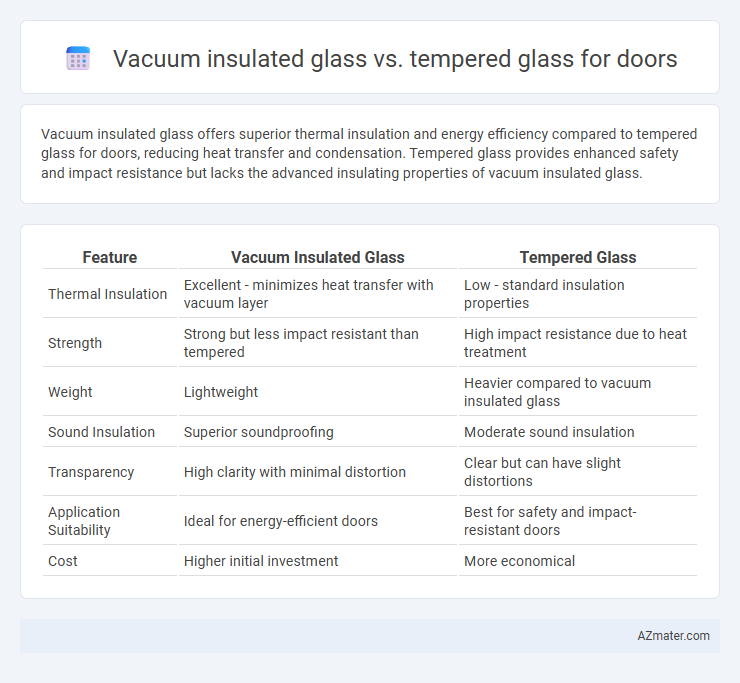
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to tempered glass for doors, reducing heat transfer and condensation. Tempered glass provides enhanced safety and impact resistance but lacks the advanced insulating properties of vacuum insulated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent - minimizes heat transfer with vacuum layer | Low - standard insulation properties |
| Strength | Strong but less impact resistant than tempered | High impact resistance due to heat treatment |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier compared to vacuum insulated glass |
| Sound Insulation | Superior soundproofing | Moderate sound insulation |
| Transparency | High clarity with minimal distortion | Clear but can have slight distortions |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for energy-efficient doors | Best for safety and impact-resistant doors |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | More economical |
Introduction to Vacuum Insulated Glass and Tempered Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum space, significantly reducing heat transfer and enhancing thermal insulation for doors. Tempered glass undergoes a heating and rapid cooling process, increasing its strength and making it resistant to impact and thermal stress. Both materials improve door performance, with VIG excelling in energy efficiency and tempered glass offering superior safety and durability.
How Vacuum Insulated Glass Works
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) for doors utilizes a vacuum layer between two glass panes to eliminate heat transfer by conduction and convection, significantly enhancing thermal insulation compared to standard tempered glass. This vacuum space acts as an ultra-efficient barrier against heat loss or gain, improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Tempered glass, while stronger and more impact-resistant due to its heat treatment, lacks the insulating vacuum layer that makes VIG superior for thermal performance in door applications.
Understanding Tempered Glass Technology
Tempered glass is produced through a controlled thermal or chemical treatment process that increases its strength by inducing compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses inside, making it up to five times stronger than regular glass. This technology ensures that when broken, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, significantly reducing the risk of injury, which is essential for door safety and durability. In contrast, vacuum insulated glass primarily focuses on thermal insulation by creating a vacuum space between glass panes, but it does not enhance impact resistance or safety features like tempered glass.
Thermal Insulation: Comparing Performance
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation compared to tempered glass due to its airless gap that significantly reduces heat transfer and minimizes energy loss. Tempered glass, while strong and impact-resistant, does not provide the same level of insulation since it contains an air-filled space that allows heat conduction. For door applications requiring enhanced energy efficiency and temperature control, vacuum insulated glass is the optimal choice.
Energy Efficiency: Which Glass Saves More?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) significantly outperforms tempered glass in energy efficiency due to its superior thermal insulation properties, reducing heat transfer by minimizing conduction and convection inside the glass layers. The vacuum layer between the glass panes in VIG effectively curtails energy loss, whereas tempered glass, though stronger and more impact-resistant, offers limited thermal resistance. Choosing vacuum insulated glass for doors results in lower heating and cooling costs and enhanced indoor comfort by maintaining stable indoor temperatures more effectively than tempered glass.
Safety and Security: Strength Differences
Vacuum insulated glass offers enhanced strength and shatter resistance compared to standard tempered glass, significantly improving safety and security for doors. Its multi-layer construction with a vacuum seal provides better impact resistance and thermal insulation, reducing the risk of break-ins and accidental damage. Tempered glass, while strong and designed to break into small, less harmful pieces, does not match the structural robustness and intrusion deterrence of vacuum insulated glass.
Sound Insulation: Noise Reduction Capabilities
Vacuum insulated glass significantly outperforms tempered glass in sound insulation, providing superior noise reduction due to the vacuum layer that eliminates air gaps, which are primary channels for sound transmission. This technology can reduce noise levels by up to 30 decibels, making it ideal for doors in noisy environments or urban settings. Tempered glass, while strong and resistant to impact, lacks the airtight vacuum space and therefore offers less effective soundproofing compared to vacuum insulated glass.
Aesthetic and Design Possibilities for Doors
Vacuum insulated glass offers sleek, minimalist aesthetics with its ultra-thin profile and high transparency, enabling modern door designs that maximize natural light while maintaining excellent thermal insulation. Tempered glass provides versatile design options through its strength and safety, allowing for larger, frameless door panels with decorative textures, tints, or patterns without compromising durability. Integrating vacuum insulated glass enhances energy-efficient visual appeal, whereas tempered glass empowers bold structural creativity in door designs.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) typically incurs higher initial installation costs compared to tempered glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized framing requirements. Maintenance expenses for VIG are generally lower, as its enhanced insulation properties reduce energy consumption and minimize condensation-related repairs. Tempered glass offers a more affordable upfront investment but may lead to increased long-term costs from higher heat transfer and potential damage vulnerability.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Door Needs
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for exterior doors in extreme climates. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety, shattering into small, less harmful pieces upon impact, which is essential for high-traffic or security-sensitive doors. Selecting the best glass depends on your priorities: opt for vacuum insulated glass for energy savings and noise reduction or tempered glass for maximum safety and durability.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com