudden temperature changes. Glass ceramic provides excellent heat distribution, enhanced scratch resistance, and aesthetic versatility, making it a popular choice for contemporary cooktops.
What is Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is a high-purity glass made from nearly 100% silica, known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures without deforming. Compared to glass ceramics, fused quartz offers superior optical clarity and higher resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for precision cooktop surfaces that require durability and heat endurance. Its unique molecular structure ensures minimal thermal expansion, preventing cracks and ensuring long-lasting performance in high-heat cooking environments.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a highly durable, heat-resistant material used in cooktops, composed of crystalline and glassy phases that provide excellent thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Unlike fused quartz, which is primarily pure silica, glass ceramic features a microstructure engineered for uniform heat distribution and resistance to cracking under rapid temperature changes. This makes glass ceramic ideal for cooktop surfaces, offering enhanced performance, safety, and longevity in high-heat cooking environments.
Thermal Properties Comparison
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance with a low coefficient of thermal expansion around 0.5 x 10^-6 /degC, making it highly durable against rapid temperature changes on cooktops. Glass ceramic, with its coefficient of thermal expansion near zero due to the crystalline structure, provides excellent heat resistance and stability, minimizing warping or cracking during high-temperature cooking. Both materials ensure efficient heat distribution, but glass ceramic typically achieves higher thermal insulation, enhancing energy efficiency in cooktop applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Fused quartz offers exceptional durability and superior scratch resistance compared to glass ceramic, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical abrasion in cooktop applications. Glass ceramic, while also durable and able to withstand high temperatures, tends to be more prone to micro-scratches and surface wear over time. The molecular structure of fused quartz provides enhanced hardness and stability, ensuring longer-lasting performance under heavy kitchen use.
Heat Distribution and Efficiency
Fused quartz offers superior heat distribution due to its high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion, ensuring even cooking surfaces and minimal hot spots. Glass ceramic excels in heat retention and energy efficiency, with its ability to heat quickly while maintaining temperature stability, reducing energy consumption during cooking. Both materials provide reliable performance, but fused quartz is preferred for precise heat control, whereas glass ceramic balances efficient heating and durability.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Fused quartz offers superior resistance to thermal shock compared to glass ceramic due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Glass ceramic, while also resistant to thermal shock, typically has a higher thermal expansion rate making it more susceptible to stress under sudden temperature fluctuations. This makes fused quartz a preferred material for cooktops requiring exceptional durability and reliable performance under extreme heating conditions.
Aesthetic Differences
Fused quartz offers a sleek, transparent surface with a natural glossy finish that enhances the modern kitchen aesthetic, while glass ceramic provides a smooth, often matte or semi-glossy appearance available in various colors and patterns for versatile design options. The subtle translucency of fused quartz creates a minimalist, high-end look, contrasting with the more customizable visual appeal of glass ceramic cooktops, which can blend seamlessly with different kitchen styles. Both materials maintain a clean, refined appearance but differ in texture and color flexibility, impacting the overall kitchen ambiance.
Cost and Availability
Fused quartz cooktops generally have higher costs due to their superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making them less common and harder to find in standard retail outlets. Glass ceramic cooktops offer more affordability and widespread availability, benefiting from mass production and established supply chains in kitchen appliance markets. While glass ceramic is the more economical and accessible choice, fused quartz remains preferred for premium applications demanding exceptional heat resilience and durability.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Cooktop
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and high temperature tolerance, making it ideal for cooktops exposed to rapid heat changes and intense cooking conditions. Glass ceramic provides superior durability and even heat distribution, reducing the risk of cracks and enhancing cooking performance for everyday use. Selecting the best material depends on your cooking habits: fused quartz suits professional and high-heat applications, while glass ceramic is preferred for durability and consistent performance in home kitchens.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com