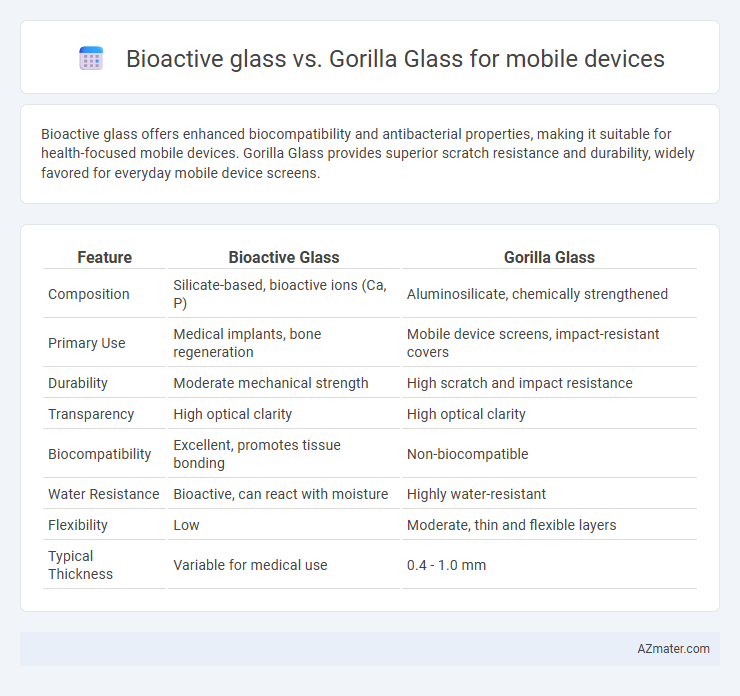
Bioactive glass offers enhanced biocompatibility and antibacterial properties, making it suitable for health-focused mobile devices. Gorilla Glass provides superior scratch resistance and durability, widely favored for everyday mobile device screens.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioactive Glass | Gorilla Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silicate-based, bioactive ions (Ca, P) | Aluminosilicate, chemically strengthened |
| Primary Use | Medical implants, bone regeneration | Mobile device screens, impact-resistant covers |
| Durability | Moderate mechanical strength | High scratch and impact resistance |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | High optical clarity |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, promotes tissue bonding | Non-biocompatible |
| Water Resistance | Bioactive, can react with moisture | Highly water-resistant |
| Flexibility | Low | Moderate, thin and flexible layers |
| Typical Thickness | Variable for medical use | 0.4 - 1.0 mm |
Introduction to Bioactive Glass and Gorilla Glass
Bioactive glass is a type of synthetic material known for its ability to bond with living tissues, primarily used in medical applications such as bone regeneration and dental repair due to its biocompatible and bioactive properties. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass engineered specifically for mobile devices, offering high durability, scratch resistance, and enhanced drop performance. While bioactive glass emphasizes biological integration and healing, Gorilla Glass prioritizes mechanical strength and impact resistance for everyday device protection.
Composition and Structure Differences
Bioactive glass consists primarily of silica, calcium oxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, forming a porous, bioactive network designed to interact with biological tissues. Gorilla Glass is an aluminosilicate glass with a dense, chemically strengthened structure that offers high scratch resistance and durability for mobile device screens. The key difference lies in bioactive glass's ability to bond with biological systems, while Gorilla Glass prioritizes mechanical hardness and impact resistance through ion-exchange strengthening.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Bioactive glass exhibits notable mechanical strength with enhanced fracture toughness and resistance to micro-cracks, making it a promising material for durable mobile devices. Gorilla Glass, engineered from aluminosilicate, offers superior scratch resistance and high impact strength, widely recognized for its robust performance in smartphones. Comparative tests reveal Gorilla Glass typically outperforms bioactive glass in drop and scratch resistance, though bioactive glass shows potential for improved crack healing and longevity under mechanical stress.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Bioactive glass offers enhanced biocompatibility and moderate scratch resistance, making it suitable for medical applications but less ideal for mobile devices. Gorilla Glass, engineered with aluminosilicate, delivers superior scratch resistance and impact durability, often achieving multiple drops without damage. The advanced chemistry and ion-exchange process in Gorilla Glass provide a robust protective layer that significantly outperforms bioactive glass in everyday mobile device use.
Durability in Real-World Usage
Bioactive glass offers enhanced antimicrobial properties and can partially repair minor surface damage, improving screen longevity in environments prone to bacteria and scratches. Gorilla Glass, engineered by Corning, is renowned for its high resistance to impact, scratches, and everyday wear, making it a preferred choice for durable mobile device screens. Real-world usage demonstrates that Gorilla Glass excels in impact durability, while bioactive glass adds value through self-healing and hygiene benefits, with durability depending on specific device requirements.
Chemical Resistance and Safety
Bioactive glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Gorilla Glass due to its unique composition that resists corrosion and biodegradation, enhancing the longevity of mobile devices in harsh environments. Gorilla Glass, while chemically resistant to common acids and alkalis, primarily prioritizes scratch and impact resistance, making it less effective against prolonged chemical exposure. In terms of safety, bioactive glass offers biocompatibility and potential antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of bacterial contamination on device surfaces, whereas Gorilla Glass focuses on shatter resistance to prevent injury from glass breakage.
Biocompatibility and Health Considerations
Bioactive glass exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to Gorilla Glass, as it actively interacts with biological tissues to promote healing and reduce inflammation, making it ideal for wearable mobile devices in health monitoring. Gorilla Glass, while offering exceptional scratch resistance and durability, lacks bioactive properties and does not support tissue integration or reduce irritation upon prolonged skin contact. Health considerations favor bioactive glass in applications requiring direct skin interface, whereas Gorilla Glass remains optimal for general device protection without biological interaction.
Applications in Modern Mobile Devices
Bioactive glass in mobile devices enhances antimicrobial properties and promotes skin health through ion release, making it ideal for wearable technology and health monitoring screens. Gorilla Glass is engineered for superior scratch resistance and impact durability, ensuring longevity and protection for smartphone displays and rugged devices. Combining bioactive glass with Gorilla Glass technologies pushes innovation in mobile device applications by integrating durability with health-oriented functionality.
Cost and Manufacturing Implications
Bioactive glass offers enhanced biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties but involves higher production costs and complex manufacturing processes compared to Gorilla Glass, which benefits from established large-scale production and lower costs. Gorilla Glass is optimized for durability and scratch resistance with efficient chemical strengthening techniques, making it economically viable for mass-market mobile devices. Transitioning to bioactive glass would require significant investment in specialized fabrication technologies and supply chain adjustments, impacting overall manufacturing scalability and product pricing.
Future Trends in Mobile Glass Technology
Bioactive glass offers potential advancements in mobile device durability by promoting self-healing properties and enhanced antimicrobial effects, contrasting with Gorilla Glass's established chemical strengthening and scratch resistance. Future trends in mobile glass technology are likely to integrate bioactive materials to improve device longevity and user hygiene, while maintaining the high transparency and toughness characteristic of Gorilla Glass. Innovations may include hybrid composites combining bioactive glass and Gorilla Glass, enabling smartphones to withstand physical damage and environmental factors more effectively.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Gorilla glass for Mobile device
 azmater.com
azmater.com