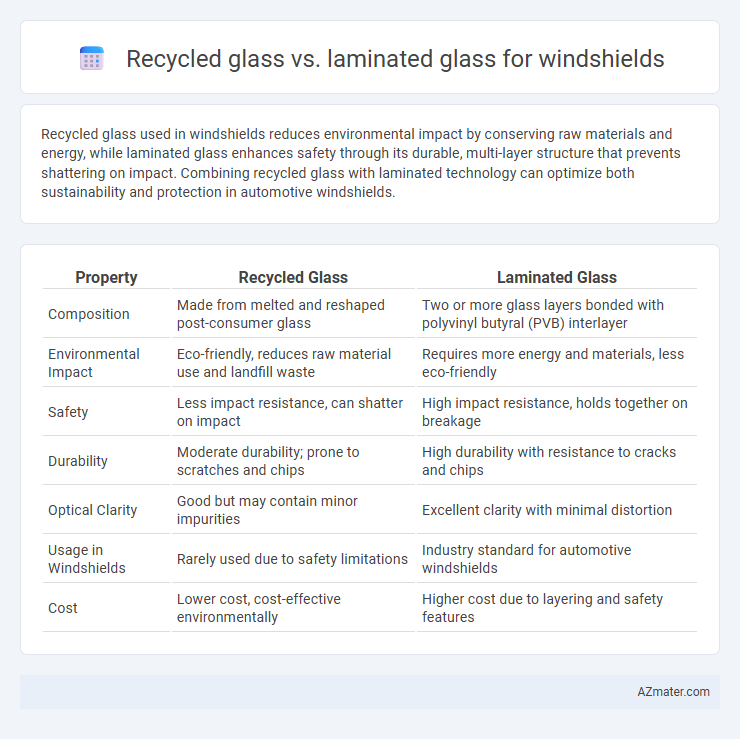
Recycled glass used in windshields reduces environmental impact by conserving raw materials and energy, while laminated glass enhances safety through its durable, multi-layer structure that prevents shattering on impact. Combining recycled glass with laminated technology can optimize both sustainability and protection in automotive windshields.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Made from melted and reshaped post-consumer glass | Two or more glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces raw material use and landfill waste | Requires more energy and materials, less eco-friendly |
| Safety | Less impact resistance, can shatter on impact | High impact resistance, holds together on breakage |
| Durability | Moderate durability; prone to scratches and chips | High durability with resistance to cracks and chips |
| Optical Clarity | Good but may contain minor impurities | Excellent clarity with minimal distortion |
| Usage in Windshields | Rarely used due to safety limitations | Industry standard for automotive windshields |
| Cost | Lower cost, cost-effective environmentally | Higher cost due to layering and safety features |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Types
Windshield glass types primarily include laminated glass and recycled glass, each offering distinct benefits for automotive safety and sustainability. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded by a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced impact resistance and prevents shattering upon collision. Recycled glass, made by repurposing post-consumer glass materials, contributes to environmental conservation while maintaining adequate clarity and durability for windshield applications.
What Is Recycled Glass?
Recycled glass is made from post-consumer or post-industrial glass that has been collected, cleaned, and processed to be reused in manufacturing, including automotive windshields. It offers environmental benefits by reducing raw material consumption and lowering energy use compared to producing new glass. While recycled glass can be used in laminated glass manufacture, ensuring safety and clarity standards requires precise control during the recycling and lamination process.
What Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is a safety glass type composed of two or more glass layers bonded with an inner plastic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the layers together upon impact, preventing shattering. It provides enhanced impact resistance, UV protection, and noise reduction compared to standard glass types, making it ideal for windshields. Recycled glass, on the other hand, refers to glass material reprocessed for environmental benefits but does not inherently offer the layered safety properties found in laminated glass for automotive applications.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Recycled glass windshields utilize crushed, melted cullet integrated with raw materials in the melting furnace, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional methods. Laminated glass manufacturing involves bonding two glass layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer under heat and pressure, ensuring safety and structural integrity. The recycled glass process emphasizes sustainability and cost efficiency, while laminated glass prioritizes durability and impact resistance through its multi-layer assembly.
Strength and Durability
Recycled glass used in windshields offers comparable strength to traditional laminated glass but may exhibit slight variability due to the re-melting and reforming process. Laminated glass, composed of two layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides superior durability and impact resistance, effectively preventing shattering upon impact. The plastic interlayer in laminated glass enhances overall windshield integrity, making it the preferred choice for safety and long-term performance.
Safety Features and Performance
Recycled glass windshields offer environmental benefits but may have variable quality control impacting safety and clarity, whereas laminated glass is engineered with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering. Laminated glass ensures superior durability against collisions and road debris, maintaining structural integrity and occupant protection by holding glass fragments in place. The consistent safety performance of laminated glass makes it the preferred choice for windshields requiring optimal visibility and crash safety compliance.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Recycled glass used in windshields significantly reduces landfill waste and lowers energy consumption during production by up to 40%, minimizing carbon emissions compared to laminated glass made from virgin materials. Laminated glass, while offering enhanced safety features, requires complex chemical bonding processes that increase environmental pollutants and limit recyclability. Opting for recycled glass promotes circular economy principles, drastically decreasing the ecological footprint associated with vehicle manufacturing and disposal.
Cost Considerations
Recycled glass windshields generally offer lower material costs compared to laminated glass, making them a budget-friendly option for vehicle repairs. Laminated glass, known for its strength and safety features, tends to have higher production and replacement expenses due to layers of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) and specialized manufacturing processes. Cost analysis should also consider long-term durability and insurance implications, as laminated glass often reduces replacement frequency and potential damage costs.
Suitability for Automotive Applications
Recycled glass used in automotive windshields offers an eco-friendly solution but may face challenges in meeting strict safety and clarity standards compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior impact resistance, shatter retention, and UV protection, making it highly suitable for vehicle windshields. The automotive industry prioritizes laminated glass for its durability, compliance with safety regulations, and ability to maintain structural integrity during collisions.
Recycled Glass vs Laminated Glass: Final Verdict
Recycled glass offers eco-friendly advantages by reducing raw material consumption and energy use, but laminated glass provides superior safety features, including crack resistance and UV protection essential for windshields. While recycled glass contributes to sustainability, laminated glass remains the preferred choice for automotive windshields due to its structural integrity and impact resilience. The final verdict prioritizes laminated glass for safety performance, with recycled glass playing a supportive role in sustainable glass manufacturing processes.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com