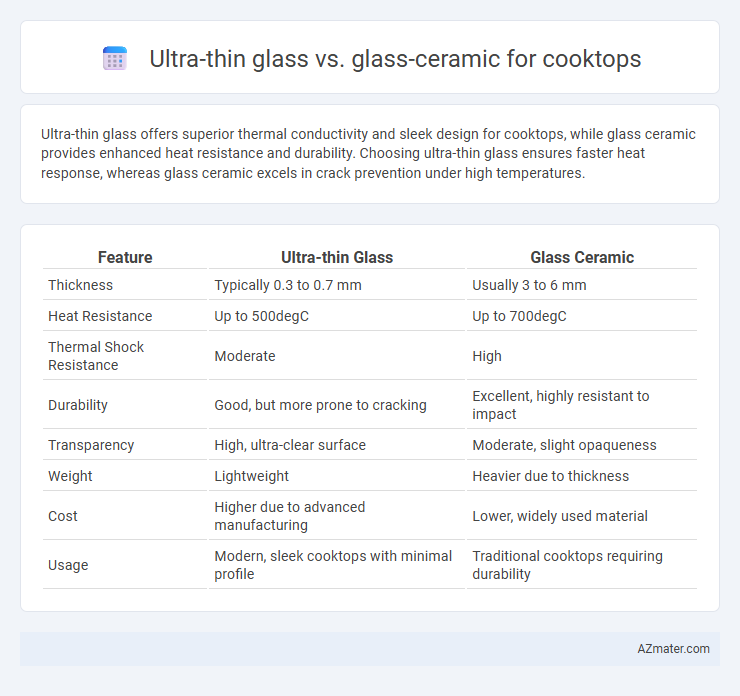
Ultra-thin glass offers superior thermal conductivity and sleek design for cooktops, while glass ceramic provides enhanced heat resistance and durability. Choosing ultra-thin glass ensures faster heat response, whereas glass ceramic excels in crack prevention under high temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-thin Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 0.3 to 0.7 mm | Usually 3 to 6 mm |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 500degC | Up to 700degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Good, but more prone to cracking | Excellent, highly resistant to impact |
| Transparency | High, ultra-clear surface | Moderate, slight opaqueness |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to thickness |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing | Lower, widely used material |
| Usage | Modern, sleek cooktops with minimal profile | Traditional cooktops requiring durability |
Introduction to Cooktop Surface Materials
Ultra-thin glass and glass ceramic are both popular materials used in modern cooktop surfaces, valued for their durability and heat resistance. Ultra-thin glass offers a sleek, lightweight profile with excellent clarity and rapid heat conduction, making it ideal for energy-efficient cooktops. Glass ceramic, on the other hand, combines heat tolerance with thermal shock resistance, supporting even heat distribution and minimizing the risk of cracking under high temperatures.
What is Ultra-thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass, typically measuring less than 0.5 mm in thickness, serves as a lightweight and highly durable surface for cooktops, offering superior thermal shock resistance and enhanced scratch resistance compared to traditional glass ceramic. Unlike glass ceramic, ultra-thin glass utilizes advanced alkali-aluminosilicate compositions that provide excellent transparency and strength, enabling sleek, modern cooktop designs without compromising performance. This innovative material supports rapid heat transfer and easy cleaning, making it a preferred choice for contemporary kitchen appliances.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a specialized material composed of both glass and crystalline phases, offering exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength ideal for cooktop surfaces. Unlike ultra-thin glass, glass ceramic withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it safer and more durable for high-heat cooking environments. Its smooth, non-porous surface also resists stains and scratches, ensuring long-lasting performance and easy maintenance.
Heat Resistance: Ultra-thin Glass vs Glass Ceramic
Ultra-thin glass offers moderate heat resistance with rapid temperature changes but is more prone to thermal shock compared to glass ceramic, which excels in enduring high heat and thermal cycling without cracking. Glass ceramic cooktops withstand temperatures up to 800degC (1472degF), making them ideal for intense cooking environments, whereas ultra-thin glass typically tolerates lower maximum temperatures around 500degC (932degF). The superior thermal stability of glass ceramic ensures longer durability and safer performance during prolonged exposure to extreme heat.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers excellent scratch resistance due to its highly polished surface but may be more prone to cracking under impact compared to thicker materials. Glass ceramic cooktops excel in durability, with a unique crystalline structure that provides superior resistance to thermal shock and heavy impacts. While both materials resist scratches effectively, glass ceramic typically outperforms ultra-thin glass in long-term durability and heat tolerance for cooktop applications.
Appearance and Design Flexibility
Ultra-thin glass offers a sleek, smooth surface with a modern, minimalist aesthetic that enhances the kitchen's overall design, while glass ceramic boasts a versatile, heat-resistant finish that can incorporate customized patterns or colors for a more tailored look. Glass ceramic cooktops provide greater design flexibility due to their ability to integrate various textures and finishes without compromising durability, unlike ultra-thin glass which emphasizes a uniform, polished appearance. Both materials maintain high clarity and reflectivity, but glass ceramic's multi-layer structure allows designers to innovate with embedded heating elements and visual effects more effectively.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Ultra-thin glass cooktops feature a smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and allows for effortless wiping, making cleaning quick and straightforward. Glass ceramic cooktops, while also smooth and resistant to spills, require careful use of specialized cleaners to avoid scratches and discoloration, slightly increasing maintenance effort. Both materials prevent the accumulation of grime effectively, but ultra-thin glass generally offers superior ease of cleaning due to its enhanced durability and minimal surface texture.
Cost Analysis
Ultra-thin glass cooktops generally offer a lower upfront cost due to reduced material usage and simpler manufacturing processes compared to glass ceramic options. Glass ceramic cooktops, while more expensive initially, provide better heat resistance and durability, potentially reducing replacement frequency and long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total ownership expenses, including energy efficiency and lifespan, is crucial for an accurate cost analysis between ultra-thin glass and glass ceramic cooktops.
Energy Efficiency and Cooking Performance
Ultra-thin glass cooktops offer rapid heat conduction and enhanced responsiveness, improving cooking precision and energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss. Glass ceramic cooktops provide superior thermal resistance and even heat distribution, maintaining stable cooking temperatures and reducing energy consumption over prolonged use. Both materials support efficient induction heating, but ultra-thin glass excels in quick heat transfer, while glass ceramic ensures consistent performance with durability.
Which Material is Best for Your Cooktop?
Ultra-thin glass offers superior heat conduction and a sleek, modern aesthetic, making it ideal for efficient, precise cooking and easy cleaning. Glass ceramic excels in durability and thermal shock resistance, maintaining stability under rapid temperature changes and heavy cookware use. Selecting the best material depends on your priorities: choose ultra-thin glass for style and responsiveness, or glass ceramic for long-lasting toughness and reliability.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com