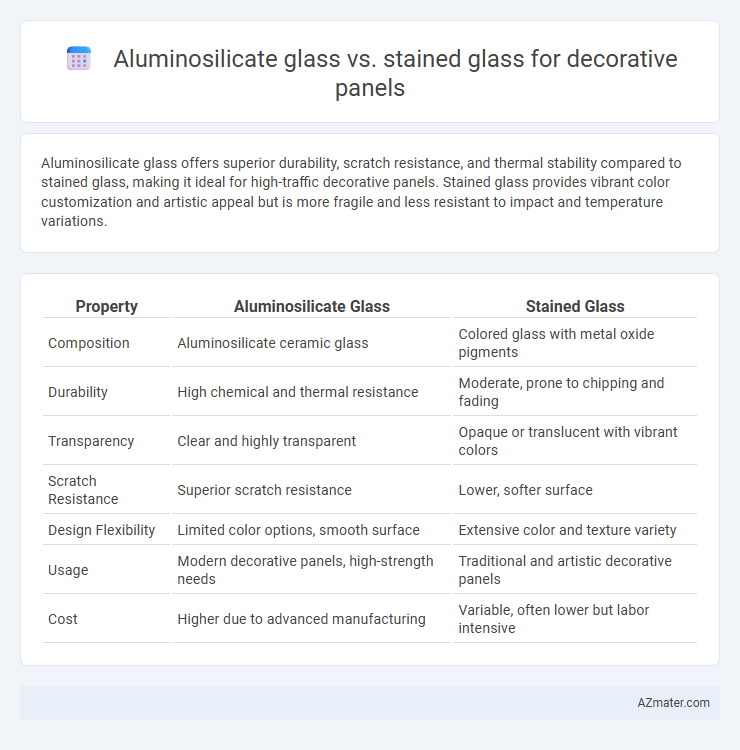
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability, scratch resistance, and thermal stability compared to stained glass, making it ideal for high-traffic decorative panels. Stained glass provides vibrant color customization and artistic appeal but is more fragile and less resistant to impact and temperature variations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Stained Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate ceramic glass | Colored glass with metal oxide pigments |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal resistance | Moderate, prone to chipping and fading |
| Transparency | Clear and highly transparent | Opaque or translucent with vibrant colors |
| Scratch Resistance | Superior scratch resistance | Lower, softer surface |
| Design Flexibility | Limited color options, smooth surface | Extensive color and texture variety |
| Usage | Modern decorative panels, high-strength needs | Traditional and artistic decorative panels |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing | Variable, often lower but labor intensive |
Introduction to Aluminosilicate Glass and Stained Glass
Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high strength, thermal resistance, and durability, is widely used in decorative panels requiring enhanced toughness and clarity. Stained glass, characterized by its vibrant colors and artistic patterns created through the inclusion of metallic salts and hand-painting techniques, adds a traditional aesthetic value to interiors. While aluminosilicate glass offers modern performance benefits, stained glass provides timeless artistic expression for decorative applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Aluminosilicate glass consists primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offering superior thermal and chemical resistance, while stained glass is composed of silica with various metal oxides that provide vibrant colors. The manufacturing of aluminosilicate glass involves high-temperature melting and rapid cooling techniques like fusion draws or float glass methods to achieve strength, whereas stained glass is traditionally handcrafted through cutting, painting, and kiln-firing to embed pigments and designs. These differences in composition and production result in aluminosilicate glass being more durable and heat-resistant, suitable for modern architectural panels, while stained glass emphasizes artistic expression through customizable coloration and intricate patterns.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and durability compared to stained glass, exhibiting higher resistance to impact and thermal stress due to its robust chemical composition and manufacturing process. Stained glass, primarily composed of silica with added metal oxides for color, tends to be more fragile and susceptible to cracking under mechanical pressure or rapid temperature changes. The enhanced toughness of aluminosilicate glass makes it ideal for decorative panels in high-traffic or outdoor environments, where long-term structural integrity is crucial.
Optical Clarity and Visual Effects
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity with minimal distortion and high light transmission, making it ideal for decorative panels where sharp, vibrant visuals are essential. Stained glass, rich in color and texture, creates unique visual effects through its varied pigments and lead cames, but may reduce light transmission and clarity. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing pure transparency and durability (aluminosilicate) versus artistic color expression and traditional aesthetics (stained glass).
Color Options and Customization
Aluminosilicate glass offers a wider range of vibrant color options due to its enhanced chemical stability and heat resistance, enabling precise color application and long-lasting hues. Stained glass features traditional handcrafted color variations with intricate patterns, which allow for highly detailed customization but may face limitations in durability and uniformity. Both materials support bespoke designs, though aluminosilicate glass excels in modern customization techniques such as digital printing and layered color effects.
Applications in Decorative Panels
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for decorative panels in high-traffic or outdoor environments where durability is critical. Stained glass, renowned for its vibrant colors and intricate designs achieved through traditional techniques, is preferred in artistic or architectural settings where aesthetic appeal and historic authenticity are paramount. Both materials serve decorative panel applications but differ significantly in performance properties and visual impact, influencing their selection based on environmental exposure and design requirements.
Maintenance and Longevity
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability and resistance to scratches, chemicals, and thermal stress compared to stained glass, resulting in lower maintenance requirements over time. Stained glass, composed of colored glass pieces joined by lead came or copper foil, is more susceptible to fading, cracking, and deteriorating solder joints, necessitating regular cleaning and occasional restoration. The longevity of aluminosilicate glass panels often exceeds decades with minimal upkeep, whereas stained glass panels typically require specialized care to preserve their appearance and structural integrity.
Cost Considerations
Aluminosilicate glass offers higher durability and thermal resistance, often commanding a higher initial cost compared to stained glass, which is generally more affordable due to simpler manufacturing processes. Stained glass panels may incur additional costs for custom designs and lead work, while aluminosilicate glass panels typically involve expenses linked to advanced fabrication techniques and specialized coatings. Long-term maintenance and replacement costs also differ, with aluminosilicate glass requiring less frequent replacement, potentially offsetting its higher upfront investment in decorative panel applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aluminosilicate glass offers a more sustainable option for decorative panels due to its durability, recyclability, and lower energy consumption during production compared to stained glass. Stained glass often involves heavy use of metals and lead-based compounds, contributing to higher environmental toxicity and challenges in recycling. Choosing aluminosilicate glass minimizes ecological impact through reduced waste and enhanced lifespan, aligning with eco-friendly design principles.
Choosing the Right Glass for Decorative Panels
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability, scratch resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for decorative panels in high-traffic or outdoor environments. Stained glass provides rich color variation and artistic expression through handcrafted designs, best suited for aesthetic-centric, low-impact settings. Selecting between aluminosilicate and stained glass depends on balancing durability requirements with desired visual impact for the specific decorative panel application.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Stained glass for Decorative panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com