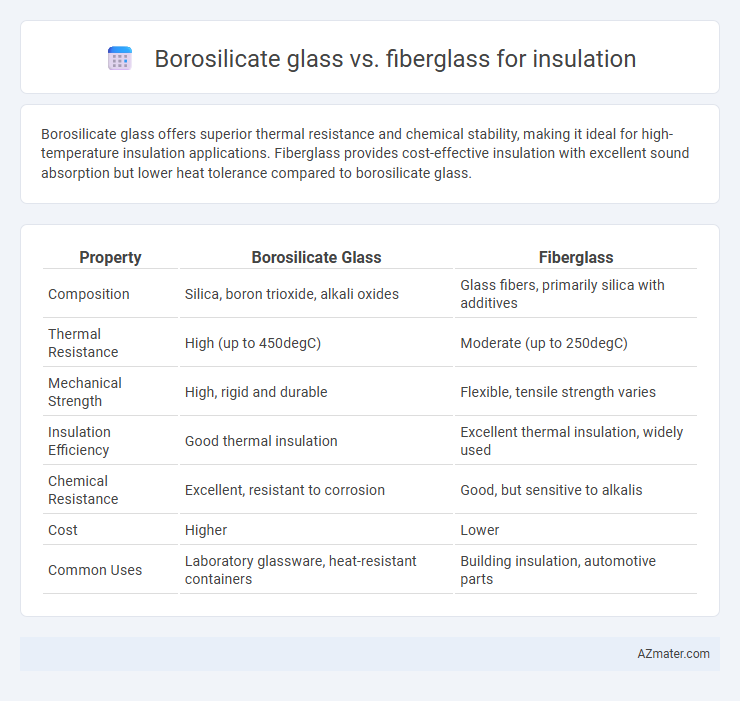
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Fiberglass provides cost-effective insulation with excellent sound absorption but lower heat tolerance compared to borosilicate glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron trioxide, alkali oxides | Glass fibers, primarily silica with additives |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Moderate (up to 250degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | High, rigid and durable | Flexible, tensile strength varies |
| Insulation Efficiency | Good thermal insulation | Excellent thermal insulation, widely used |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to corrosion | Good, but sensitive to alkalis |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses | Laboratory glassware, heat-resistant containers | Building insulation, automotive parts |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Borosilicate glass and fiberglass are both widely used thermal insulation materials known for their high heat resistance and low thermal conductivity. Borosilicate glass is favored in applications requiring chemical durability and thermal stability up to around 500degC, while fiberglass excels in insulation efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and fire resistance across a broad temperature range. These materials play critical roles in reducing heat transfer in industrial, residential, and scientific contexts due to their unique microstructures and thermal properties.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for insulation in high-temperature environments. It is composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, which enhance its durability and chemical resistance compared to regular glass. Unlike fiberglass, which consists of fine glass fibers used mainly for thermal and acoustic insulation, borosilicate glass is often utilized in applications requiring robust thermal stability and strength.
What is Fiberglass Insulation?
Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers woven into a material that traps air, creating an effective thermal barrier commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. Its high resistance to heat flow and sound absorption properties make it a popular choice for energy efficiency and noise reduction. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is engineered for high thermal shock resistance, fiberglass insulation specifically targets thermal performance and ease of installation.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal performance with a low thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 3.3 x 10-6 /degC, enabling excellent resistance to thermal shock and stable insulation properties at high temperatures up to 500degC. Fiberglass insulation typically provides thermal conductivity values ranging from 0.035 to 0.045 W/m*K, effective for general insulation but less resistant to extreme temperature fluctuations compared to borosilicate glass. The enhanced thermal stability and durability of borosilicate glass make it ideal for high-heat and industrial applications, whereas fiberglass remains cost-effective for conventional insulation needs.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to fiberglass, making it highly durable for insulation applications exposed to extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. Its low thermal expansion and high resistance to chemical corrosion contribute to prolonged service life and structural integrity in harsh environments. Fiberglass, while cost-effective and flexible, generally offers lower tensile strength and degrades faster under mechanical fatigue and moisture exposure.
Moisture Resistance and Chemical Stability
Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical stability with high resistance to acids and alkalis, making it ideal for environments exposed to harsh chemicals, while fiberglass provides excellent moisture resistance due to its non-porous structure that prevents water absorption. Borosilicate glass maintains dimensional stability and strength even under thermal cycling, reducing degradation in moist or chemically aggressive conditions. Fiberglass insulation, however, can retain moisture if not properly sealed, potentially compromising its insulating properties and leading to mold growth, unlike borosilicate glass which remains inert and stable.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability with less environmental impact due to its recyclability and longer lifespan compared to fiberglass, which often contains resins and binders that complicate recycling and cause more landfill waste. The production of borosilicate glass involves lower emissions and less energy consumption relative to fiberglass manufacturing, making it a more sustainable choice for insulation applications. Using borosilicate glass insulation reduces greenhouse gas emissions and promotes circular economy principles by enabling material reuse and reducing hazardous waste.
Health and Safety Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior health and safety features compared to fiberglass due to its chemical stability and resistance to thermal shock, reducing the release of harmful particles during use. Unlike fiberglass, which can cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, and requires protective handling due to its fine glass fibers, borosilicate glass insulation is inert and non-toxic, posing minimal health risks. Safety protocols for fiberglass include wearing protective gear to prevent inhalation and contact, whereas borosilicate glass typically requires less stringent precautions, making it a safer choice for insulation applications.
Cost and Installation Factors
Borosilicate glass offers higher temperature resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to fiberglass insulation. Fiberglass insulation provides a more affordable solution with easier and faster installation, requiring less specialized handling. The choice between borosilicate glass and fiberglass depends largely on budget constraints and the specific thermal performance requirements of the project.
Choosing the Right Insulation: Borosilicate Glass vs Fiberglass
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation in industrial applications. Fiberglass insulation provides effective thermal performance with greater flexibility and cost-efficiency, suited for residential and commercial buildings. Selecting between borosilicate glass and fiberglass depends on specific insulation needs such as temperature tolerance, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com