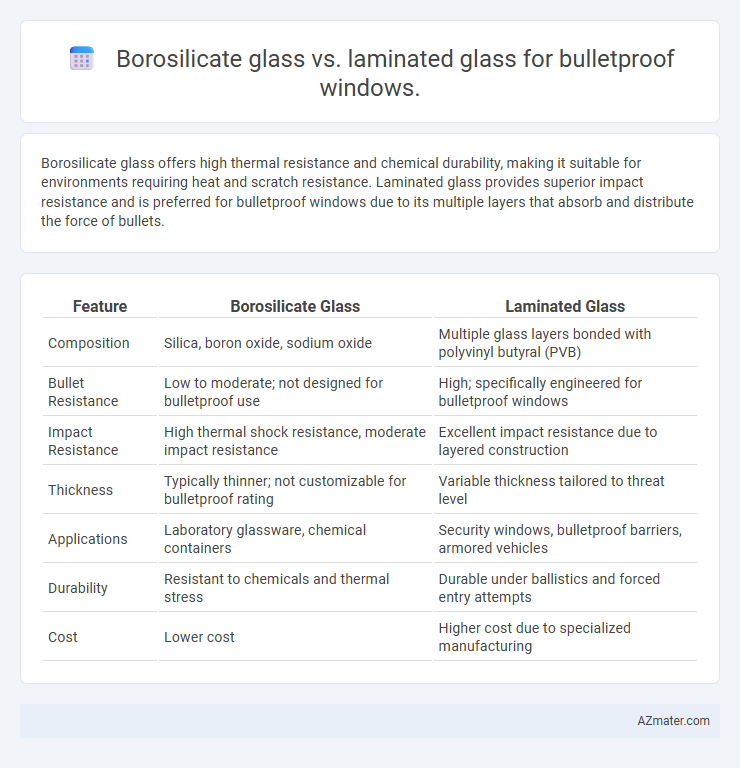
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it suitable for environments requiring heat and scratch resistance. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and is preferred for bulletproof windows due to its multiple layers that absorb and distribute the force of bullets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron oxide, sodium oxide | Multiple glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) |
| Bullet Resistance | Low to moderate; not designed for bulletproof use | High; specifically engineered for bulletproof windows |
| Impact Resistance | High thermal shock resistance, moderate impact resistance | Excellent impact resistance due to layered construction |
| Thickness | Typically thinner; not customizable for bulletproof rating | Variable thickness tailored to threat level |
| Applications | Laboratory glassware, chemical containers | Security windows, bulletproof barriers, armored vehicles |
| Durability | Resistant to chemicals and thermal stress | Durable under ballistics and forced entry attempts |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Bulletproof Windows
Bulletproof windows utilize advanced materials to provide protection against ballistic threats. Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and chemical durability but requires lamination with polycarbonate layers to enhance impact resistance for bulletproof applications. Laminated glass, composed of multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers like polyvinyl butyral (PVB), achieves superior ballistic performance by absorbing and dispersing the energy from projectiles effectively.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of high-strength glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability, making it an ideal material for bulletproof windows. Unlike laminated glass, which is composed of multiple layers of glass and interlayer materials designed to hold shards together upon impact, borosilicate glass offers superior resistance to heat and chemical corrosion while maintaining high optical clarity. Its unique composition enhances its ability to withstand high-velocity impacts, providing effective protection in ballistic applications.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass for bulletproof windows consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering upon high-velocity impacts. Unlike borosilicate glass, known for thermal resistance and chemical stability, laminated glass prioritizes safety by absorbing and dispersing bullet energy, maintaining structural integrity. This makes laminated glass a preferred choice for bulletproof applications due to its ability to hold layers together even when broken, reducing the risk of penetration and injury.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Borosilicate glass features a high silica and boron oxide composition, offering enhanced thermal resistance and chemical durability, while laminated glass consists of multiple layers of glass bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers to absorb and disperse energy. Manufacturing borosilicate glass involves melting raw materials at high temperatures followed by controlled cooling, whereas laminated glass production combines glass sheets and polymer layers through heat and pressure lamination. These compositional and manufacturing differences impact the materials' ability to withstand ballistic impact, with laminated glass providing multi-layered resistance and borosilicate glass enhancing structural integrity under extreme conditions.
Impact Resistance: Borosilicate vs Laminated Glass
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and moderate impact strength but lacks the layered structure necessary for effective bullet resistance. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded with interlayers like polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing superior impact resistance by absorbing and distributing the force of a bullet, preventing penetration and shattering. For bulletproof window applications, laminated glass significantly outperforms borosilicate glass in impact resistance and energy absorption.
Transparency and Visual Clarity Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical durability and thermal resistance but typically has slightly lower transparency compared to laminated glass, which provides enhanced optical clarity due to its multilayer structure that reduces distortion. Laminated glass for bulletproof windows often incorporates heat-treated layers and PVB interlayers that maintain high light transmittance, resulting in clearer and more consistent visibility under various lighting conditions. The visual clarity of laminated bulletproof glass generally surpasses that of borosilicate, making it preferable for applications requiring unobstructed sightlines and minimal optical aberrations.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability with relatively lower weight compared to laminated glass, making it a preferred choice for bulletproof windows requiring thinner and lighter protection. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers of glass and interlayers, tends to be thicker and heavier, offering enhanced impact resistance but adding significant weight to the structure. When prioritizing weight and thickness for bulletproof windows, borosilicate glass provides a more compact solution, while laminated glass ensures greater mass and layered strength for higher levels of ballistic protection.
Cost and Availability
Borosilicate glass offers moderate bullet resistance at a lower cost and is widely available for various construction applications. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with interlayers, provides superior bulletproof protection but comes at a higher price and may require custom orders, affecting availability. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and the level of security required for the bulletproof window installation.
Applications in Security and Architecture
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it suitable for bulletproof windows in security applications requiring heat exposure, such as labs and armored vehicles. Laminated glass, consisting of multiple layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB), provides superior impact resistance and shatterproof qualities essential in architectural security for banks, government buildings, and storefronts. Security applications prioritize laminated glass for its ability to absorb and disperse bullet energy, while borosilicate glass is favored in environments demanding both bullet resistance and thermal stability.
Choosing the Right Glass for Bulletproof Windows
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability for bulletproof windows but is generally less effective at stopping high-velocity projectiles compared to laminated glass, which combines multiple layers of glass and polyvinyl butyral (PVB) to absorb and dissipate impact energy. Laminated glass provides enhanced bullet resistance through its multi-layered structure, making it the preferred choice for security applications requiring certified ballistic protection levels, such as UL 752 standards. When choosing the right glass for bulletproof windows, it is crucial to balance impact resistance, weight, and clarity according to the specific ballistic threat level and environmental conditions.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Laminated glass for Bulletproof window
 azmater.com
azmater.com