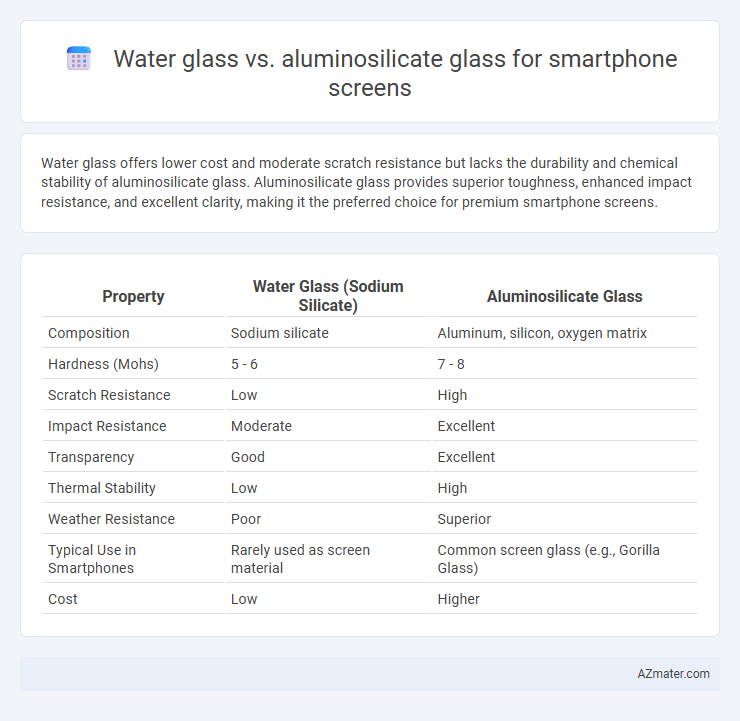
Water glass offers lower cost and moderate scratch resistance but lacks the durability and chemical stability of aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass provides superior toughness, enhanced impact resistance, and excellent clarity, making it the preferred choice for premium smartphone screens.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass (Sodium Silicate) | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate | Aluminum, silicon, oxygen matrix |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 5 - 6 | 7 - 8 |
| Scratch Resistance | Low | High |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Transparency | Good | Excellent |
| Thermal Stability | Low | High |
| Weather Resistance | Poor | Superior |
| Typical Use in Smartphones | Rarely used as screen material | Common screen glass (e.g., Gorilla Glass) |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
Introduction to Smartphone Glass Materials
Smartphone screens predominantly use water glass, a sodium silicate-based glass known for its cost-effectiveness and moderate strength, while aluminosilicate glass offers enhanced durability due to its aluminum and silicon oxide composition. Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior scratch resistance and impact toughness, making it the preferred choice for premium smartphones requiring higher resilience. The distinction primarily lies in chemical composition and resulting mechanical properties, influencing device longevity and user experience.
What is Water Glass?
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is a clear, inorganic compound commonly used as an adhesive or sealant rather than a material for smartphone screens. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, which is chemically strengthened and widely used for durable smartphone displays due to its high scratch resistance and impact strength, water glass lacks the physical properties needed for screen protection. Aluminosilicate glass is favored in the industry for its combination of lightweight, thin design, and superior hardness essential for everyday smartphone durability.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a specialized type of glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, engineered for exceptional strength and durability. It offers superior resistance to scratches, impacts, and thermal stress compared to traditional water glass, making it ideal for smartphone screens. The high alumina content enhances chemical stability, ensuring long-lasting clarity and protective performance in mobile devices.
Mechanical Strength: Water Glass vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength compared to water glass, making it the preferred choice for smartphone screens due to its enhanced scratch resistance and higher tensile strength. Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to impact and abrasion. The aluminosilicate composition incorporates aluminum oxide, significantly improving durability and resistance to fractures under everyday use.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to water glass due to its enhanced chemical composition and reinforcement processes, making it ideal for smartphone screens exposed to daily wear and impact. Water glass, primarily a sodium silicate compound, lacks the structural strength and abrasion resistance found in aluminosilicate variants, resulting in faster surface degradation and vulnerability to scratches. Smartphone screens using aluminosilicate glass benefit from higher hardness ratings and improved resistance to micro-abrasions, prolonging display clarity and overall device longevity.
Optical Clarity and Display Quality
Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate, offers decent optical clarity but often falls short compared to aluminosilicate glass commonly used in smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass features superior transparency and light transmittance, enhancing display brightness and color accuracy for high-resolution screens. Its enhanced durability also maintains optical clarity under stress, providing an overall better display quality experience.
Chemical Resistance and Corrosion
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to water glass, making it highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and environmental pollutants that typically cause corrosion and surface degradation. Water glass, primarily a sodium silicate solution, tends to be more susceptible to chemical attack and may degrade faster when exposed to harsh chemicals or moisture, leading to reduced screen durability. The high alumina content in aluminosilicate glass enhances its structural and chemical stability, providing longer-lasting protection for smartphone screens against corrosion and chemical wear.
Manufacturing Process Differences
The manufacturing process of water glass involves a sol-gel method where sodium silicate solutions are dried and hardened to form a durable, transparent layer, which is simpler and less energy-intensive compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass production requires melting aluminum oxide with silica at temperatures above 1700degC, followed by precision cooling and chemical strengthening through ion exchange to enhance toughness and scratch resistance. These process differences result in water glass being a cost-effective option with moderate durability, whereas aluminosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength and longevity suitable for high-end smartphone screens.
Cost Implications for Smartphone Manufacturers
Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate, offers a lower-cost alternative for smartphone screen protection compared to aluminosilicate glass, which contains aluminum oxide for enhanced durability. Smartphone manufacturers face higher production expenses with aluminosilicate glass due to its complex manufacturing process and superior scratch resistance, which justifies a premium price in high-end devices. Cost implications drive many manufacturers to balance performance and budget by selecting water glass for budget and mid-range smartphones while reserving aluminosilicate glass for flagship models to optimize profitability.
Future Trends in Smartphone Screen Technologies
Water glass, known for its excellent thermal and chemical resistance, offers promising durability enhancements in smartphone screens but faces challenges in flexibility and scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, widely used in current flagship smartphones like Gorilla Glass, provides superior hardness, impact resistance, and thinness, driving its dominance in future foldable and flexible display technologies. Emerging innovations focus on hybrid composites combining water glass's resilience with aluminosilicate's toughness to meet evolving demands for ultra-durable, lightweight, and scratch-proof smartphone screens.
Infographic: Water glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com