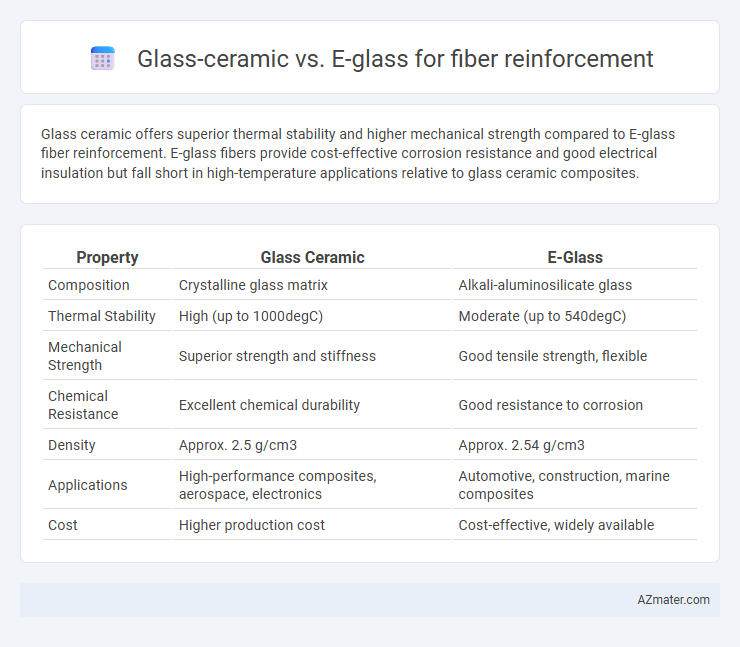
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and higher mechanical strength compared to E-glass fiber reinforcement. E-glass fibers provide cost-effective corrosion resistance and good electrical insulation but fall short in high-temperature applications relative to glass ceramic composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Crystalline glass matrix | Alkali-aluminosilicate glass |
| Thermal Stability | High (up to 1000degC) | Moderate (up to 540degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior strength and stiffness | Good tensile strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical durability | Good resistance to corrosion |
| Density | Approx. 2.5 g/cm3 | Approx. 2.54 g/cm3 |
| Applications | High-performance composites, aerospace, electronics | Automotive, construction, marine composites |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Cost-effective, widely available |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforcement Materials
Fiber reinforcement materials play a critical role in enhancing the mechanical properties of composites, with Glass ceramic and E-glass fibers being prominent choices. Glass ceramic fibers offer superior thermal stability and resistance to high-temperature environments, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability. E-glass fibers, characterized by their excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, are widely used in structural reinforcement across automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
Overview of Glass Ceramics
Glass ceramics are advanced materials formed by controlled crystallization of certain glasses, resulting in a composite structure with both glassy and crystalline phases. These materials exhibit superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to conventional E-glass fibers commonly used in fiber reinforcement. Their unique microstructure provides enhanced durability and dimensional stability, making glass ceramics advantageous for high-performance composite applications requiring enhanced toughness and heat resistance.
Overview of E-Glass Fiber
E-Glass fiber is a type of fiberglass made primarily from alumino-borosilicate glass, widely used in fiber reinforcement due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and electrical insulation properties. It offers high tensile strength, good chemical resistance, and cost-effective performance, making it ideal for composite materials in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. Compared to glass ceramic fibers, E-Glass fibers provide greater flexibility and ease of processing but typically have lower temperature resistance and thermal stability.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Glass ceramic fibers exhibit superior thermal stability and higher modulus of elasticity compared to E-glass fibers, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. E-glass fibers offer excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness but have lower resistance to thermal degradation and chemical corrosion. The difference in composition, with glass ceramics containing controlled crystallinity, enhances fracture toughness and dimensional stability over the amorphous structure of E-glass.
Mechanical Strength: Glass Ceramic vs. E-Glass
Glass ceramic fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to E-glass fibers due to their crystallized microstructure, which enhances stiffness and fracture toughness. E-glass fibers, predominantly composed of alumino-borosilicate glass, offer moderate tensile strength and higher flexibility but typically lower resistance to mechanical wear and thermal degradation. The enhanced mechanical strength of glass ceramic fibers makes them more suitable for high-stress applications requiring exceptional durability and thermal stability.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Glass ceramic fibers exhibit superior thermal stability compared to E-glass fibers, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, whereas E-glass typically degrades above 600degC. This enhanced thermal resistance makes glass ceramic fibers ideal for high-performance applications requiring prolonged exposure to extreme heat. The crystalline microstructure of glass ceramics contributes to improved mechanical performance under thermal stress, surpassing the amorphous nature of E-glass fibers.
Chemical Resistance and Longevity
Glass ceramic fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to E-glass fibers, particularly in harsh alkaline and acidic environments commonly found in industrial applications. The enhanced chemical stability of glass ceramic fibers translates to significantly improved longevity and durability in composite materials exposed to corrosive agents. E-glass fibers, while cost-effective, tend to degrade faster under chemical attack, limiting their lifespan in environments where chemical resistance is critical.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Glass ceramic fibers exhibit superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to E-glass fibers, making them ideal for high-temperature construction applications such as fire-resistant panels and refractory linings. E-glass fibers, known for their cost-effectiveness and high tensile strength, are extensively used in reinforcing concrete, composites, and insulation materials in both construction and industrial sectors. The choice between glass ceramic and E-glass fibers hinges on specific performance requirements, with glass ceramic favored for extreme thermal environments and E-glass preferred for general structural reinforcement.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Glass ceramic fibers offer superior thermal stability and mechanical strength but come at a higher cost and limited availability compared to E-glass fibers. E-glass fibers are widely produced, providing a cost-effective option with consistent quality, making them the preferred choice for large-scale industrial applications. The extensive supply chain and lower material costs of E-glass contribute to its dominant position in the fiber reinforcement market.
Choosing the Right Material for Fiber Reinforcement
Glass ceramic fibers exhibit superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to E-glass, making them ideal for high-temperature and harsh environment applications. E-glass fibers provide excellent cost-effectiveness, high tensile strength, and good electrical insulation, making them suitable for general-purpose composites and structural reinforcements. Selecting the right fiber reinforcement material depends on the specific performance requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints of the intended application.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs E-glass for Fiber reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com