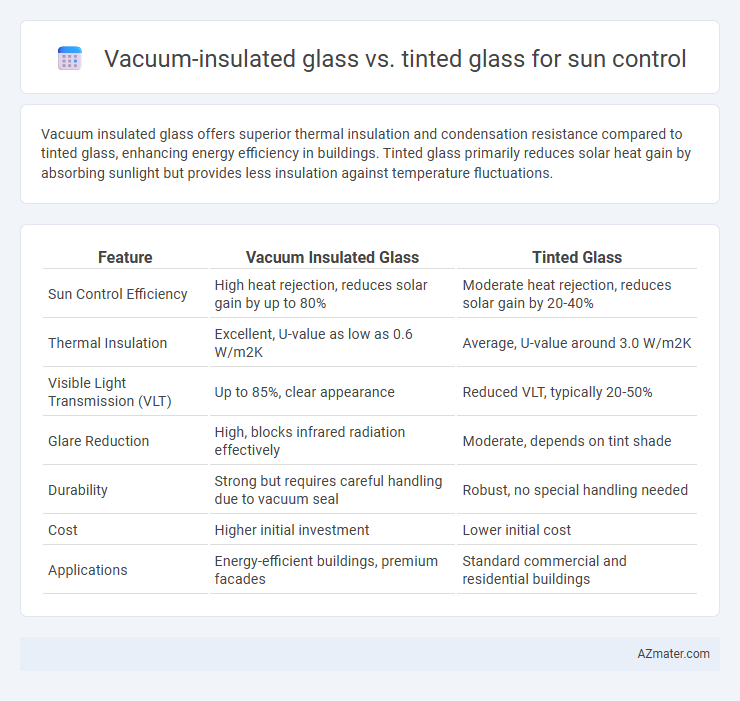
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance compared to tinted glass, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain by absorbing sunlight but provides less insulation against temperature fluctuations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Sun Control Efficiency | High heat rejection, reduces solar gain by up to 80% | Moderate heat rejection, reduces solar gain by 20-40% |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, U-value as low as 0.6 W/m2K | Average, U-value around 3.0 W/m2K |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | Up to 85%, clear appearance | Reduced VLT, typically 20-50% |
| Glare Reduction | High, blocks infrared radiation effectively | Moderate, depends on tint shade |
| Durability | Strong but requires careful handling due to vacuum seal | Robust, no special handling needed |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial cost |
| Applications | Energy-efficient buildings, premium facades | Standard commercial and residential buildings |
Introduction to Sun Control Glass Solutions
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by creating a vacuum layer that minimizes heat transfer, making it highly effective for sun control in buildings. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting a portion of sunlight, providing glare reduction and improved energy efficiency. Both solutions contribute to enhanced indoor comfort and energy savings, with vacuum insulated glass emphasizing insulation performance and tinted glass focusing on solar control.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG)?
Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) consists of two panes of glass separated by a vacuum layer, significantly reducing heat transfer through conduction and convection. Unlike tinted glass that absorbs and reduces solar heat gain by coloring, VIG maintains natural light while providing superior thermal insulation and minimizing heat loss. This advanced technology enhances energy efficiency in buildings by reducing the demand for cooling and heating systems without compromising visibility.
Understanding Tinted Glass for Sun Control
Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting specific wavelengths of sunlight, effectively lowering indoor temperatures and enhancing energy efficiency. It provides glare reduction and UV protection while maintaining visibility, making it a practical choice for sun control in residential and commercial buildings. When compared to vacuum insulated glass, tinted glass offers immediate solar heat management without significant insulation benefits or higher energy efficiency ratings.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass outperforms tinted glass in thermal performance by significantly reducing heat transfer due to its near-complete insulation provided by a vacuum layer between glass panes. Tinted glass lowers solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting sunlight but often compromises visible light transmission and can lead to higher heat loss in colder environments. For energy-efficient sun control, vacuum insulated glass delivers superior insulating properties, maintaining indoor temperature stability with lower reliance on HVAC systems.
Solar Heat Gain Reduction: VIG vs Tinted Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) significantly outperforms tinted glass in solar heat gain reduction by creating an insulating air gap that minimizes heat transfer through conduction and convection, achieving solar heat gain coefficients (SHGC) as low as 0.20. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, with SHGC values typically ranging from 0.30 to 0.50, but can cause reduced visible light transmission. VIG offers superior thermal performance and daylighting benefits without compromising visibility, making it a more effective choice for energy-efficient sun control.
Light Transmission and Visual Comfort
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior sun control by significantly reducing heat transfer while maintaining high visible light transmission, enhancing daylight without compromising energy efficiency. Tinted glass lowers solar heat gain by absorbing sunlight, but often decreases visible light transmission, potentially reducing indoor brightness and visual comfort. For optimal light transmission and visual comfort, vacuum insulated glass provides a clearer view and more consistent daylight levels compared to the darker appearance of tinted glass.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer through its double-pane vacuum layer, significantly reducing HVAC costs compared to traditional tinted glass. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain by absorbing or reflecting sunlight, lowering cooling loads but often less effectively than vacuum insulated options. Despite higher upfront costs, vacuum insulated glass delivers greater long-term savings by enhancing thermal insulation and reducing energy consumption in both heating and cooling seasons.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability due to its robust sealed airspace that resists moisture and thermal stress, reducing fogging and structural degradation over time. Tinted glass, while effective at sun control by absorbing and reducing solar heat, may experience fading, scratches, and surface degradation with prolonged exposure to UV rays, requiring more frequent cleaning and potential replacement. Maintenance for vacuum insulated glass is minimal, mostly limited to cleaning the exterior surfaces, whereas tinted glass demands careful upkeep to preserve its tint and prevent surface damage.
Aesthetic Impact on Building Design
Vacuum insulated glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with minimal visible framing, enhancing building design through its clarity and slim profile while providing superior thermal insulation. Tinted glass contributes to sun control with varied color options that influence the building's exterior appearance, creating distinctive visual effects but often compromising natural light transmission. Designers weigh the clean, unobtrusive look of vacuum insulated glass against the dynamic, stylistic possibilities presented by tinted glass when optimizing both sun control and aesthetic impact.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by reducing heat transfer through its airtight space, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings in extreme climates. Tinted glass controls solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, reducing glare and cooling costs in sunny environments. Choosing the right glass depends on climate conditions, energy efficiency goals, and specific sun control requirements for optimal comfort and cost savings.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Tinted glass for Sun control
 azmater.com
azmater.com