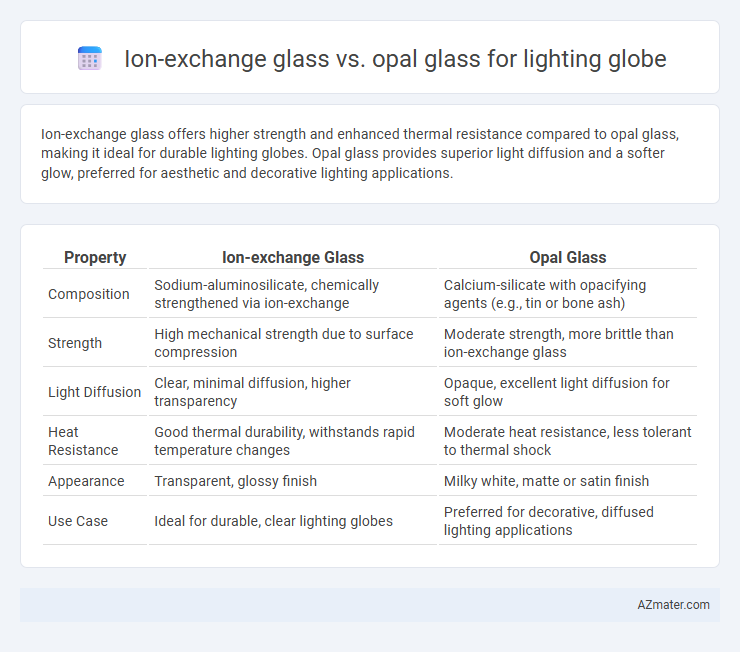
Ion-exchange glass offers higher strength and enhanced thermal resistance compared to opal glass, making it ideal for durable lighting globes. Opal glass provides superior light diffusion and a softer glow, preferred for aesthetic and decorative lighting applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-exchange Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium-aluminosilicate, chemically strengthened via ion-exchange | Calcium-silicate with opacifying agents (e.g., tin or bone ash) |
| Strength | High mechanical strength due to surface compression | Moderate strength, more brittle than ion-exchange glass |
| Light Diffusion | Clear, minimal diffusion, higher transparency | Opaque, excellent light diffusion for soft glow |
| Heat Resistance | Good thermal durability, withstands rapid temperature changes | Moderate heat resistance, less tolerant to thermal shock |
| Appearance | Transparent, glossy finish | Milky white, matte or satin finish |
| Use Case | Ideal for durable, clear lighting globes | Preferred for decorative, diffused lighting applications |
Introduction to Lighting Globe Materials
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it ideal for high-performance lighting globes. Opal glass provides excellent light diffusion and a soft, uniform glow, commonly used to reduce glare in decorative and ambient lighting. Both materials bring distinct advantages in thermal stability and aesthetic appeal, crucial for optimizing lighting efficiency and longevity.
Overview of Ion-Exchange Glass
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced strength and durability by replacing smaller ions in the glass matrix with larger ones, resulting in increased resistance to scratches and thermal stress, which is critical for lighting globes exposed to heat. This glass type provides superior chemical stability and maintains clarity under prolonged use, making it ideal for high-performance lighting applications. Compared to opal glass, ion-exchange glass delivers better mechanical properties and longer service life, supporting energy-efficient lighting solutions.
Overview of Opal Glass
Opal glass offers a diffused, soft white light output, enhancing visual comfort in lighting globes by reducing glare and hotspots. Unlike ion-exchange glass, which emphasizes surface strength through chemical treatment, opal glass is valued for its aesthetic qualities and light-scattering properties. Its uniform translucency makes it ideal for decorative lighting fixtures requiring a smooth, even glow.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Ion-exchange glass for lighting globes undergoes a chemical strengthening process where alkali ions in the glass surface are replaced by larger ions, enhancing durability and scratch resistance without affecting transparency. Opal glass is produced by adding opacifying agents like bone ash or tin oxide during melting, creating a diffused, milky appearance that softens light output but requires more precise temperature control to prevent defects. The ion-exchange method improves mechanical strength post-production, whereas opal glass manufacturing integrates visual properties directly during the glass melting stage.
Optical Performance in Lighting Applications
Ion-exchange glass offers superior optical clarity and enhanced light transmission, making it ideal for high-precision lighting applications where uniform illumination is critical. Opal glass, with its diffused translucency, provides excellent glare reduction and soft light diffusion, creating a more evenly distributed and comfortable light output. The choice between ion-exchange and opal glass depends on whether sharp optical performance or gentle light diffusion is prioritized in the lighting globe design.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior durability and strength compared to opal glass due to the chemical strengthening process that creates a compressive stress layer on the surface, enhancing resistance to scratches and impact. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing with its diffuse light properties, typically shows lower mechanical strength and is more prone to chipping and cracking under stress. The enhanced fracture toughness and surface hardness of ion-exchange glass make it a preferred choice for lighting globes requiring long-term durability and reliable performance in demanding environments.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Ion-exchange glass offers a sleek, uniform surface with enhanced durability and vibrant light diffusion, ideal for modern, minimalist lighting designs. Opal glass provides a soft, diffused glow with a matte, milky appearance that enhances warmth and vintage or classic aesthetics in lighting fixtures. Selecting between ion-exchange and opal glass depends on desired light ambiance and design style, with ion-exchange emphasizing clarity and longevity while opal focuses on softness and traditional appeal.
Energy Efficiency and Light Diffusion
Ion-exchange glass enhances energy efficiency in lighting globes by providing superior surface hardness and durability, which prolongs lifespan and reduces replacement frequency, indirectly saving energy costs. Opal glass excels in light diffusion, offering uniform, soft light distribution that minimizes glare and enhances visual comfort, crucial for creating ambient lighting environments. Combining ion-exchange glass's durability with opal glass's superior diffusion properties results in lighting globes that deliver both long-lasting performance and high-quality illumination.
Cost Implications and Market Availability
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance, commanding a higher price compared to opal glass, which is more affordable but less robust. Opal glass remains widely available in the market due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility in diffusing light evenly. Cost-conscious buyers and mass-market lighting manufacturers tend to prefer opal glass, while premium lighting applications often invest in ion-exchange glass for its superior performance despite the increased expense.
Choosing the Right Globe: Ion-Exchange vs Opal
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced surface durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for lighting globes in high-impact or outdoor environments. Opal glass provides superior light diffusion with a soft, uniform glow that reduces glare, perfect for ambient indoor lighting applications. Selecting the right globe depends on balancing durability needs with desired light quality and distribution.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Opal glass for Lighting globe
 azmater.com
azmater.com