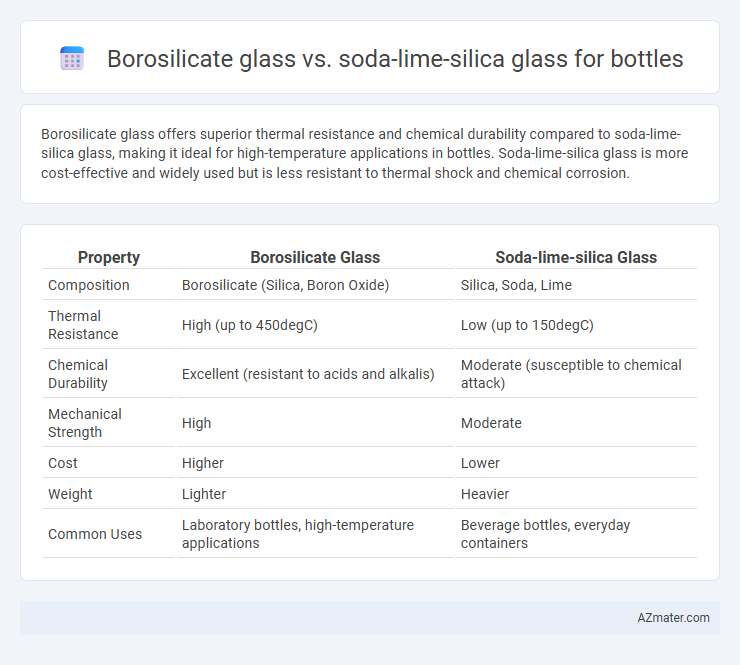
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to soda-lime-silica glass, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in bottles. Soda-lime-silica glass is more cost-effective and widely used but is less resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Soda-lime-silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Borosilicate (Silica, Boron Oxide) | Silica, Soda, Lime |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Low (up to 150degC) |
| Chemical Durability | Excellent (resistant to acids and alkalis) | Moderate (susceptible to chemical attack) |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Common Uses | Laboratory bottles, high-temperature applications | Beverage bottles, everyday containers |
Introduction to Glass Types for Bottling
Borosilicate glass for bottles is highly valued due to its superior thermal resistance, chemical durability, and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications requiring sterilization and exposure to temperature fluctuations. Soda-lime-silica glass, the most common glass type used in bottling, offers cost-effective manufacturing with adequate strength and clarity, suitable for everyday packaging of beverages and consumer goods. Choosing between borosilicate and soda-lime-silica glass depends on the bottle's intended use, balancing performance requirements with production costs.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its superior thermal resistance and durability, composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide. Unlike soda-lime-silica glass, which contains sodium and calcium oxides, borosilicate glass can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for bottles used in scientific and high-heat applications. Its low thermal expansion and chemical stability ensure bottles remain resistant to thermal shock and corrosion over time.
What is Soda-Lime-Silica Glass?
Soda-lime-silica glass is the most common type of glass used in bottle manufacturing, composed primarily of silica (SiO2), soda (Na2O), and lime (CaO). It offers good chemical durability and cost-effectiveness but has lower thermal and chemical resistance compared to borosilicate glass. This type of glass is widely favored for beverage containers due to its ease of production and ability to withstand typical storage conditions without significant degradation.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to soda-lime-silica glass, making it highly resistant to acids, bases, and solvents commonly found in bottle contents. Its low thermal expansion reduces the risk of chemical-induced stress and corrosion, ensuring long-term durability. In contrast, soda-lime-silica glass is more prone to chemical degradation and leaching, which can compromise bottle integrity and safety over time.
Thermal Shock Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Borosilicate glass outperforms soda-lime-silica glass in thermal shock resistance due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion (approximately 3.3 x 10-6 /degC), allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. It tolerates temperatures up to 450degC consistently, making it ideal for applications requiring heat durability, whereas soda-lime-silica glass typically withstands temperatures only up to around 150degC before deforming or shattering. The superior thermal properties of borosilicate make it the preferred choice for bottles used in extreme temperature conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to soda-lime-silica glass, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress in bottle applications. Its low thermal expansion coefficient (approximately 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC) enhances durability, preventing cracks and fractures under rapid temperature changes. In contrast, soda-lime-silica glass, with a higher thermal expansion coefficient (~9 x 10^-6 /degC), is more prone to breakage and less durable under harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Differences in Production and Usage
Borosilicate glass exhibits higher production costs due to its complex manufacturing process and raw materials like boron oxide, making it more expensive than soda-lime-silica glass, which is cheaper and widely used in bottle production for cost efficiency. Despite the higher initial cost, borosilicate glass offers superior thermal and chemical resistance, reducing replacement frequency and overall lifecycle costs in specific applications. Soda-lime-silica glass, while more affordable upfront, may incur higher long-term costs in environments requiring enhanced durability and thermal shock resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to soda-lime-silica glass, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced environmental waste in bottle applications. Soda-lime-silica glass, being the most common glass type, has a well-established, energy-efficient recycling infrastructure, enabling high recyclability rates up to 90%. Despite its durability, borosilicate glass recycling is less widespread due to specialized processing requirements, which can limit its environmental benefits in bottle manufacturing.
Applications in the Beverage and Pharmaceutical Industries
Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal durability, making it ideal for pharmaceutical bottles requiring sterilization and exposure to high temperatures without leaching contaminants. Soda-lime-silica glass, commonly used for beverage bottles, provides cost-effective packaging with adequate strength and clarity for carbonated drinks and water but lacks the thermal stability needed for medical applications. The beverage industry prioritizes soda-lime-silica for mass production and recyclability, while pharmaceuticals depend on borosilicate glass to ensure product safety and integrity under rigorous storage and handling conditions.
Choosing the Right Glass for Bottles: Key Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to soda-lime-silica glass, making it ideal for bottles requiring high temperature tolerance and longevity. Soda-lime-silica glass is more cost-effective and widely available, suitable for standard beverage containers but less resistant to thermal shock. Selecting the right glass depends on factors such as intended use temperature, chemical exposure, budget constraints, and required durability.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Soda-lime-silica glass for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com